2004 AP Psych Test - Solon City Schools
advertisement

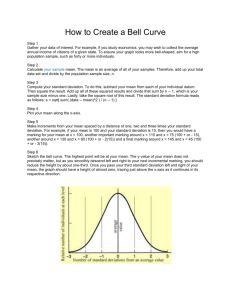
AP Psych Practice Test • 1. the answer is B. Sensory adaptation explains why our eyes adapt to the dark, and why we don’t smell cat urine after a while. It happens because our senses are constantly stimulated and get fatigued • 2. D. social – how we interact with other people • A. experimental – in a lab • B. cognitive – how we think • C. developmental – how we develop • E. clinical – in a clinic or hospital • 3. The answer is A. It helps people diagnose and classify disorders. • 4. The answer is E. • • • • Post = after traumatic = trauma. PTSD is common with war veterans but it also happens with other horrific events. A. GAD – anxiety disorder with a constantly low level of autonomic nervous system arousal B. Major Depressive Disorder – 5 signs of depression (lack of energy, loss of appetite, loss of interest in friends and activities etc.) lasting 2 or more weeks C. Hypochondriasis – Somatoform disorder worrying about having a serious illness D. Histrionic – personality disorder – dramatic, attention seeking • 5. The answer is D. Humanists emphasize free will, self actualization, self-discovery. Believe all Humans are good. Humanists – hippies. • 6. Remember the ticking clock??? • The answer is A. selective attention (similar to the cocktail party effect). • B. Subliminal perception – below the absolute threshold, outside conscious awareness • 7. C. Stimulus Generalization - Just like Little Albert, you generalize your association to similar things. • A. stimulus discrimination is when you know the difference – only respond to 1 specific thing • B. second order conditioning - when you train a dog to drool to a bell, then train the dog to associate light with the bell then drools to – CR is not as strong • E. Spontaneous Recovery – after extinction the CR or the behavior returns • 8. C. cross sectional studies study different sections of the population (different ages, class levels, race). • A. Longitudinal studies - Same people followed over a long long long time (like decades). Scientist measure how things change over time. • D. Case studies study something in depth • E. Observational – observe and take notes. If it’s a naturalistic observation the observation takes place usually in a public setting where the observer goes unnoticed by the subjects • 9. The answer is C. People who do things for the love of it are intrinsically motivated. – Intrinsic – inside (the heart) • A. Functional Fixedness – unable to see another use for an object other than it’s intended use – don’t have a hammer, don’t think to use your shoe • C. Inductive Reasoning – Going from a general to a specific. All men are mortal. John is a man, therefore John is mortal. • D. Incubation – a stage of creative thought • E. Heuristics – a short cut to solving a problem –using something that worked in the past, narrowing down your choices • 10. The answer is D. D is the definition of figure ground • 11. E. A dog drooling to a bell but not a gong. • 12. C (racial) • This tiger apparently doesn’t discriminate! • 13. D The 3 D’s – Deviant (lowstatistically prevalent), Distressful, Disordered (maladaptive) abnormal, gender is not a consideration. • 14. B. If twins are reared apart then their environment is different. Since IQ scores have a lower correlation when reared apart, then environment is important. • 15. D. validity - tests the material that its supposed to. • A. standardization - it was given the same way to a representative group of test takers and the results form a bell curve. • B. Norms – an informal way to behave in a culture • C. fairness? • E. reliability - results are the same again and again. • 16. The answer is A. Reason for split brain. • 17. The answer is C. maturation. Biologically, process that can’t be sped up no matter what parents/environment do – Roll-over, sit-up, crawl, walk (order is universal, timing is not. • 18. E. Behavioral therapy involves reinforcements and punishments to change a behavior. • A. Cognitive = thinking. The psychologist is trying to change Wade’s behavior, not his thinking. • B. Biological – give Wade medicine or surgery • C. Psychodynamic – probe Wade’s unconscious mind through dream analysis or transference • D. Humanistic – help Wade remove barriers to self actualization or find himself • 19. a. RET therapy is a technique that challenges a person’s irrational thoughts, so it’s very confrontational! • B. Psychoanalysis – uncovering unconscious conflicts • C. aversive conditioning- might involve shocking one’s testicles every time something is done or thought (classical cond.) • D. person-centered usually means the client does most of the talking. • E. systematic desensitazion involves gradually exposing someone to their source of fear or anxiety. • 20. B. Think optical – occipital; Hearing goes to the temporal lobe (think ears are near the temple) • A. Parietal – touch • C. Frontal – planning, reasoning, moral thinking, controlling emotion • 21. c. Internal Locus of Control • 22.A. Pick the answer that is closest to 24 hours. • Circa means about dian means day • Circadian rhythms are your day/night cycles. • If constantly exposed to artificial light or shut in a cave, Circadian rhythms are 25 hrs. • 23. B. 10 - If you know the variance, the standard deviation is the square root of the variance – • If you know the standard deviation, the variance in the standard deviation squared • Standard deviation is always smaller than the variance • 24. D. Psychoanalytic is an insight therapy • a. behavior – behavioral therapy • B. reach full potential – self actualization – humanistic therapy • C. alter thought processes – cognitive therapy • E. get rid of irrational thoughts – cognitive (RET) • 25. The answer is D. If the mean is 70, and the standard deviation is 10, How many test takers scored above 60? 