Photosynthesis Study Guide Answer Key
advertisement
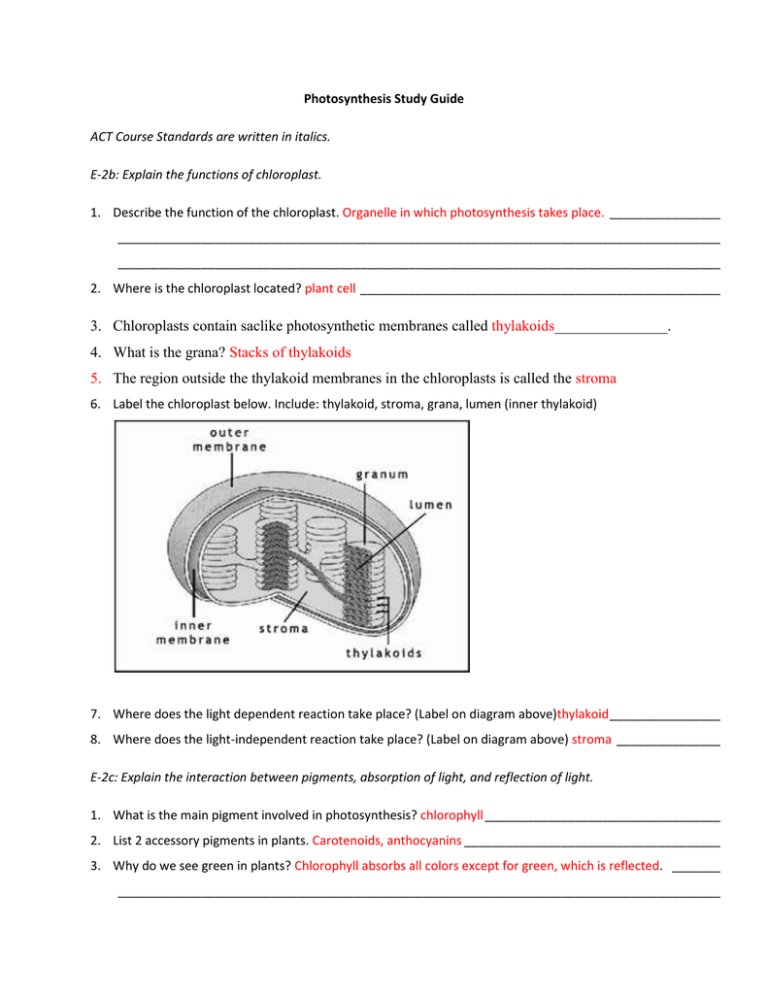
Photosynthesis Study Guide ACT Course Standards are written in italics. E-2b: Explain the functions of chloroplast. 1. Describe the function of the chloroplast. Organelle in which photosynthesis takes place. ________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Where is the chloroplast located? plant cell ____________________________________________________ 3. Chloroplasts contain saclike photosynthetic membranes called thylakoids_______________. 4. What is the grana? Stacks of thylakoids 5. The region outside the thylakoid membranes in the chloroplasts is called the stroma 6. Label the chloroplast below. Include: thylakoid, stroma, grana, lumen (inner thylakoid) 7. Where does the light dependent reaction take place? (Label on diagram above)thylakoid ________________ 8. Where does the light-independent reaction take place? (Label on diagram above) stroma _______________ E-2c: Explain the interaction between pigments, absorption of light, and reflection of light. 1. What is the main pigment involved in photosynthesis? chlorophyll __________________________________ 2. List 2 accessory pigments in plants. Carotenoids, anthocyanins _____________________________________ 3. Why do we see green in plants? Chlorophyll absorbs all colors except for green, which is reflected. _______ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Where is chlorophyll located in the plant cell? Be specific! In the photosystems within the chloroplast 5. What role does chlorophyll play in photosynthesis? Absorbs solar energy (sunlight) ____________________ 6. If a plant has purple leaves, does it still undergo photosynthesis? Explain. Yes, the plant still has chlorophyll, which is required for photosynthesis, but the purple pigments mask the chlorophyll. E-2d: Describe the light dependent and light independent reactions of photosynthesis. 1. What occurs in the process of photosynthesis? _Plants use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into high energy sugars (glucose) and oxygen. 2. Write the overall equation for photosynthesis using words. Plants use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into high energy sugars (glucose) and oxygen. 3. Write the overall equation for photosynthesis using chemical formulas. CO2 + H2O + sunlight C6H12O6 + O2 4. What does photosynthesis require in addition to water and carbon dioxide? ___sunlight______ ___________ _______________________________________________________________________ ____________________ 5. What are the 2 stages of photosynthesis called? Light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions ___________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Label the following diagram. Describe what happens during each step of the light dependent reaction. 7. What is used during the light dependent reaction? Water (H2O) and sunlight ___________________________ 8. What is produced during the light dependent reaction? Oxygen (O2), NADPH, and ATP ____________________ 9. How does oxygen leave the plant? Through the stomata ____________________________________________ 10. