Cells! - WordPress.com
advertisement

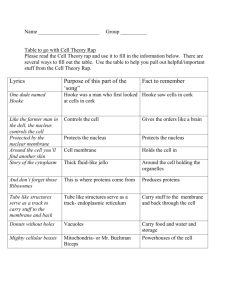
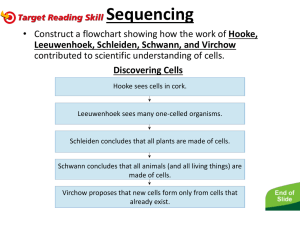
Cells! By: Ellie Hobelman Cell Theory… states that all living organisms have a basic unit of structure and function, which is the cell. This was a significant statement because it suggested that all living things have a common denominator. Almost 200 years of research by many different scientists led to this conclusion. The initial discovery of cells was done by Robert Hooke, an English scientist, in 1665. Robert Hooke designed one of the first microscopes and used it to look at plant material. One specimen he examined was thinly sliced pieces of cork. By look at the cork through the microscope, he discovered that it was made up of many small units. Hooke named these units cells. Hooke Hooke and other scientists observed other samples of plant material and discovered that they were also made up of cells. As more and more material was examined, scientists began to recognize a pattern. Matthias Schleiden, a German scientists in 1838 stated that all plant material was made up of cells. Theodor Schwann The following year, Theodor Schwann came to the same conclusion about animals. Their findings are what have become known as the cell theory. Rudolf Virchow, a German physician suggested an adjustment to the cell theory. In 1858, he suggested that the cell theory be changed to include that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Louis Pasteur In the following years, experiments conducted by Louis Pasteur provided the proof for Virchow’s proposal. Pasteur carried out experiments to determine how milk curdled. Through controlled environments, he proved that exposure to air particles is what causes the change. The “modern” Cell Theory With the development of the electron microscope, the theory has continued to evolve. As more living material has been observed at higher magnifications, much more has been learned about cells and cell theory. o All living things are made up of cells o All cells arise from other cells cells are capable of reproducing themselves… Parts of Cells… All living things including plants and animals are made up of cells. Cells are made up of atoms, which are smallest units of matter. Parts of Cells Surrounding the cell Cell Wall Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria Supports & protects cells Cell Membrane Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell Double layer Inside the cell Nucleus Directs cell activities Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane Contains genetic material – DNA Nuclear Membrane Surrounds nucleus Made of two layers Openings allow material to enter and leave nucleus Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Gel-like mixture Surrounded by cell membrane Contains hereditary material Ribosomes Each cell contains thousands Make proteins Found on ribosomes & floating throughout the cell Cell Movement… Passive Transport: A cell continually exchanges molecules and ions with its environment. When a cell takes substances that are in greater concentration outside the cell, the cell does not need to expend energy. This is called passive transport. It occurs by either facilitated diffusion or simple diffusion. Cell Movement… Active Transport: For a cell to control its internal environment, a cell must often extend energy to bring substances into or out of the cell. Energy is required in active transport. Vocabulary… Cell membrane- protective covering of the cell, controls material coming in or out of the cell Cytoplasm- gelatin-like material inside cell, work of cell carried out here Nucleus-contains the genetic material of the cell Organelle- any part of the cell that is enclosed by membrane Cell wall- tough outer covering, outside the cell membrane, only plants Chloroplast- only in plants, organelle that use the energy from sunlight to make sugar Vocabulary… Mitochondria- makes energy available to the cell Golgi apparatus- package proteins Lysosome- gets rid of waste in the cell Vacuole- storage for the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- transports protein through the cell Ribosomes- protein synthesis takes place