Cell Division - byrdistheword
advertisement

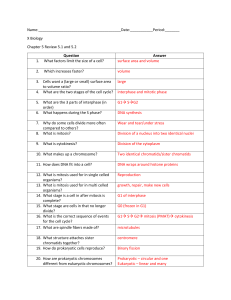
The Cell Cycle Cell division is what allows cells to reproduce so you grow and heal certain injuries. Each time a cell completes a cycle, it becomes two cells. The 3 main stages of the cell cycle are: 1. Interphase – the cell grows and copies its DNA 2. Mitosis – the cell’s nucleus and DNA divide 3. Cytokinesis – the cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell. *can take anywhere from 8 hours to 1 year (averages about 12-24 hrs.) Interphase The cell grows and matures DNA is duplicated and prepares for division 3 stages: 1. G1 –the cell grows and carries out normal cell functions (occurs right after it finished dividing) 2. S – the cell copies its DNA 3. G2 – the cell continues to grow and prepares to divide; DNA condenses and thickens. Centrioles appear. TAKE A MINUTE AND DRAW WHAT IS HAPPENING. Mitosis This is the stage where the DNA is separated and passed into two new genetically identical daughter cells. Also used to repair damaged cells (under the scab, existing skin cells created new skin cells to fill in the gap caused by the injury) THE STEPS OF MITOSIS • • • • • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Remember – PMAT OR Please Make Another Taco) Mitosis cont - Prophase Prophase is the first stage of mitosis (and where the dividing cell spends the most time) Each chromosome condenses, until it is now a single structure that contains the genetic material that was replicated in interphase (each half of the X is called a sister chromatid) Sister chromatids are structures that contain identical copies of DNA. The center of the chromosome where the sister chromatids are attached is called a centromere DRAW AND LABEL WHAT IS HAPPENING Mitosis – Prophase cont. Spindle fibers form in the cytoplasm, and centrioles migrate to the ends (poles) of the cell (these form the spindle apparatus). The nuclear envelope seems to disappear Spindle fibers attach to the sister chromatids of each chromosome (on both sides both sides of the centromere), then attach to opposite poles of the cell (this way each new cell gets one complete copy of the DNA) DRAW AND LABEL WHAT IS HAPPENING Mitosis cont. - Metaphase 2nd phase of mitosis The sister chromatids are pulled by motor proteins along the spindle fibers toward the center of the cell and line up in the middle (or equator) of the cell. DRAW AND LABEL WHAT IS HAPPENING Mitosis cont - Anaphase 3rd stage of mitosis Chromatids are pulled apart The walls of the centrioles (microtubules) begin to shorten, which pulls at the centromere of each sister chromatid, causing them to separate into 2 identical chromosomes All the sister chromatids separate simultaneously (we don’t know how) Finally, the chromosomes move toward the poles of the cell DRAW AND LABEL WHAT IS HAPPENING Mitosis cont - Telophase The last stage The chromosomes arrive at the poles and begin to relax (or decondense) 2 new nuclear membranes begin to form and the nucleoli reappear. The spindle apparatus comes apart DRAW AND LABEL WHAT IS HAPPENING Cytokinesis – The last step in the cell cycle (not part of mitosis) The cytoplasm divides and pinches off Results in two new cells, each with identical nuclei These two cells then begin Interphase DRAW AND LABEL WHAT IS HAPPENING Cell Death Apoptosis – programmed cell death (the cells shrink and shrivel in a controlled process) Happens in your hands and feet as they begin to develop, or when a leaf falls from a tree Necrosis – cell death due to injury or illness of the tissue