AP Psychology The Brain!
advertisement

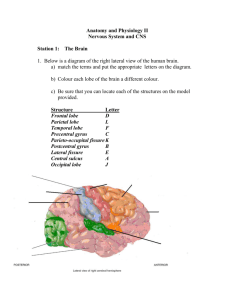
AP Psychology The Brain! EQ: How do different brain areas influence our physical behavior? 9/16/13 Pinky & the Brain • One of those stupid videos teachers like to show from when they were growing up… • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=snO68aJT OpM Sections of the brain • • • • Older sections Limbic system Cerebral cortex Language centers Brainstem • Brainstem is the oldest & lowest part of the brain (fits with evolution). • Made up of the medulla & pons. Medulla Oblongata • Lower section of brainstem—controls autonomic functions (heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, etc.) Pons • Pons means “bridge”—connects brainstem (Medulla) & brain (Thalamus) • Regulates sleep, dreaming cycle, etc. Reticular formation • Reticular = “netlike” • Neural system primarily responsible for arousal from sleep & alertness • Coma cat Thalamus • Little eggs on top of the brainstem • Routes information to proper places in the brain—makes sense, as it is the first thing after the brainstem Cerebellum • “Little brain” • Primarily motor control—does not initiate, but it influences coordination, precision, and timing of movements. • Motor learning Limbic System • Emotions & memory Amygdala • Bean-sized neural clusters • Aggression & fear • Messing with animals… Hypothalamus • Influences temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, etc. • Extremely important for homeostasis • Works with pituitary gland • “Pleasure center” Hippocampus • Means “sea horse” • Extremely important in converting short- to long-term memory (Patient HM) • Spatial memory & navigation Cerebral Cortex • Frontal lobe (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FrULrWRl GBA) • Parietal lobe • Occipital lobe • Temporal lobe Frontal Lobe • Planning, deciding, perceiving, personality/temperament (Phineas Gage) • Motor cortex—inside frontal lobe Parietal Lobe • Specialize in sensation (touch, temperature, pain, pressure) • Somatosensory (sensory) cortex—inside parietal lobe • Which body parts take up the most space in the motor & sensory cortexes? Occipital Lobe & Temporal Lobe • Occipital: back of brain…visual • Temporal: side of brain…sound • Remember Avatar fMRI • They (mostly) correspond with location of eyes/ears. Cerebral Cortex • Motor cortex • Sensory cortex • Association areas Association areas • Large difference between humans and animals • Sensory inputs tied to memory Language centers • • • • • Visual cortex Angular gyrus Wernicke’s area Broca’s area Motor cortex Language centers (functions) • Visual cortex Processes written info • Angular gyrus Turns written info into auditory info • Wernicke’s area Interprets auditory info • Broca’s area Controls speech muscles in motor cortex • Motor cortex Words are pronounced Aphasia • How would damage to Wernicke’s area & Broca’s area lead to different forms of aphasia? • Wernicke’s: no motor issues, but comprehension issues • Broca’s: major motor issues, but comprehension issues may be intact Corpus Callosum • Connects the two hemispheres • Can be cut… Brain posters… • Pick 1 part of the brain (everyone needs a different one). • Your poster should have these parts: 1. Picture of the brain with location labeled 2. General overview of its function 3. What happens if the section is lesioned 4. At least 1 extra fact (preferably interesting) 5. Some tips for classmates on how to remember the information Present posters Yay! A legion of lesions… • Jot down a list of each part of the brain and what would happen if it was lesioned. Brain plasticity • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VaDlLD97 CLM • What is plasticity? What happens to it over time? • What is the relationship between brain plasticity and behavior? Brain hemispheres • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dFs9WO2 B8uI • Cerebral dominance (certain tasks, but hemispheres cooperate) • Wernicke’s area & Broca’s area: 95% only have them in left hemisphere • Plasticity shows the brain can compensate in the case of a hemispherectomy Right/left handedness • http://www.nytimes.com/1991/04/04/us/bei ng-left-handed-may-be-dangerous-to-lifestudy-says.html Homework • Pages 95-106 in Myers