Chapter 9 Chemical Names and Formulas
advertisement

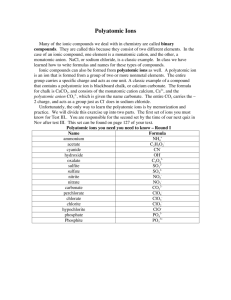
Chapter 9 Chemical Names and Formulas 9.1 Naming Ions 9.2 Naming and Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds 9.3 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds 9.4 Naming and Writing Formulas for Acids and Bases Created by B. Shia 11-07 9.1 Naming Ions Monatomic Ions: How are the charges of Group A metal and nonmetal ions related to their positions in the periodic table? Monatomic ions consist of a single atom with a positive or negative charge resulting from the loss or gain of one or more valence electrons, respectively. Monatomic Ions Cations When the metals in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A lose electrons, they form cations with positive charges equal to their group number. The names of the cations of the Group 1A, Group 2A, and Group 3A metals are the same as the name of the metal, followed by the word ion or cation. Monatomic Ions These elements have ionic charges that can be obtained from their group numbers Monatomic Ions Anions The charge of any ion of a Group A nonmetal is determined by subtracting 8 from the group number. Anion names start with the stem of the element name and end in -ide. These Group A elements form anions. Monatomic Ions Monatomic Ions Ions of Transition Metals How are the charges of some transition metal ions determined? The charges of the cations of many transition metal ions must be determined from the number of electrons lost. Monatomic Ions There are two methods are used to name the ions of transition metals: the Stock system and the classical method In the Stock system, a Roman numeral in parentheses is placed after the name of the element to indicate the numerical value of the charge. (Cu+ is copper (I) ion) In an older less, useful method, the classical name of the element is used to form the root name for the element. (Cu+ is cuprous ion) Conceptual Problem 9.1 a) K+, cation, potassium ion b) I-, anion, iodide ion c) S2-, anion, sulfide ion d) Pb4+, cation, lead (IV) ion Polyatomic Ions What are the two endings of the names of most polyatomic ions? Some ions, called polyatomic ions, are composed of more than one atom. The names of most polyatomic anions end in -ite or -ate. Polyatomic Ion These models show the structures of four common polyatomic ions. Polyatomic Ions Names and formulas of some common polyatomic ions Know nitrate, hydroxide, sulfate, carbonate, phosphate, ammonium; possibly acetate 9.1 Section Quiz 1. When metals from groups 1A, 2A, and 3A form cations, the charge on the ion is equal to a. 8 minus the group number. b. the group number minus 8. c. the period number. d. the group number. 9.1 Section Quiz 2. Which of the following are positively charged polyatomic ions? –(I) ammonium ion –(II) perchlorate ion –(III) ferric ion a) I only b) II only c) III only d) I and III 9.1 Section Quiz 3. If the name of an ion ends in -ite or -ate, the ion is a a) polyatomic cation. b) polyatomic anion. c) transition metal cation. d) monatomic anion. 9.2 Naming and Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds Binary Ionic Compounds: How are the names of binary ionic compounds determined? •A binary compound is composed of two elements and can be either ionic or molecular. •To name any binary ionic compound, place the cation name first, followed by the anion name. How do you write the formulas for binary ionic compounds? •Write the symbol of the cation and then the anion. Add whatever subscripts are needed to balance the charges. Conceptual Problem 9.2 Conceptual Problem 9.2 Conceptual Problem 9.2 a) NaI c) K2S b) SnCl2 d) CaI2 Compounds With Polyatomic Ions How do you write the formulas and names of compounds containing polyatomic ions? Write the symbol for the cation followed by the formula for the polyatomic ion and balance the charges. For example, calcium nitrate is composed of a calcium cation (Ca2+) and a polyatomic nitrate anion (NO3–). In calcium nitrate, two nitrate anions, each with a 1– charge, are needed to balance the 2+ charge of each calcium cation. The formula for calcium nitrate is Ca(NO3)2. Conceptual Problem 9.2 Conceptual Problem 9.2 Conceptual Problem 9.2 Conceptual Problem 9.2 a) (NH4)2SO3 b) Ca3(PO4)2 Compounds With Polyatomic Ions Naming Compounds with Polyatomic Ions To name a compound containing a polyatomic ion, state the cation first and then the anion, just as you did in naming binary ionic compounds. ex. (NH4)2SO3 ammonium sulfite Ca3(PO4)2 calcium phosphate Don’t change polyatomic ion names like you would a monotomic anion! 