ALAT Chapter 9
advertisement

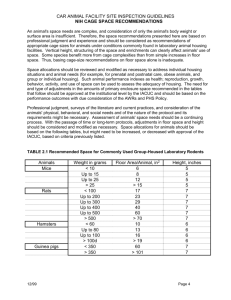
Chapter Nine Facility Equipment ALAT Presentations Study Tips If viewing this in PowerPoint, use the icon to run the show (bottom left of screen). Mac users go to “Slide Show > View Show” in menu bar Click on the Audio icon: when it appears on the left of the slide to hear the narration. From “File > Print” in the menu bar, choose “notes pages”, “slides 3 per page” or “outline view” for taking notes as you listen and watch the presentation. Start your own notebook with a 3 ring binder, for later study! Facility Equipment Specialized equipment = cage racks, floor scrubbers, autoclaves, vacuum cleaners and cage washers a large capital expense in the operating budget It is important that animal technicians learn the appropriate care and use for each piece of equipment. When equipment fails to operate properly, it must be immediately taken out of use. The failure can then be reported to the appropriate manager and the equipment repaired or replaced as quickly as possible. Caging Depends on nature of research & husbandry Safe cages have smooth surfaces with no jagged edges, broken wire rungs or rust. Escape-proof & well ventilated to maintain environment Poorly ventilated cages - water and urine may soak animals and increase humidity. Dirt and waste deposits collect cracks & crevices. Proper cage design permits safe handling of animals & protects animal handlers. Caging Materials Stainless steel smooth, durable, no rust & is impervious to descalers expensive, but durability offsets high price Aluminum weighs less than stainless steel but is less durable Galvanized steel, iron, & wood not suitable caging materials rust & don’t stand up to most chemical cleaners wood - rough, splintery surface, difficult to sanitize sealed w/ epoxy paint is more easily sanitized, but does not stand up to high wash temps or scrubbing Plastic Caging Materials Polystyrene melts or warps at wash temp, moderate strength used for single use disposable rodent caging Polypropylene holds up at high wash temperatures but is opaque non-transparent may be preferable for solitary species Polycarbonate high impact strength, transparent, holds up at high temps Plastics do not rust, their surfaces are smooth, & they are impervious to chemical cleaners Shoebox Rodent Cages Solid-bottomed plastic or stainless steel cage Contact bedding is generally used. The water bottle and feeder are easily visible. Microisolation systems > control of environment Micro-Isolator™ has own filter top to limit air exchange between room & cage interior. May sit on standard rack, or ventilated rack. Procedures inside hooded, ventilated workbench. feeding, watering, cage changing & manipulations (Images) Microisolator Changing Hood Micro-Isolator™ Courtesy of Lab Products, Inc. Suspended Cage Systems Have perforated or solid bottom Wastes drop through bottom into collection pan. routinely emptied and cleaned Flooring can injure or irritate animals’ feet & legs. Plastic-coated mesh and bars reduce irritation & provide a warmer, more comfortable surface. Smooth metal floors are comfortable alternative. May have individual lids, or suspended on runners which enable shelves to serve as lids. Wire mesh cages better ventilation than solid. Newborns fall through wire; direct contact w/ metal draws heat away from animals’ bodies. Front-Opening & Metabolism Cages Front-Opening Cages Available as individual or multiple-cage rack Bar or wire mesh flooring w/ collection trays Feeders & bottle holders attach to cage door. Rabbits, cats, dogs & primates usually housed in frontopening cages. Metabolism cages designed to separate urine & feces for specimen collection. frequently & carefully hand cleaned prevent feed & water from mixing with specimens powdered feed helps prevent dropping into collection drinking valve outside cage to avoid contamination of collected urine sample Two Types of Mouse Metabolism Cages Gang Cages House groups of same animal species Resting boards or perches make better use of space. Bedding on the cage floor depends on species. Feed and water offered in >1 location to avoid food hoarding by dominant animals. Cats, primates & sheep Introducing/creating group may result in fighting. Make careful observation of group. Transport Cages Shipping cartons - temporary transport housing Moist mash, fresh fruits or vegetables can be source of moisture. AWA regulates shipment of certain species, such as guinea pigs, hamsters, rabbits, cats, dogs & nonhuman primates. Regulations cover shipping carton construction, space requirements, documentation, feed & water schedules. Transport cages within a facility Feed, water & bedding usually not required, since animals only in