Cell History Notes
advertisement

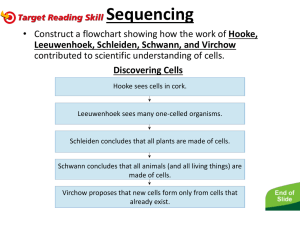
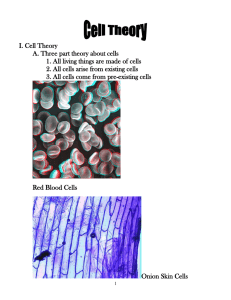
Objective 1. Students will explain the contributions of Robert Hooke to the discovery of cells. 2. Students will name the creators of the cell theory and their contributions to the discovery of cells. 3. Students will explain the cell theory. 4. Students will name and explain the importance of others to the discovery of cells. III. Cell History a. One of the first people to observe cells was Robert Hooke. In 1663, an English scientist and inventor, Hooke observed the structure of a thin slice of cork using a compound microscope he had built himself. To Hooke, the cork looked like tiny rectangular rooms, which he called “cells.” b. About the same time that Hooke was observing cork, a Dutch business man and amateur scientist, Anton van Leeuwenhoek began to observe tiny objects with microscopes. He crafted his own lenses which he used to construct simple microscopes. Using one of these microscopes, he was surprised to observe one celled organisms in pond water. He called the organisms “animalcules” which means “little animals.” He also looked at scrapings from teeth and was the first to see the single celled organisms that we call bacteria. c. Leeuwenhoek’s research interested others like Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow. Schleiden, in 1838, after observing different plants, concluded that all plants are made of cells. The next year, another German scientist Theodor Schwann concluded that all animals are also made up of cells. Thus, the conclusion was reached that, all living things are made up of cells. An important step to the development of the cell theory. However, Schleiden and Schwann still did not understand where cells came from. Until the work with cells began, most people believed that living things could come from non-living matter, an idea known as “spontaneous generation.” In 1855, a German doctor, Rudolph Virchow proposed that new cells are formed only from existing cells. Another important step to the development of the cell theory. As work continued with the study of cells, it became clear that cells are the basis upon which life exists. Thus came the last important step of the cell theory, cells are the building blocks of life. So, the cell theory states: 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. All cells are produced from other living cells. d. While credit should be given to those who studied cells, there were scientists who were curious about the origins of life for many years before cells were in the forefront and even when the research was all about cells. In the mid 1600’s there was an Italian doctor, Francesco Redi who was trying to dispel the idea of spontaneous generation. Redi designed one of the first controlled experiments in an attempt to prove that flies do not spontaneously generate from meat. However, it was not until the mid-1800’s that Louis Pasteur proved by boiling broth in flask that spontaneous generation did not exist. Which confirmed the idea that living cells produce other cells. Research continued about the origins of life and in 1953, two American scientists Harold Urey and Stanley miller provided the first clue about how life may have started on Earth. Using water and gases, thought to be similar to those that composed early earth atmosphere in a flask, they sent an electric current through it. The mixture darkened and within the dark fluid, Miller and Urey found small chemicals that could form proteins-one of the building blocks of life.