60 is 1 standard deviation below the mean. • Steps to figure this out • 1. draw an normal bell curve just like the one below (but leave out the Welchsler IQ scores) • Put the mean (70) at 0 then add the standard deviation(10) to the mean (70) = 80 place it on the graph at +1 standard deviation. Add 10+80 =90 and put it on the graph at +2 standard deviations 90+10 = 100 at 3 standard deviation. Subtract 10 from each number going down (ie 70-10 = 60) • Look where you placed 60 on the graph and add all of the % from the normal bell curve to the right or 60. • NOTE: You will need to memorize the % on the normal bell curve! • 26. Na+ = Salt (sodium and K+ = bananas (potassium)! • The answer is B. • 27. A. correlation = relationship, measured by a correlation coefficient (#between 0-1, closer to 1 the stronger the correlation. Can be plotted on a scatterplot. • B. Central Tendency – mean, median, mode • C. Histogram – graph of numerical distrib. • D. Standard Deviation – tells us how far the scores are spread out from the mean • 28. B. Hippocampus – hippos attend college campus to remember. • A. Amygdala – Amy is afraid and angry • C. Pituitary – Master Gland • D. Hypothalamus – 4 F’s (fight, flight, food, fornication) and Teddy (Temperature), Roosevelt (Rewards) • E. Thalamus – Thalia the switchboard operator – Routes sensory info. to correct lobe except smell • 29. B semicircular canals – vestibular sense tells you where your head is in relationship to your body—are you upside down or horizontal • A. skin = touch • C. taste buds – gustatory sense • D. Olfactory – smell • E. rods and cones - sight • 30. D. alcohol is the answer – causes you to slur your words • A. cocaine is a stimulant • B. marijuana is a hallucinogen • C. dopamine is a neurotransmitter • E. nicotine is not a stimulant • 31. E. Only an experiment can establish cause and effect. • 32. C – the lipstick test or the smudge test • 33. C. “interpret” is another work for cognition • Here are some others – think, memorize, recall, process, recognize, realize, perceive, believe, etc. • 34.A. The Stanford-Binet test is the actual name for what we call the IQ test. • Binet wanted to find away to identify Parisian children that needed extra help in school • 35. D. Too difficult ant they might get too aroused. Too easy, not enough arousal – Yerkes Dodson law • 36. C. diffusion means spread. This is the bystander effect • A. prejudice – unjustified and negative attitude • B. Social facilitation – you perform better in a group (as long as the task isn’t too difficult) • Group polarization – like minded people who discuss an issue get more extreme in their views • Self-efficacy – your confidence that you cah complete a task • 37. The answer is A. Confirmation bias is when we only notice things that confirm our already held beliefs. 38. A schema is a set of expectations, a mental construct, that we have about something that helps us organize information. 30 people were asked about this office picture below. • • • • 29 out of 30 recalled Chair, desk, and walls Only 8 subjects recalled it had a skull 9 subjects recalled it had books which it did not Memory for location is influenced by the person’s schema for that location. • 39. C. If you catch a virus, then eat at a Mexican food restaurant, throw up, then you will NOT want to eat at that restaurant, even if you know that’s not where you got the virus. That’s the Garcia effect. • Garcia said we are biologically predisposed to learn some behaviors more readily than others. • 40. A. Rods – on the periphery of our retina, help see black and white and in the dim light • Cones are in the center area of the retina called the fovea)C C C C Cones C C C C C Color. . • 41. D. Temperament – the part of our personality that we are born with – emotional reactivity (excitability)and outgoingness (extroversion/introversion) 42. D. Observational learning (like the Bobo doll experiment) A. Classical conditioning deals with reflex-like responses. Like a dog drooling to a bell. B-E are all classical and operant conditioning terms • 43. E. • 44. The answer is B. A client will “project” their personality onto the therapist. Any vague stimuli that the therapist interprets is a projection test • This example is the Thermatic Apperception Test . Rorchoch inkblot test is another E. Behaviorism. John B. Watson - the B. stands for Behaviorism - was famous for the Little Albert experiment when he classically conditioned a baby to fear a white rat (and generalized that fear to all white furry things). • 45. • 46. What is the brain made of? What are nerves made of? • The answer is B. neuron • 47. If you give an 11-year-old non-alcoholic beer, he’ll start acting drunk because he expects the alcohol to make him feel that way. • The answer is A. expectations. – causes the placebo effect. If we expect a drug to make us feel better it will! • 48. B. Which answer deals with an individual conforming