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the light dependent reactions. Correct the false statements. a. They convert ADP into ATP b. They produce oxygen gas c. They convert oxygen into carbon dioxide (They convert water into oxygen.) d. They convert NADP+ into NADPH e. High energy electrons move through the electron transport chain from photosystem II to photosystem I. f. Photosynthesis begins when pigments in photosystem I absorb light. (photosystem II) g. The difference in charges across the thylakoid membrane (more Hydrogen ions inside the thylakoid than outside) provides the energy to make ATP. 11. The light energy from the sun is converted into chemical energy and stored in the NADPH and ATP. 12. What happens to CO2 in the Calvin cycle (light-independent reaction)? It is converted into glucose ________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 13. CO2 goes into the Calvin cycle from the atmosphere. It enters the plant through the stomata. 14. ATP and NADPH provide energy for the Calvin cycle. This energy comes from the ______light dependent reactions_. 15. Circle the statement that is true about the Calvin cycle. Correct the false statements. a. The main products of the Calvin cycle are six carbon dioxide molecules. (reactants) b. Carbon dioxide molecules enter the Calvin cycle from the atmosphere. c. Energy from ATP and high-energy electrons from NADPH are used to convert 3carbon molecules into similar 3-carbon molecules. d. The Calvin cycle uses six molecules of carbon dioxide to produce a single 6-carbon sugar molecule. 16. What are the products of the Calvin cycle? C6H12O6 (glucose), ADP, NADPH 17. Label the diagram below. Be able to describe what happens at each phase. E-2e: Relate the products of the light-dependent reactions to the products of the light-independent reactions. 1. Complete the illustration of the overview of photosynthesis by writing the products and reactants of the process, as well as the energy source that excites electrons. CO2 O2 sunlight ADP NADP+ Light dep. reactions Light indep. reactions ATP NADPH Cellulose 2 3-C Mol C6H12O6 starch H2O 2. Relate the products of the light-dependent reactions to the products of the light-independent reactions. ATP and NADPH are produced during the light-dependent reactions. These products are used in the Calvin Cycle (light independent reactions) to produce glucose. (They provide energy to fuel the reactions.) The resulting ADP and NADP+ then go back to the thylakoid to accept more energy in the light dependent reactions. 3. Complete the Venn Diagram. Thylakoid Uses H2O, sunlight Produces O2, ATP, NADPH Share products. (ATP, NADPH, ADP, NADP+) Occurs in plant cells Stroma Uses ATP, NADPH, CO2 Produces glucose, ADP, NADPH Light Dependent Reactions Light Independent Reactions 4. What are 3 factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis? Temperature, carbon dioxide, water, sunlight 5. Is the following statement true or false? Increasing the intensity of light decreases the rate of photosynthesis. False Section 8-1 Autotrophs and Heterotrophs 1. Where does the energy of food originally come from? The sun 2. Complete the table describing the types of organisms. Type Description Examples Autotrophs Organisms that make their own food. Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat. Plants (apple tree, daisy) Heterotrophs Animals (lion, human) Chemical Energy and ATP 3. What is one of the principle chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has 3 phosphate groups and ADP only has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Adenine Ribose Phosphate groups ATP 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? In can add a phosphate group to ADP, producing ATP.






