Beyond Mendel - loudoun.k12.va.us
advertisement

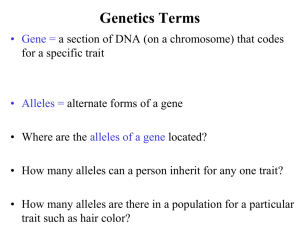
BEYOND MENDEL Other patterns of inheritance Mendel’s laws • 1st Law of Dominance—allele that is always expressed when the organism is a heterozygote is the dominant allele. The other type of allele is NOT expressed. • 2nd Principle of Segregation—homologous chromosomes separate into different gametes. Each allele has equal probability of ending up in any given gamete. How does meiosis sort chromosomes? • 3rd Principle of Independent Assortment Genes on different chromosomes sort into gametes independently. • In metaphase II, pairs of chromosomes line up down the middle. One chromosome goes to each new daughter cell. Only one. • Haploid cells receive one of each type of chromosome, 23 in all. • Which daughter cell receives which of the parent’s two homologous chromosomes is a RANDOM event. Dihybrid • A dihybrid is the result of a cross between individuals with 2 different forms for 2 genes. • Try crossing peas with different seed color and different seed shape. • Check your understanding • Color Yellow (dominant) YY x green (recessive) yy • All offspring are Yy with color________________ • Shape Round (dominant) RR x wrinkled (recessive) rr • All offspring are Rr with shape_______________ • Apply the independent assortment principle to 2 genes on 2 different chromosomes. Complete a dihybrid • Separate alleles— each combination is equally likely to occur. • Try FOIL method. Be sure one letter for each gene is included! Y R Y R • (½ Y + ½ y) * ( ½ R + ½ r) = ¼YR + ¼ Yr + ¼ yR + ¼ yr • Place one of the gamete combinations in front of one of the squares. • Pass out the letters in the same way for a monohybrid. Yy Rr Yr Yy Rr Yr yR YYRR YYRr YyRR YyRr YYRr YYrr YyRr Yyrr YyRR YyRr yyRR yyRr YyRr Yyrr yyRr yyrr yr yR yr Look at the seeds from the cross • How many are yellow and • • • • round? How many are yellow and wrinkled? How many are green and round? How many are wrinkled and green? 9:3:3:1 Write the ratio____________ YYRR YYRr YyRR YyRr YYRr YYrr YyRr Yyrr YyRR YyRr yyRR yyRr YyRr Yyrr yyRr yyrr Complete dominance • Mendel did his work with a plant that had only complete dominance • The seven genes in peas had one dominant allele and one recessive allele. • The dominant allele does the ‘talking’ and the recessive allele is hidden in a heterozygote. The next plant Mendel tried did not have complete dominance. His experiments did not support his hypothesis. It took 34 years before other scientists recognized his work and added to it. Incomplete dominance • The homozygous individual shows the form of the allele. RR is red. • The heterozygote will show a blending of the two versions. Rr is pink. • The presence of two different alleles result in a form that is an intermediate to the parental forms. Incomplete dominance example • In humans, the texture of the hair shows incomplete • • • • dominance. Homozygous for curly, CC, results in curly hair. Homozygous for straight, SS, results in straight hair. The heterozygous state, SC, results in the intermediate form with all wavy hair. C and S are both incompletely dominant, neither one are recessive. What are the percentages of the phenotypes? ___%, ___%, ___% Curly/Wavy/Straight Label X S C S C Codominance • A trait that shows codominance has heterozygotes that show the effect of both alleles. • Each allele is expressed in the organism • Color in cattle • red x r d w it s o t d offspring Sickle Cell Anemia • Sickle cell anemia results from a change in the • • • • hemoglobin. A single base in the DNA changes and one amino acid is changed. The molecule becomes long. With two normal hemoglobin alleles HbA HbA, a person has all normal red blood cells. Heterozygotes HbA HbS, have both normal red blood cells and some long sickle cells. Heterozygous condition helps people survive malaria. With two sickle cells HbS HbS, the person has sickle cell anemia, a painful condition with clots. Which pattern of inheritance does this gene show? Codominance: both red blood cell types are present. Check your understanding. • A white homozygous cow is crossed with a homozygous red bull and the calf is roan with red and white patches of fur. What type of inheritance is roan? codominance • Two parents with poor night vision have three children, one with normal night vision, one who is night blind, and one with poor night vision. What pattern of inheritance is this? Incomplete dominance Multiple alleles • Blood type includes four main phenotypes: A, B, AB, and • • • • • • Omore than two alleles. Each blood type has specific antigens on the cell membrane, and it is named for the antigens on the cell. A and B are codominant: IA or IB O is recessive: I AA and Ao Type A has two genotypes. Name them. Type B has two genotypes. Name them. BB and Bo Type O has one genotype. Name it. oo Determine the paternity of the child • The mother is type A, and the father is type B. Can a type O child possibly be their offspring? (Hint: start with the child who X is recessive.) ___________ ____________ ___________ ___________ • Could an AB father have a type O child? Why? X ___________ ___________ ___________ ____________ Check your understanding • Alleles of a single gene can interact with other alleles of the same gene or with the environment. Name the type of inheritance • When heterozygous offspring look like one parent but not the other • complete dominance. • When heterozygotes show a phenotype unlike that of either parent • incomplete dominance. • When heterozygotes show characteristics of both parents • co-dominance. Resources • Monohybrids, 2014, The Biology Project, http://www.biology.arizona.edu/mendelian_genetics/proble m_sets/monohybrid_cross/09t.html