Health Insurance Fund
advertisement

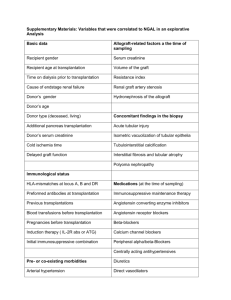
Transplantation in Macedonia – challenges in program financing and budgeting Maja Parnardzieva Zmejkova, MA - HIFM CEO 21 June 2011 Contents 1 Health Insurance Fund 2 Transplantation prices and contracts 3 Action Plan 4 Steps in Developing 5 3 Conclusion 2 Republic of Macedonia Population: 2.06 million citizens HIF insured population: 1.8 million citizens Area: 25 713 km2 GDP in 2010: $9.1 billion USD Government healthcare insurance fund (4.6 of GDP) Life expectancy at birth: – Men 73 years – Women 77 years Mandatory health insurance system Insurance premium stipulated by law (7.3 % from the gross salary) 3 Health Contribution Rate • Rate for employed persons is 7,3% (+0,5%) from gross salary 20% 17% 15.50% 15% 15% 15% 14% 14% 13.50% 13.25% 12.30% 9% 10% 7.30% 5% 6% 3.40% 0% Source: WHO Source: WHO (2010) Албанија Бугарија Латвија Белорусија Романија Украина Македонија Израел Естонија Турција Унгарија Литванија Молдавија Полска Словачка Грција Црна Гора Србија Луксембург Хрватска Чешка Финска Швајцарија Босна и Херцеговина Словенија Шпанија Италија Португалија Ирска Шведска Норвешка Белгија Велика Британија Австрија Германија Франција Холандија Данска Cross country comparison % of total public health expenditures to GDP 10.00 8.00 6.00 4.00 2.00 0.00 Health System Institutions The Ministry of Health creates the health policy at the national level and legal health framework. Health Insurance Fund of Macedonia is an exclusive provider of the compulsory health insurance. The Fund is defined as a purchaser of health services provided by the health care network. The health care network consisted from public and private health providers 6 Health care network The health care network is consisted from the public and private health providers who negotiate the delivery of their health services at the primary, secondary and tertiary levels. Primary HC - 2646, private health providers Secondary HC – 207, private and public health providers Tertiary HC – 33, public health providers 7 Health Insurance Fund Revenues 2012 Employed Maternity Leave Budget transfer Pensioners Other Copayments Unemployed Uninsured 1% 1% 1% 7% 7% 6% 55% 22% 371 mil EUR 8 Health Insurance Fund Expenditures 2012 Health Services Leaves Orthopedic Administration Treatments abroad 2% Transplantations 2 mil EUR 1% 1% 11% Medications for transplantations Dialysis 14 mil EUR 85% 0.4 million EUR 9 Dialysis • 1,399 patients • 16,178 treatments p.a. • 14 mil EUR p.a Distribution of patients in 19 dialysis centers Centers for dialysis in Macedonia DRG Prices 2010 and 2011 Analysis of the transplantation surgery with the clinics and increased prices: A01Z Transplantation of pancreas 10,380 EUR A07Z Alogenic Transplantation of Bone Marrow 12,400 EUR A08B Autologic Transplantation of Bone Marrow 8,700 EUR A09A Transplantation of kidney with pancreas 15,900 EUR A09B Transplantation of kidney w/out pancreas 11,200 EUR Currently Prepared new DRG prices for the associated surgery: A10Z Transplantation of cornea 1,140 EUR A11Z Donor preparation, multiorgan and tissue explantation 5,170 EUR A12Z Donor preparation and multiorgan explantation 4,900 EUR A13Z Donor preparation and organ explantation 5,035 EUR A14Z Donor preparation and cornea explantation/ eyeball one and/or both 255 EUR A42Z Serologic analysis of donor organs/tissues 205 EUR 11 Dialysis vs Transplantation • Dialysis price 80 EUR • One patient on dialysis annually 12,400 EUR 12500 12000 11500 11000 10500 Annualy Transplantation Dialysis • Transplantation price 11,200 EUR Transplantation and Health Insurance Fund Current Up coming • Waiting list for Living Donor • Establishing national kidney transplantation – 32 program in transplantation persons • National registry for • Non existing Deceased Donor donation and waiting list for transplant program kidney transplantation • In 2011 there were 32 • Developing Donation from transplantations in RM: Deceased Donors • Transparent waiting list for • 10 - kidney transplantation, o/w 2 children kidney transplantation from • 1 - children liver transplantation living donor • 22 - bone marrow transplantation • Program for permanent education 13 Conditional Contracting For surgery Clinic for Urology Clinic for Children Surgery Clinic for Hematology For HLA analyses Institute for Transfusion Institute with the Medical Faculty 14 Action Plan 2012 Change in the Law for transplantations and enacting 13 bylaws Appointing the national coordinator Preparation of clinical pathways Accreditation of laboratories Creation of donors registry Software for the transplantation waiting list Education National Campaign for Transplantation 15 Coordination Action plan Ideas and joint work Fund Ministry of Health Public health care institutions and Experts NGO, Religious and political authorities 16 Expected results • • • • • • • Enabled legal framework Adequate prices Coordinated clinics Increased number of transplantations Creation of the donors registry Joining the Eurotransplant Cooperation with other countries 17 Conclusion Acquisition from Transplantations Quality of life - long-term survival with a high quality of life Economic benefit - national health care budget expenditure savings. Organ transplantation is the most costeffective and humane treatment for end stage 18 renal failure. Most valuable sentence The most valuable sentence in ``Croatian donation network`` »Sve što može poslužiti životu, grijeh je pokopati.« Pope Johan Paul II 19 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION Website: www.fzo.org.mk E-mail: majap@fzo.org.mk 20