9.2 Section Quiz 1. The correct name for CrCl3 is a) chromium chlorine. b) chromium(III) chloride. c) monochromium trichloride. d) chromium(III) trichloride. 9.2 Section Quiz 2. What is the correct formula for strontium nitride? a) Sr3N2 b) SrN2 c) Sr2N3 d) Sr3N 9.2 Section Quiz 3.Which one of the following compounds is named correctly? a) sodium chlorite, NaClO b) potassium nitrate, KNO2 c) sodium acetate, NaC2H3O2 d) lithium sulfate, Li2SO3 9.3 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds What does a prefix in the name of a binary molecular compound tell you about the compound’s composition? A prefix in the name of a binary molecular compound tells how many atoms of an element are present in each molecule of the compound. •9. Naming Binary Molecular Compounds 3 Carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2), but these two invisible gases are very different. Sitting in a room with small amounts of CO2 in the air would not present any problems. If the same amount of CO were in the room, you could die of asphyxiation. A naming system that distinguishes between these two compounds is needed. Writing Formulas for Binary Molecular Compounds How do you write the formula for a binary molecular compound? Use the prefixes in the name to tell you the subscript of each element in the formula. Then write the correct symbols for the two elements with the appropriate subscripts. •9. Naming Binary Molecular Compounds 3 Some guidelines for naming binary molecular compounds: – Name the elements in the order listed in the formula. – Use prefixes to indicate the number of each kind of atom. – Omit the prefix mono- when the formula contains only one atom of the first element in the name. – The suffix of the name of the second element is -ide. Ex. Silicon carbide is a hard material like diamond. The name silicon carbide has no prefixes, so the subscripts of silicon and carbon must be one. Thus, the formula for silicon carbide is SiC. 9.3 Section Quiz 1. Which of the following compounds is named INCORRECTLY? a) CS2, carbon disulfide b) BCl3, boron trichloride c) IF7, iodine heptafluoride d) PCl5, phosphorus hexachloride 9.3 Section Quiz 2. Which of the following molecular compounds is named INCORRECTLY? a) SbCl3, antimony trichloride b) C2O5, dicarbon pentoxide c) CF4, carbon tetrafluoride d) H3As, hydrogen arsenide 9.3 Section Quiz 3. The correct formula for tetraphosphorus trisulfide is a) P3S4 b) S3P4 c) P4S3 d) S4P3 9.4 Naming and Writing Formulas for Acids and Bases Three rules can help you name an acid with the general formula HnX. 1) When the name of the anion (X) ends in -ide, the acid name begins with the prefix hydro-. The stem of the anion has the suffix -ic and is followed by the word acid. 2) When the anion name ends in -ite, the acid name is the stem of the anion with the suffix -ous, followed by the word acid. 3) When the anion name ends in -ate, the acid name is the stem of the anion with the suffix -ic followed by the word acid. An acid is a compound that contains one or more hydrogen atoms and produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. Acids have various uses. Summary of Naming Acids How are the formulas of acids determined? Use the rules for writing the names of acids in reverse to write the formulas for acids. What is the formula for hydrobromic acid? Following Rule 1, hydrobromic acid (hydro- prefix and -ic suffix) must be a combination of hydrogen ion (H+) and bromide ion (Br–). The formula of hydrobromic acid is HBr. Know these acids (except carbonic) and the other hydro- examples How are bases named? Bases are named in the same way as other ionic compounds—the name of the cation is followed by the name of the anion. For example, aluminum hydroxide consists of the aluminum cation (Al3+) and the hydroxide anion (OH–). The formula for aluminum hydroxide is Al(OH)3. Be able to name bases. 9.4 Section Quiz 1. The name for H2S(aq) is a) sulfuric acid. b) hydrosulfuric acid. c) sulfurous acid. d) hydrosulfurous acid. 9.4 Section Quiz 2. The correct chemical name for NH4OH is a) nitrogen tetrahydrogen hydroxide. b) nitrogen pentahydrogen oxide. c) ammonium oxyhydride. d) ammonium hydroxide.