to the group? B. – 2 types of Conformity – Normative Social Influence – we go along with the group to be accepted or avoid rejection – Informational Social Influence – we going along with the group because we think they are right • 49. C. based on the ideas of unconditional positive regard, even mass murderers are good inside. • A. No. That’s behaviorism • B. Although Abraham Maslow talked about peak experiences, he said that not all people have them. No. • D. Humanists are more positive than that! • E. Nah, they valued free will more than that. • 50. Remember, the brain evolved from the bottom to the top. The bottom of the brain deals with basic life support. So, what is at the very top of the brain?? • C. The cerebral cortex, the source of higher level thinking and conscious thought. The outer wrinkly part of the brain where the lobes are. • • • • A. Occipital – seeing B. cerebellum – Sarah Balances D.homunculus – picture of the parts of the brain E. Pituitary gland – master gland of the endocrine system • 51. E. Retro = backward with Amnesia, so we forget things that happened before the accident. Don’t get this mixed up with Retroactive interference – Use PORN for that • A. Simple failure to encode • B. reconstruction errors after the event • C. the inability to form NEW memories is called antereograde amnesia (50 first dates) • D. state dependent memory • 52. B. hallucination is when you see or hear things that are not there. • a. fixation - freudian term for being stuck in a psychosexual stage of development or it could be the inability to solve a problem from a different perspective • c. illusion is a disortion of perception (ie. Optical illusion) • D. An eidetic image is formed if you can still see, at least in some degree of detail, an "image" of the original stimulus (picture) after it has been removed. The image will appear to "linger" on the original surface it was seen, something like an after-image (except in the original color). A true eidetic image can literally be "seen" by the subject until it fades. Sometimes eidetic images can be recalled at will without significant fading. • E. phobia is an uncontrollable fear of something, not a hallucination. The individual may have a phobia but s/he is not “experiencing” it in this question. • 53. The answer is C. • There is something called instinctive drift. One time psychologists tried to train raccoons to deposit coins in a slot. However, they ALWAYS wanted to rub 2 coins together and “wash” them like they wash food in a stream. • Garcia is known for understanding biological predispositions play a part in whether an animal learns something and how quickly they learn it. • 54. A. Schizophrenia is associated with an abundance of dopamine, hallucinations and Enlarged, fluid-filled areas in the brain. • 55. D. psychoanalysis focuses on unconscious, unresolved conflicts from childhood. • A. ntm imbalance is the biological perspective • B. thoughts – cognitive perspective • C. biopsychosocial perspective • 56. A. hippocampus - memory • B. Hypothalamus (remember the 4 F’s plus Teddy Roosevelt) • C. Thalamus – relay station • D. Pons – facial expressions, basic biological processes • E. medulla – heart beat, blood pressure • 57. a. Fixation – being stuck in a psychosexual stage • B. repression – motivated forgetting • C. regression – acting immature in times of stress • D. sublimation – doing something positive with your “faults” • E. reaction formation – acting the opposite of how you truly feel • 58. C. behavioral (After all, the question is asking about behaviors) • Maladaptive behaviors, like overeating, can be reinforced or learned through observation just like any other behavior. • 59. B. systematic (gradual) desensitization • The picture is virtual reality exposure therapy. • 60. D. Set point - It theorizes that our body gets comfortable at a certain weight and is resistant to change—we tend to keep going back to the original weight • 61. This prompt deals with Ainsworth’s studies on attachment styles. She described the secure attachment, avoidant, and the answer, C. resistant or ambivalent attachment style (generally this is called an insecure attachment) • 62. The answer is D. The stimulus causes your autonomic nervous system (physiological arousal) to react and you cognitively label the stimulus. • My heart beats, I think “I’m scared”, I feel the emotion • Schacter-Singer is the 2 Factor Theory of Emotion • 63. Standard deviation is how far apart are the numbers away from each other. How much do they deviate from each other. If the numbers are all close together, then the standard deviation is low • The answer is B. • 64. A. Soma = body somataform disorders are the brain leading to some sensation of the body. • 65. D. Classical conditioning – associative learning • When a person or animal creates an automatic/involuntary association between 2 things without reinforcements, that is classical conditioning (like Pavlov training a dog to drool to a bell) • In this case the involuntary response (CR) is the immune suppression and the (CS) is the sweetwater • 66. D. Early behaviorists were uber-scientists who took things a bit too far. They said we should only study observable behavior like a pigeon pecking on a disk. • 67. C. Deindividuation (not an individual for the moment). They riot because they get lose our selfawareness and get swept up by the crowd—like what’s