Chapter 14
advertisement

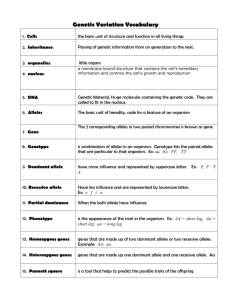
Chapter 9.1~ Mendel & The Gene Idea Mendelian genetics Character: heritable feature, i.e., fur color Trait : variant for a character, i.e., brown True-bred: all offspring of same variety Hybridization: crossing of 2 different true-breds P generation: parents F1 generation: first generation Leading to the Law of Segregation Alternative versions of genes (alleles) account for variations in inherited characteristics Org inherits 2 alleles per character dominant allele - fully expressed in orgs appearance. recessive allele - no noticeable effect on appearance The alleles for each character segregate (separate) during gamete production (meiosis). Mendel’s Law of Segregation Genetic vocabulary……. Punnett square: predicts the results of a genetic cross between individuals of known genotype Homozygous: pair of identical alleles for a character Heterozygous: two different alleles for a gene Phenotype: an organism’s traits Genotype: an organism’s genetic makeup Testcross: breeding of a recessive homozygote X dominate phenotype (but unknown genotype) Practice monohybrid crosses Reporting results… %, fraction, ratios… Phenotypic results: Genotypic results: TRAIT KEY Hairline: Tongue: Earlobes Eye shape Blood type Hair Freckles Middle toe Fingers Lip size Knuckle Thumb W= widow’s peak R = can roll F = free hanging L = almond shaped A = type A blood C = curly K = freckles D = short S = six T = thick lips H = hair on middle knuckle B = hitchhikers w= straight hairline r = can’t roll f = attached = round shaped B = type B blood c = straight k = no freckles d = long s = five t = thin lips h = no hair on middle knuckle b = straight thumb The Law of Independent Assortment Law of Segregation involves 1 character. What about 2 (or more) characters? Monohybrid cross vs. dihybrid cross The two pairs of alleles segregate independently of each other. Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment Cross a yR with YR Yr yR YyRR YyRr yyRR yr yyRr Results: 6/16 yr YyRr Yyrr yyRr yyrr 6/16 2/16 yR YyRR YyRr yyRR yyRr yr YyRr Yyrr yyRr yyrr 2/16 Practice Slide Results: Using the rule of multiplication to find particular genotypes or phenotypes What is the probability of getting a yyRR if a is crossed with a ? Complete a monohybrid cross for each character & then multiply the two fractions. … so chance of getting a yy if cross a Yy & yy? … chance of getting a RR if cross a Rr & Rr? Using the rule of multiplication to find particular genotypes or phenotypes What is the probability of getting a green round if a is crossed with a ? Complete a monohybrid cross for each character & then multiply the two fractions. … so chance of getting a green if cross a Yy & yy? … chance of getting a round if cross a Rr & Rr? Extending Mendelian Genetics, I Incomplete dominance: appearance between the phenotypes of the 2 parents. Results in 3 possible phenotypes – one being intermediate. Ex: snapdragons Molecular explanation for incomplete dominance One allele carries the code for a functional protein and the other doesn’t. Since there’s only one copy of the functional allele, not enough proteins are synthesized which results in the intermediate phenotype in the heterozygote. How is this different from complete dominance? Extending Mendelian Genetics, II Codominance: two alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways. Ex: human blood types Multiple alleles: more than 2 possible alleles for a gene. Ex: human blood types Extending Mendelian Genetics, III Pleiotropy: genes with multiple phenotypic effect. Ex: sickle-cell anemia Extending Mendelian Genetics, IV Epistasis: a gene at one locus (chromosomal location) affects the phenotypic expression of a gene at a second locus. Ex: mice coat color B = black b = brown C = pigment production c = no pigment production Epistasis Problem • In a certain breed of plants, D produces dark red color and is dominant over d which produces a light red color. Another gene determines in which cells the pigment will be synthesized. Allele w allows synthesis of the pigment throughout the petals but the mutant allele W prevents pigment production. D = dark red d = light red w = pigment production W = no pigment production You cross two plants that are DdWw. What will be the genotype and phenotype ratios of the crosses? Possible phenotypes: Dark red = 3/16 Light red = 1/16 DW Dw dW White = 12/16 (3/4) DW DDWW DDWw DdWW dw DdWw Dw DDWw DDww DdWw Ddww dW DdWW DdWw ddWW ddWw dw DdWw Ddww ddWw ddww Possible genotypes: DDWW = 1/16 DDWw = 2/16 (1/8) DdWW = 2/16 (1/8) DdWw = 4/16 (1/4) DDww = 1/16 Ddww = 2/16 ddWW = 1/16 ddWw = 2/16 (1/8) Ddww = 1/16 Same problem