Organic vs. Inorganic Inorganic molecules
advertisement

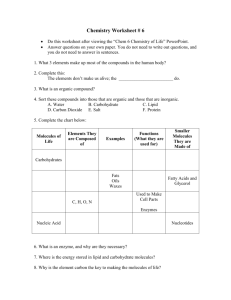
1. What is the difference between inorganic and organic? 2. What is a monomer? 3. What are macromolecules? 4. What does “-saccharide” mean? 5. What is a hypothesis? Study Island ◦ You have to do 20 questions every time you do an assignment ◦ It does not save Learning logs due Sat. Crossword due today Progress reports tomorrow Notebook/ spiral check Friday What gas molecules were in the early atmosphere? How were primitive cells thought to have arose? What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells? What is a plasma membrane? What is an autotroph compared to a heterotroph? What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic? No ozone, so energy was created by lightening Major Gases included: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ carbon dioxide Methane NH3 H20 Organic molecules are the chemicals of life ◦ compounds composed of more than one type of element ◦ usually found in and produced by living organisms ◦ molecule contain carbon-hydrogen bonds, C-C, long chains or rings of carbon ◦ Ex:The four major classes of organic molecules include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids Inorganic molecules ◦ Inanimate, non biological, not normally found in living things ◦ Can contain carbon, but not rings or chains of many carbons ◦ No multiple carbon-hydrogen bonds ◦ Ex: methane, water, carbon dioxide, ammonia 1920s- Primordial soup ◦ Early earth’s oceans contained large amounts of organic molecules. So where did the organic molecules come from? ◦ Gases of early atmosphere: CO2, H2O, NH3, CH4 Chemical evolution- organic molecules formed spontaneously from inorganic molecules (gas) and energy (lightning) 1953- tested the primordial soup model (Oparin’s hypothesis) Put the gases they proposed had existed on early Earth in a beaker Stimulated lightning by using electrical sparks Days later- Miller and Urey found a bunch of organic molecules ◦ Amino acids ◦ Fatty acids ◦ Hydrocarbons (hydrogen and carbon) Results supported Oparin’s hypothesis *****Chemical evolution: organic molecules can be created from energy (lightening/spark) and gas molecules(inorganic molecules) that exist on Early Earth 0. Inorganic matter- in the early atmosphere 1. Simple organic monomers 2. Polymers 3. Protocells (very simple membrane bound cell with no organelles, can grow and divide) ◦ Make in lab 4. Cells (DNA present)- hasn’t been created in a lab Abiogenesis- process by which life arises from inorganic matter (theory) Prokaryotic or eukaryotic? Why? 1. Infolding of outer membrane to create endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, vacuoles 2. Endosymbiosis: chloroplasts and mitochondria came from bacteria ◦ A larger cell engulfs a small prokaryotic (bacteria) cell ◦ The large and small cell work together to survive ◦ Instead of being digested, the bacteria began to live inside the host cell where they performed either respiration (mitochondria) or photosynthesis (chloroplasts) ◦ Mitochondria and chloroplasts have own DNA No oxygen No ozone layer Lots of UV Volcanos (lava) Lots of CO2 and ammonia Intense lightning storms Lots O2 Ozone layer Not much UV More land Less CO2 and ammonia Less lightning storms Explain the Miller and Urey experiment in your own words Draw a picture of the experiment apparatus Compare and contrast organic and inorganic molecules