Closing the WestRegsNotes#112
advertisement

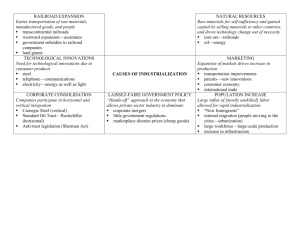
Closing of the Western Frontier The Three key questions this week: • What does a nation need to industrialize? • How did these come together between the 1865 – 1920 time period in the U.S.? • What were the effects of this industrialization process on the U.S.? • Industrialization – Rapid Industrialization occurs in the U.S. from 1865 to 1920. • In general, industrialization refers to the process through which machines replace direct human manipulation of objects in work (usually in specialized factories) resulting in a process of social and economic change whereby a society is transformed from an agrarian, rural, handcraft economy to one dominated by industry and machine manufacture in urban cities. What does a country need to industrialize? Land/Resources Includes both land but also what is in the land – natural resources Examples from the time period: The west, gold, silver – iron, coal, oil Labor Labor = work force – needed to run new machines Examples from the time period: Immigrants from Southern and Eastern Europe and Asia Technology Inventions and capital goods (machines used to make consumer products also known as physical capital Examples from time period include Light bulb (electric generator, Bessemer process, Assembly line Connections Transportation of goods allowing resources to get to factories and products to get to markets to be sold Key example from the time period - Transcontinental Railroad Capital • Money used investment in business – needed to pay for technology, connections, labor and resources Key examples from time period - Corporations, monopolies, trusts Favorable Government Policy A government that promotes industrialization Key examples from time period – free land for railroads, laissez-faire economic policy Why does industrialization happen when it does (1865-1920) • Civil war settles question of the future of the country – industry (Hamilton) or agriculture (Jefferson) – Industry wins • Does not mean agriculture stops or is not important – Does not stop: Agriculture changes – it industrializes (machines replace human labor) – Still important: provide food for cities/factories Today… • Connections and land – How did these come together between the 1865 – 1920 time period in the U.S.? – What were the effects of this industrialization process on the U.S.? Connections • The transcontinental Railroad was a key factor in industrialization – Trans means across – Continental means Continent – Transcontinental railroad – railroad that runs from Atlantic to Pacific • Trans RR is the key connection needed to: – Move natural resources (beef, wheat, iron, coal) from West to the Eastern factories/cities – Move farmers (homesteaders), miners and cowboys from East to West allowing for the settlement of the West after the Civil War – Move products made in factories all over U.S. (allows companies to sell to more people than ever before) • Two companies built railroad – Union Pacific worked East to West – Central Pacific worked West to East – Met at Promontory Point Utah • Others followed – – 1865: 30,000 miles or track – 1900: 180,000 miles of track Transcontinental Railroad • Federal Government provides 100 million acres of public land to railroads when it passed Pacific Railway Act of 1862. – All republican congress (Civil War – no South) – Republicans promote business and industry Who Built the Railroad? • From the East: Irish immigrants • From the West: Chinese immigrants • Faced terrible working conditions, low pay and discrimination • As many as 10,000 died while building the RR How Did the Railroad Change the US? • Creation of time zones • Transportation of settlers to the West • Transportation of products to/from the West is more efficient then ever before (wagons before) therefore, all types of businesses and farmers are helped Land/Resources Includes both land but also what is in the land – natural resources Examples from the time period: The west, gold, silver – iron, coal, oil Before the Civil War…After Civil War • Before the Civil War… – The U.S. rapidly expanding West – Manifest Destiny • God given right for the U.S. to control the land from the Atlantic to the Pacific • Louisiana Purchase (1803) • Adams-Onis Treaty (Florida) (1819) • Mexican American War (1846-48) – U.S. achieves Manifest Destiny • However, the U.S. does not settle the area in great numbers partly because the North and South are fighting over the extension of slavery • After the Civil War… – U.S. settles the slavery question allowing the area to be settled in larger numbers (before the war, the only way to move west was by wagon – Oregon trail – very difficult) – West was essential to Industrialization • Land/resources: (cowboys and farmers become the food basket for eastern cities/factories & miners provides coal and iron that the 2nd industrial revolution was built on) What brought people West? Land and economic opportunities Farmers Provide the food for Eastern factories Cattlemen Provide beef for eastern factories Miners Provide natural resources for Eastern factories Railroad How people moved west and how they supplied the east Farming the West • Between 1860 and 1910, the area farmed more than doubled from 160 million to 352 million hectares. • Why? The Great Plains…the area settled What was the Homestead Act? • Passed in 1862 – Claim land, improve land, make it primary residence to gain ownership (5 years) – 160 acres • Life was very tough but it was a chance to own your own land Land Settled by Farmers Why else did agriculture production increase? • The farmer of 1800, used a hand sickle, could hope to cut a 1/5 of a hectare of wheat a day. • After the Civil War, farming was industrialized: – Cyrus McCormick invented a reaper which could cut 2 ½ hectares a day – John Deere invents steel plow – could till tougher soil – Barbed wire – protected crops from wild animals • This also effectively killed cowboys and their culture because once farmers fenced their lands the long cattle drives on the Chisholm trail became impossible. – Steel Windmill – used underground water as a irrigation source. – Finally the Transcontinental Railroad was the final key piece • Transported products to the east. • Impact of this industrialization of farming – Before - Bushel of grain took 183 minutes to harvest – After - Bushel of grain took 10 minutes to harvest – Other effects: • Farming becomes very expensive – need to borrow $ to pay for many of these new machines • Transporting goods on railroad will be expensive for smaller farmers How does the movement West aid industrialization? • Became breadbasket for eastern cities – Cattle – Americans become beef eaters • Thanks to cowboys and the open trail – Corn • Natural resources – Iron + Coal = • Steel – industrialization in this time period was built on steel • Transcontinental Railroad essential to get these resources back to eastern factories Rest of Today…and Tomorrow • What were the effects of the industrialization process?... • What was life like as a person living in the west? • What would be the impact of the settlement of the Western United States on the people already living there?