continued… DW Dw dW dw DW DDWW DDWw DdWW DdWw Dw DDWw DDww DdWw Ddww dW DdWW DdWw ddWW ddWw dw DdWw Ddww ddWw ddww Extending Mendelian Genetics, V Polygenic Inheritance: an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character Ex: human skin pigmentation and height Human disorders The family pedigree – trace a character through generations Square = male, circle = female, shaded = has trait What is it about the recessive allele that causes the disease phenotype? codes for malfunctional protein or none at all Hetero normal b/c dom allele produces enough of the needed protein Recessive Human Genetic Disorders Tay-Sachs fatal genetic lipid storage disorder in which harmful quantities of a fatty substance called ganglioside GM2 build up in tissues and nerve cells in the brain. Cystic fibrosis Build up of mucus in the lungs and digestive tract due to the lack of a transport protein in the cell membranes. Sickle-cell Substitution of single amino acid in hemoglobin of RBC 1/400 African Americans 1/10 are hetero for it Treatment = blood transfusions Hetero have disease b/c alleles are codom on molecular level. High hetero b/c they are res to malaria! Cystic fibrosis Build up of mucus in the lungs and digestive tract due to the lack of a transport protein in the cell membranes. Most lethal in US 1/2500 whites of Euro decent have it 1/25 are carriers Antibiotic & pounding Dominant Human Genetic Disorders •Huntington’s results from genetically programmed degeneration of brain cells, called neurons, in certain areas of the brain. This degeneration causes uncontrolled movements, loss of intellectual faculties, and emotional disturbance. Testing •amniocentesis •chorionic villus sampling (aka: CVS) Quiz tomorrow on ch 14 Get out snowflake problems, ch 12 review sheet w/ aliens on it, pedigree practice sheet… we’re going over them. Photosnythesis labs due Fri. Ch 9 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Chromosomal theory in inheritance – mendelian genes have specific loci on chromosomes & it is the chromosomes that undergo segregation & independent assortment Morgan traced genes to specific chrom fruit flies Prolific breeders New gen every 2 wks Only 4 pair chrom. Normal (wild type) = lower case of mutant w/ + Mutant = lower case Use different symbols with these problems… Lower case of mutant + = dominant So… b+ = gray b = black vg+ = normal wings vg = vestigial wings b+ b vg+ vg x bbvgvg b+ vg+ b vg b vg b vg b vg b+ vg b vg+ b vg Recombination Frequency Using recombination frequencies to construct a genetic map – ordered list of the genetic loci along a chromosome Farther apart 2 genes are – higher probability x-over will occur. AP Bio 12/16 Do It Now… What fraction of offspring would you expect to be bald if you crossed a bald man with a woman who is heterozygous for the bald allele. Sex Linked Traits – traits that are determined by genes on the X chromosome Unique patterns of inheritance Why? Males need only 1 rec allele to have a sex linked disorder Colorblindness, hemophilia (blood won’t clot), baldness, duchenne muscular dystrophy All recessive disorders More men than women have sex linked traits. Explanation: XH XH = Homozygous Dominant Woman XH Xh = Heterozygous Woman Xh Xh = Homozygous Recessive woman so hemophilia XH Y = Dominant male so no hemophilia Xh Y = Recessive male so hemophilia So… males only need one recessive allele to have a sex linked trait since they only have one X Women have 2 X chromosomes so they have to inherit 2 recessive alleles to have a sex linked trait. Males inherit sex linked traits from their mothers. Why? B/c males inherit their X chromosomes from their moms – their dads give them their Y chromosomes. So… men inherit baldness from their moms! Sex linked trait problems: Cross a woman heterozygous for baldness with a man who is not bald. Hint: show chromosomes too XB Xb XB X X X Y Y B B B XBXb XbY ¼ chance that child will be bald. ½ chance that they have a boy that’s bald. Everyone should be able to see a 12 Nomal =5 color blind = 2 X inactivation in female mammals 1 of the 2 X chromosomes in each cell becomes almost completely inactivated during embryonic development. Barr body – condensed form of inactive X located along inside of nuc mem Random from cell to cell… mosaic of active X s Ex: calico cats, human females lacking sweat glands 15.5 from ch 15 study guide 2 normal colorsighted individuals produce the following children & grandkids. #1 from ch 15 study guide p 108 Scientists use recombination frequencies to determine the order of genes on a chromosome. Try to figure out the order of these 5 genes given the following recombination frequencies. D 16 B 4 C 10 A 6 E