cage for a short time. If transporting in public areas, advisable to use covering. Runs or Pens Runs or pens are used for larger animals. Large enclosures usually with waterproof flooring & often with a resting area elevated above floor Floor slopes to aid drainage of water and urine away from housing & feeding areas. Surfaces should be easy to clean and sanitize. When built outdoors, pens & runs must also include shelter from inclement weather. Pens and runs are commonly used to house dogs, sheep, pigs and goats. Feeding & Watering Accessories Pelleted feed held in slotted V-shaped feeders in cage lids or in feeders clipped onto cages. J-shaped feeders used for smaller sized pelleted rabbit and guinea pig feed. Feed & water bowls on floor used for dogs & cats. Suspended or detachable feeders that keep feed off the floor help eliminate contamination. Water - glass or plastic bottles, stainless steel or rubber bowls, pails or automatic watering system Bottles or bowls to monitor amount consumed Some types of medications administered in water. (Image) Watering and Feeding Devices Automatic Watering Eliminates work associated with water bottles. Water through piping to animal area, where pressure is reduced to suitable levels. Pressure reducing station has 1 - 2 pressure regulators filters out particulates from the water supply Water then passes into room distribution system to direct water to cage rack Retractable recoil hoses tie room system with animal cage rack manifold system. Designed to pipe water to each cage and provide a direct source of water via a drinking valve device. 2 Pressure Water Flow (Images) Automatic Automatic Reduction Station 1 Treatment Tanks 4 Sipper Water Flow 3 Recoil Hose Automatic Watering II Individual valves must be checked regularly. Clogged or leaking valves should be replaced immediately or identified as nonfunctional. Check pressure station gauges daily. Flush to reduce accumulation of microorganisms. Some facilities use chemicals such as chlorine to sanitize water systems. It may be necessary to provide newly received animals with water bottles until they learn to use the automatic watering system. Rabbits often require several days to adjust. An animal that is thirsty will not eat. Cage Wash Equipment Cabinet washers - loaded & sanitized in chamber Washer goes through washing & rinsing cycles followed by a drying cycle. Rack washers are large versions of cabinet washers - racks of caging directly rolled in. single door or pass-through Tunnel cage washer is like a commercial car wash. carries equipment through washer on a conveyor belt series of stations wash, rinse & dry Cage wash controls permit temp control, timing of cycles, detergent addition & emergency shutoff. also have monitoring and/or recording gauges (Images) Scenes From Cage Wash Cage Wash Equipment II Cleaning filters & spray valves ensure that spray valves do not become plugged. Experienced specialists examine & service motors, gaskets & electrical components. Check timers & gauges daily to ensure equipment is properly sanitized. Some facilities use pressurized steam cleaners to complement initial hand cleaning of cages. When no cage washers are available, these cleaners may be primary method for cage sanitation in conjunction with disinfectants and detergents. (Images) Cage Wash Equipment Balances Technicians may weigh animals, obtain body temperatures or take other measurements. Capacity of a scale or balance refers to max. weight device can measure accurately. Accuracy of a balance refers to degree measured weight = actual weight. An efficient balance allows small weight increments to be distinguished with accuracy. Speed and ease of operation important in choosing the balance best suited for a particular job. Top-loading balances are most common. Balances II Triple-beam & double-pan for smaller species. Large species platform scales read weight directly, similar to a home bathroom scale. Some are designed so animal is restrained. Top-loading balances w/ digital readouts. Pan weight set at zero automatically to eliminate weight of restrainers before measuring animal. Some models provide printout. Electronic balances can input data to a computer. Cleaning scales after each use is important to prevent transmission of disease & prevent dirt & hair accumulation from affecting scale operation. Additional Reading Poole, Trevor (ed.). The UFAW Handbook on the Care and Management of Laboratory Animals, 6th. Ed. Longman Scientific and Technical, Essex, England. 1987 Rollin, Bernard E., and M. Lynne Kesel (ed.). The Experimental Animal in Biomedical Research. Volume II: Care, Husbandry and Well-Being — An Overview By Species. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. 1992