happening in Baltimore • A. Group polarization – when we’re with like minded people and discuss and issue we agree on, our position on the issue becomes more extreme • B. Mere Exposure - the more we are around someone, the more we like them • E. Fundamental Attribution Error – we attribute other’s behavior more to their disposition than the situation • 68. B. Humanists were the pioneers of group therapy. It makes sense since they are into client-centered therapy. In a group, the therapist doesn’t dominate the conversation—self-help groups, encounter groups etc. • 69. A. Seyle’s General adaptation syndrome • 70. Reliability means you get the same results again and again, even if the test is crap. • A. no because it needs to be the same test • B. that’s predictive validity • C. needs to be the same people • D. there needs to be some sort of retake • E. This is the best answer, its an example of test-retest • 71. D. Heuristics are mental shortcuts • Use a heuristic to unscramble this word: EQEUN Using a heuristic you might put the q and the u together. Using an algorithm, you would try all 1000 letter combinations until you get it. • 72. E. absolute threshold - the point at which we notice a stimulus—remember the ticking clock. • B. JND – the point at which we notice the difference between 2 similar things • 73. A. semantic – the meaning of words • B. episodic – an “episode” of your life (that time you farted in class) • C. priming – hints • D. procedural – “procedures” like playing a piano, walking • 74. The answer is B. Serotonin deals with depression. These drugs are called Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI’s) • 75. When people work in large groups (like in a tug of war game), the individual does not work as hard. This is called social loafing. The answer is C. • 76. B. Biological – deals with the physical body (brain, hormones, neurotransmitters) • 77. The answer is D. You “know” the answer but just can’t access it for some reason. • 78. B.Token economy is when you use positive reinforcement with a large group of people like elementary schools or classrooms or mental wards. (Pizza party if everyone passes the test) • 79. Think how old does a child need to be before s/he understands that water conserves its mass even if it’s poured into a taller beaker. • The answer is C. • 80. Dissonance = discomfort • cognitive = thinking • We experience cognitive dissonance (discomfort) when our behavior doesn’t match our attitudes. The answer is B. • 81. For the evolutionary perspective, always look for words and phrases like “adaptive” “survival of the fittest” “evolution” Darwin • The answer is B. • 82. D. Signal detection theory says we are more likely to hear something if we expect to hear something. • 83. The answer is D. Intensity • 84. Just think, which one comes first? Especially, which comes last??? • The answer is E. • 85. Cognitive therapy is about changing maladaptive thoughts. He would challenge irrational thoughts that would stress or depress the clients. (He’s where Dr. Phil got a lot of inspiration.) The answer is A • 86. a. Decay is a gradual forgetting over a long period of time • B. amnesia is brought on by some sort of trauma • C. no reconstruction error in remembering the number 9 • PORN • Proactive-Old info gets in the way of new • Retroactive-New info gets in the way of old • The answer is E because channel 16 is making her forget channel 9. • 87. E.The self serving bias is when we attribute our successes to internal (dispositional) causes such as our hard work and intelligence. . . While we attribute our failures to external causes (the teacher was a jerk; the test was too hard). • 88. Just rule out all the BAD things. • The answer is E. • 89. First, antisocial does NOT mean introverted. It means one does not have a conscience (like a serial killer). • The answer is D. • E. that’s narcissism • 90. Psychoanalysts use projective personality tests, meaning they seek to access your unconscious mind by how you interpret pictures or fill in blanks. • The MMPI is a self-report test, even more respected than the Myers-Briggs. • The answer is B. 91. The answer is D. Acetylcholine • Its function is motor movement and maybe memory. To much and you will…. Not enough and you will…. Lack of ACH has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease. • 92. The psychoanalytic perspective focuses on unconscious desires and conflicts. • The answer is C. • 93. Self report tests (like the MMPI and the Myers-Briggs and the Big Five) are trait tests. The trait approach to psychology says our personality is based on the sum of our traits (such as introversion, openness) • The answer is B. • 94. When we commit the FAE, we overestimate dispositional (internal) factors and we underestimate situational factors. • The answer is A. • 95. I feel Starbucky today. Language is creative. If we had a language acquisition device, then we couldn’t be so creative. • The answer is A. • 96. What are we doing to the subjects to study this? The answer is C • 97. What are we measuring? The answer is B. • 98. C. (same as 96.) (the independent variables) • 99. Stage 2 has sleep spindles. (A) • The sleep cycle has changed. I’m not sure this question is valid. • 100. C. Social – people facil – easy • Sometimes, athletes and musicians play better on game day in front of people than at practice. • (The Yerkes-Dodson law supports this as well!)