File - ESTHER WU
advertisement

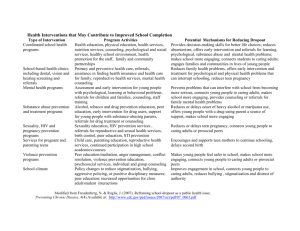
ADVOCACY PLAN OUTLINE Esther Wu FOCUS – All students, but Black males in particular. PLAN – Tack on to what the school and teachers already have working. School-wide systems level – rules and rewards. Classroom level – classroom guidance and classroom behavior charts. Individual/Group level – behavior regulation. JUSTIFICATION – Moral: Students should all have the opportunity to learn. Obstacles that may hinder that process, and thus their ability to advance in life, need to be addressed. Black males in particular need to be given the resources to be successful, and perhaps bicultural, in all settings. Holcomb-McCoy’s School counseling to close the achievement gap: A social justice framework for success. “I (Don’t) Hate School: Revisiting Oppositional Culture Theory of Blacks’ Resistance to Schooling” by Angel L. Harris. “Overcoming Negative School Experiences for African American Adolescents” by Dana Griffin and Julia Bryan. “Schools, Prisons, and Social Implications of Punishment: Rethinking Disciplinary Practices” and “The Trouble with Black Boys” by Pedro A. Noguera. “Educating and Counseling African American Students” by James L. Moore III and Delila Owens. DATA – Data supports that Black and Hispanic boys are more often referred for behavior issues as well as learning disabilities. Data also supports the skillstreaming techniques that teach prosocial behaviors in a step-by-step process using modeling, role-playing, performance feedback, and generalization. (Skillstreaming the Elementary School Child by Dr. Arnold P. Goldstein and Dr. Ellen McGinnis) OBJECTIVES – The overall goal is to provide a healthy environment for learning where individuals are not hindered by actual or perceived behavioral issues. Objectives would include reduced behavior referrals, more engagement in class, increased academic performance, fewer conflicts with peers, etc. POTENTIAL BARRIERS – Potential barriers depend on the school environment and teacher cooperation; however, clearly communicating and committing to common goals can help build collaborative relationships. POTENTIAL COLLABORATORS – At the most basic level teachers would be involved in this process since students are under their care and tutelage at school. Behavior management and the teaching of prosocial behavior is highly dependent on the styling of the school and teachers. Teachers and students would be directly involved in the behavior contract system, and in reinforcing positive behaviors. RISKS – If the administration and staff are all on board, the school and students stand to benefit greatly. It will also make teaching “easier” and more efficient, and students will be able to learn in a happy and healthy environment. However, if this is not the case, there may be some backlash from unwilling teachers, administration, and parents. ADVOCACY PLAN OUTLINE Esther Wu DISPOSITIONS - Using a 1-10 scale with 1 being low and 10 being high I would rate my dispositions in a, b, c and e as 8, and d as 9 or 10. 8 a. 8 b. 8 c. 9 d. 7 e. the belief that advocacy is a part of their jobs a commitment to their code of ethics the belief that the purpose of education and school counselors specifically is to empower students and their family the belief that caring should underpin educational and counseling practice a passionate approach to helping. SKILLS - Using a 1-10 scale, with 1 being low and 10 being high I would rate a, b, e, and f as 6, d and g as 7, and c as 8. I feel that while I have the skills, I am not always able to convey them amongst all crowds. I do not look my age and I can be quite shy and reserved initially, so these scores are reflection of those occasions when I may not be at my best. 6 a. 6 b. 8 c. 7 d. 6 e. 6 f. 7 g. assertive communication systematic problem solving small problem-solving group leadership conflict resolution forming advocacy teams data and information collection collaborative leadership skills EVALUATION – Effectiveness may be measured in a multitude of ways, both quantitative and qualitative. Students currently receive Manatee Tickets for exhibiting “good behavior” and entire classes can work together to show their collective “good behavior” in the schoolwide “bucket-filling” competition. Data may also be collected with regards to classroom behavior charts, academic performance, behavior referrals, peer mediation sessions, referrals for SAP, etc.