Unit 7 Section 3 Notes Compound Names and Formulas
advertisement

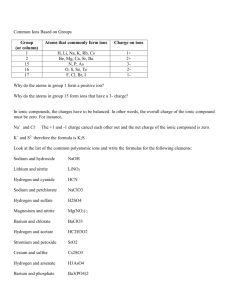
I. Naming Ionic Compounds A. Ionic compounds are formed by the strong attraction between oppositely charged particles, cations (positive ions) and anions (negative ions) B. Both ions are important to the compound’s structure, so both ions are included in the name. C. The names of ionic compounds consist of the names of the ions that make up the compounds. D. In many cases, the name of the cation is just like the name of its element. E. Where an atom is located can be used as a tool for figuring out what ions are formed by different elements: i. Atoms of Group 1: form ions with a +1 charge ii. Atoms of Group 2: form ions with a +2 charge iii. Atoms of Group 13: form ions with a +3 charge iv. Atoms of Group 15: form ions with a -3 charge v. Atoms of Group 16: form ions with a -2 charge vi. Atoms of Group 17: form ions with a -1 charge vii.Atoms of Group 18: do not form ions because they have a full outer energy level F. Names of anions are altered names of elements; the difference is in the ending. i. For anions, drop the ending and add –ide. G.An ionic compound must have a total charge of zero. i. Example: Calcium fluoride: Calcium has a +2 charge and fluoride has a -1 charge. For calcium fluoride to have a total charge of zero, there must be 2 fluoride ions for every calcium ion. So, the formula is CaF2. H.Transition metals must show their charge when they form ions. i. Example: FeO and Fe2O3 would both be named iron oxide by the above rules. They are not the same compound, so their compound names are different. The charge of the iron cation in Fe2O3 is different from the charge of the iron cation in FeO. Fe2O3, Iron (III) oxide is a component of rust. FeO, Iron (II) oxide is a black powdery substance. 1. When this happens, the cation name MUST be followed by a Roman numeral in parentheses. 2. The roman numeral shows the cation’s charge. 3. Fe2O3 is made of Fe3+ ions, so it is named iron (III) oxide. How do you know the charge on iron is +3? Each oxygen ion has a -2 charge, and there are 3 of them. -2 times 3 is -6, so the charge on iron has to be +6. There are 2 iron ions, so 6/2 = 3. 4. FeO is made of Fe2+ ions, so it is named Iron (II) Oxide. How do you know the charge on iron is +2? Each oxygen ion has a -2 charge, and there is only 1 of them. The charge on Fe has to be +2 because there is only one of them. I. Once you have determined a chemical formula, always check the formula to see if it makes a neutral compound. Compounds are ALWAYS neutral. II. Writing Ionic Compounds: Write the chemical formula for aluminum fluoride. A. Steps used to write formulas for Ionic Compounds: i. Write the symbols and charges for the ions with the cation first. Al+3 F-1 ii. Write the Lewis structure for each element and show the transfer of electrons or use the puzzle pieces. Al F F F iii. Write the chemical formula. Show with subscripts the number of each ion needed to make a neutral compound. AlF3 B. Practice: Write the formulas for the following ionic compounds: i. Lithium oxide ii. Beryllium chloride iii. Titanium (III) nitride iv. Rubidium Oxide Naming Covalent Compounds I. Numerical prefixes are used to name covalent compounds A. i. Numerical prefixes tell how many atoms of each element are in the molecule. Rules: B. i. If there is only one atom of the first element, it doesn’t get a prefix. 1. Example: CO is named Carbon Monoxide ii. iii. The element that is farther to the right in the periodic table is second and ends in –ide. 1. Example: BF3 is named Boron Trifluoride Sometimes, the a in prefixes is dropped if it is next to a vowel. i. Example: N2O4 is named Dinitrogen Tetroxide instead of Dinitrogen Tetraoxide.