SOCIAL MARKETING applications in public health
advertisement

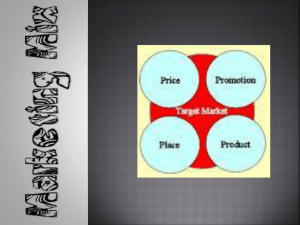
SOCIAL MARKETING applications in public health Dr Babar T Shaikh The Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan SOCIAL MARKETING Enabling Objectives: • To learn the basic concepts of social marketing • to understand ways of performing social marketing in developing countries • To learn four Ps of social marketing Social Marketing Performance Objectives: By the end of the presentation, learners will be able to • conceptualize basic concepts of social marketing • understand its important components • apply the knowledge in medical practice What is Social Marketing? It is a marketing strategy modeled after corporate marketing, used by health professionals to develop successful health messages. Social Marketing • What makes social marketing different than other social change strategies? • How is it different from what you are doing right now? Social Marketing Key concepts • Uses commercial marketing technologies and theory • Brings about voluntary behavior change • Targets specific audiences • Focus is on personal welfare and that of society Social Marketing Potential Applications • • • • • Promote healthy behavior Promote services Increase utilization rates Improve customer satisfaction Enhance compliance Social Marketing Social Marketing’s Popularity • It works by bringing about behavior change • More cost effective • Reaches larger numbers Social Marketing Distinguishing Features of Social Marketing • • • • • Exchange theory Consumer orientation Data based decision making Competition Willingness to change offer Social Marketing # 1 Consumer Orientation • Understand consumer perceptions • Which benefits they find attractive • Costs or barriers that deter them Social Marketing Put Simply, Consumer Orientation Means • Understand what they want and need • Respond to their wants and needs Social Marketing #2 Exchange Theory • Exchange time and effort for benefits • Make an attractive offer • Create an awareness that the problem exists • Demonstrate the product’s benefits • Help lower the price Social Marketing #3 Data Based Decision Making • • • • • Logical model for planning How you plan to help What you will help them to do Which factors you must address Data based decision making Social Marketing #4 Competition • Marketers keep a steady eye on the competition • Marketers position products relative to the competition Social Marketing #5 Willingness to Change Offer • Committed to designing products consumers want • Committed to modifying programs • Committed to addressing facts that influence their behavior Social Marketing Traditional Approach to Health Education Messages Top Down Planning • Expert driven • Best practices • Literature review Social Marketing In Other Words… • We will tell you what you need and want (expert driven) • Offer everyone same product, price, place and promotion Social Marketing Social Marketing Uses A Interdisciplinary Approach • • • • • Social anthropology Behavior psychology Communications Education Commercial Marketing Social Marketing Demographics • • • • • Age Gender Ethnicity Geographical area Education level Social Marketing Psychographics • Attitude toward new behaviors (early vs. Late adopters) • Types of people who share similar hopes, concerns, or who they admire • Aspirations, personality types, lifestyles • Willing to take risks and try new behaviors • Tend to follow the crowd Social Marketing Commercial Marketing • Satisfying customer needs and wants • Process for individuals and groups to obtain what they need and want by creating/ exchanging products and value with others Social Marketing Marketing • • • • • Audience segmentation Product development Pricing Testing Distribution Social Marketing Segmentation: Marketing Model • Marketers know they can’t appeal to all buyers in the same way • Political marketers: who do they try to reach? • Coca cola: what proportion of market do they try to reach? Social Marketing Segmentation Strategy • Divide heterogeneous group in homogenous subgroups • Identify targets of opportunity • Identify subgroups to respond to same offer • Design interventions effective for each segment Social Marketing The Four P’s of Social Marketing Product Price Place Promotion Social Marketing Product What we’re offering people: • Service • Behavior • Commodity (tangible goods) Social Marketing Product Must Be Solution to a problem: • Benefits • Unique • Competitive Real: • Defined in terms of the user’s beliefs, practices, and values Social Marketing Price The cost of adopting the product: • • • • • Money Time Pleasure Loss of self-esteem Embarrassment Social Marketing Place Channels for information: • • • • • • • Where service is provided Where information is received Where tangible product is purchased Available Easy to find and use Appropriate Timely Social Marketing Promotion Message design elements: • Type of appeal • Tone • Spokesperson Social Marketing Social Marketing Works! • It brings about behavior change • More cost effective by reaching larger numbers