here - CPALMS.org
advertisement

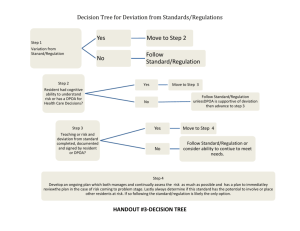
How to Create a Bell Curve Step 1 Gather your data of interest. For example, if you study economics, you may wish to collect the average annual income of citizens of a given state. To ensure your graph looks more bell-shaped, aim for a high population sample, such as forty or more individuals. Step 2 Calculate your sample mean. The mean is an average of all of your samples. Therefore, add up your total data set and divide by the population sample size, n. Step 3 Compute your standard deviation. To do this, subtract your mean from each of your individual datum. Then square the result. Add up all of these squared results and divide that sum by n -- 1, which is your sample size minus one. Lastly, take the square root of this result. The standard deviation formula reads as follows: s = sqrt[ sum( (data -- mean)^2 ) / (n -- 1) ]. Step 4 Plot your mean along the x-axis. Step 5 Make increments from your mean spaced by a distance of one, two and three times your standard deviation. For example, if your mean is 100 and your standard deviation is 15, then you would have a marking for your mean at x = 100, another important marking around x = 115 and x = 75 (100 + or - 15), another around x = 130 and x = 60 (100 + or - 2(15)) and a final marking around x = 145 and x = 45 (100 + or - 3(15)). Step 6 Sketch the bell curve. The highest point will be at your mean. The y-value of your mean does not precisely matter, but as you smoothly descend left and right to your next incremental marking, you should reduce the height by about one-third. Once you pass your third standard deviation left and right of your mean, the graph should have a height of almost zero, tracing just above the x-axis as it continues in its respective direction.