Chemistry HP Final Review Spring 2013 1. Convert between
advertisement

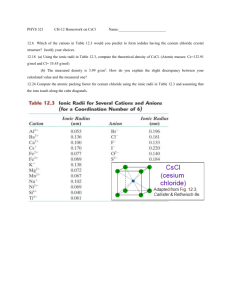
Chemistry HP Final Review Spring 2013 1. Convert between standard form and scientific notation. -8 (a) 8 900 000 = ________________ (c) 4.5x10 = ________________ 4 (b) 0.00056 = ________________ (d) 2.7x10 = ________________ 2. Convert between the units indicated. (a) 35 cm = _________ m (b) (b) 280 mL = _________ L 3. Complete the following temperature conversions. (a) _____ °C = 300 F = _____ K (b) -20 °C = _____ F = _____ K MATTER AND CHANGE 4. A gold block measures 1.50 cm by 1.00 cm by 0.900 cm. (a) What is the volume of the block? (b) What is the density of gold? (c) What is the mass of the block? 5. A graduated cylinder contains 50 mL of water. When a small stone is placed in the graduated cylinder the water level rises to 70 mL. If the stone weighs 40 g, what is the density? ATOMIC STRUCTURE 6. Determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in the following elements. (a) Cr (b) Br - (c) Sr 2+ 7. Draw a Bohr Diagram for the following elements. Include the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons. (a) N (b) Ca 8. Chromium has four isotopes: Cr-50 (4.35%), Cr-52 (83.79%), Cr-53 (9.50%), and Cr-54 (2.37%) (a) Determine the number of neutrons of each isotope. (b) Determine the average atomic mass of Chromium. c) Write the nuclide name and symbol for Cr-50. 9. Referring back to #8, the average atomic mass of chromium should be closest to which isotope of Cr? Why? 10. List 3 physical changes and 3 chemical changes of matter. 11. Write orbital notation for the following elements/ions. (a) Si (b) V (c) S 2- 12. Write electron configuration notation for the following elements/ions. (a) Cl (b) Ge (c) Y 3+ 13. Write the noble gas notation for the following elements/ions. (a) Rb (b) Sc (c) I - 14. Determine the number of valance electrons in each of the following elements: (a) S (b) Ca (c) Ar PERIODIC TRENDS AND BONDING 15. Complete the following table: a) Na or P? Which element has a larger atomic radius? Explain. Which elements has a higher ionization energy? Explain. Which element has a higher electronegativity? Explain. Which element has more metallic character? Why? 16. Which has a larger radius, the atom or the ion? Explain. 4+ (a) P or P3(b) Zr or Zr b) Li or K 17. For each molecule: 1. Draw the Lewis Structure 2. Draw the VSEPR diagram &classify the shape of the molecule (a) F O *(e) PF (b) PH (f) CBr 2 3 *c) SF (g) BF 6 (d) CS 5 4 3 2 NOMENCLATURE 18. Name the following compounds (a) LiCl _________________________ (f) H CO _______________________ (b) MgCO ______________________ (g) FePO _______________________ 3 2 4 (c) CuS _________________________ (d) NiCl ________________________ 3 (e) N O ________________________ 2 2 5 (h) CCl ________________________ 4 (i) HBr _________________________ (j) MnO ________________________ 2 19. Write the chemical formula for the following compounds. (a) sodium sulfide ___________________ (f) cobalt (II) chloride _____________________ (b) lithium carbonate ___________________ (g) scandium phosphate_______________________ (c) chromium (III) oxide_________________ (h) sulphur hexafluoride ___________________ (d) nitrogen dioxide ____________________ (i) hydroiodic acid________________________ (e) nitric acid__________________________ (j) lead (IV) sulfide ______________________ CHEMICAL QUANTITIES 20. Determine the molar mass of the following elements/compounds (a) phosphorus (b) chlorine c) calcium fluoride (d) MgCO 3 21. Complete the following mole conversions. (a) 0.25 mol Al = ____________ g Al (b) 45 g NaCl = ____________ mol NaCl 23 (c) 2.25x10 atoms Au = ____________ mol Au (d) 220 g magnesium chloride = ____________ molecules magnesium chloride 24 (e) 5.0x10 molecules of potassium phosphate = ____________ kg of potassium phosphate 22. If there are 400 molecules of water, how many atoms are there of hydrogen and of oxygen? 23. Calculate the percent composition of each element in the following compounds (a) Na S 2 (b) silver nitrate 24. Determine the empirical formula for the following compounds. Name each compound. (a) 36.5% Na, 25.4 % S, 38.0% O (b) 32.4% Na, 22.6 % S, 45.1% O 25. A 10.0 g sample of powder was found to contain 1.36 g lithium, 2.36 g carbon, and the remainder was oxygen. The molecular weight of the compound is 101.898 g/mol. Determine the empirical and molecular formula. Name the molecular compound. TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS 26. Classify the reactions as Synthesis (S), Decomposition (D), Single Replacement (SR), Double Replacement (DR), Combustion (C), or Neutralization (N). Balance the chemical equations. ______ (a) CaCl + Na → NaCl + Ca 2 ______ (b) Na PO + Li CO → Na CO + Li PO 3 4 2 3 2 ______ (c) MgCl + O → MgO + Cl 2 2 3 3 4 2 ______ (d) Ba(OH) + HBr → BaBr + H O 2 2 ______ (e) Al + O → Al O 2 2 2 3 27. Classify the reaction as Synthesis (S), Decomposition (D), Single Replacement (SR), Double Replacement (DR), Combustion (C), or Neutralization (N). Predict the products and balance the chemical equation. ______ (a) C H + O → 6 6 2 ______ (b) NaOH + CaCl → 2 ______ (c) BaO → ______ (d) SrBr2 + O2 → ______ (e) H2SO4 + KOH → STOICHIOMETRY 28. Aluminum reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following balanced chemical equation: 2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2 (a) If 0.250 mol of Al reacts, determine the moles of H2 produced. (b) If 5.0 mol of AlCl3 are produced, determine the moles of HCl reacting. (c) If 50 g of Al react, what mass of HCl is required? 29. Ammonia (NH3), is prepared by combining hydrogen and nitrogen. (a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. (b) When 28 g of nitrogen are reacted, what mass of hydrogen is required? (c) If the reaction yields 30 g of ammonia, what is the percent yield of the reaction? 30. Titanium (IV) chloride reacts magnesium to form titanium and magnesium chloride: TiCl4 +2 Mg → Ti + 2MgCl2 a) If 120 g of titanium (IV) chloride are reacted with 60g of magnesium, how much titanium can be produced? (b) which reactant is limiting and which is in excess? (c) If only 20 g of titanium are produced, what is the percent yield of the reaction? GASES 31. A sample of helium has a volume of 400 mL at 1.2 atm. What will the volume be at 1.5 atm if the temperature remains constant? 32. A balloon has a volume of 8.0 L at 220 K. At what temperature will the balloon have a volume of 7.6 L, if pressure remains constant? 6 33. A gas cylinder has a pressure reading of 7.8x10 Pa at 295 K. What will the pressure read at 310 K, if the volume remains constant? 34. A sample of gas has a volume of 500 mL at 2.2 atm & 300 K. What will the pressure be if the sample is expanded to 600 mL at 310 K? 35i). What is the mass of 6.2 L of carbon dioxide at STP? 35ii) Which gas effuses faster: HCl or NH3? Why? 36i). What is the mass of a sample of helium that occupies 400 mL at 3.4 atm and 60 ºC? 36ii) Determine the total pressure in a rigid flask that contains the following gases: PCO2=1.2 atm, PH2= 0.56 atm, and PO2=0.45 atm 37. Methane (CH ) gas reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. 4 (a) Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. (b) If 400 mL of methane are present at STP, what mass and volume of oxygen are required in the reaction? SOLUTIONS 38. Determine the concentration of a solution containing 0.0500 mol hydrochloric acid in 800 mL. 39. What is the volume if a 0.14 M solution contains 0.24 mol of sodium chloride? 40. Determine the final concentration if 40 mL of water are added to 60 mL of 0.025 M silver nitrate solution. 41. Write a dissociation equation and determine the concentration of each ion in the solution. (a) 0.056 M Na SO (b) 0.40 M AlBr 2 4 3 42. Write the formula equation, complete ionic equation, and net ionic equation for the reaction between NaI and Pb(NO ) . 3 2 43. 150 mL of 0.25 M strontium chloride solution are reacted with 140 mL of silver nitrate solution. (a) Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. (b) What is the concentration of the silver nitrate solution? (c) What is the mass of the precipitate? ACIDS AND BASES 44. List three properties of acids and three properties of bases. 45. Complete the following table: [H+] pH Acidic, basic, or neutral? [OH-] pOH 3.15 3.2 x 10-4 M 2.8 x 10-6 M 5.05 46. Classify each reaction as endothermic or exothermic. _______________ (a) CO (g) + SiO (s) + 590.2 kJ/mol → SiO (g) + CO 2 2 _______________ (b) 2ZnS (s) + 3O (g) → 2ZnO (s) + 2SO (g) + 878.3 kJ/mol 2 2 EQUILIBRIUM 47a). Is the reaction below endothermic or exothermic? How do you know? b) Which way will the reaction shift and what would happen to [C H N] when each of the following stresses are applied? 5 11 C5H5N (g) + 3H2 (g) + 1.4 kJ/mol ↔ C H11N (g) 5 Direction of shift i. increase pressure ii. decrease temperature iii. increase in volume iv. increase [H2] 48. Write a Keq expression for each of the following equilibria. (a) 2CO (g) + O (g) ↔ 2CO (g) 2 2 How does [C H N] change? 5 11 (b) 4HCl (g) + O (g) ↔ 2H O (l) + 2Cl (g) 2 2 2 49. Write a Keq expression for each of the following equilbria. Determine the value of Keq. Does the equilibrium favor the products or the reactants? (a) 2H O (l) + 2F (g) ↔ 4HF (g) + O (g) (b) 2CH (g) ↔ C H (g) + 3H (g) At equilibrium, [F ]= 0.16 M, [HF] = 1.2 M, and [O ] = 0.20 M At equilibrium, a 10 L container holds 2.0 mol CH , 0.4 mol C H , and 6.0 mol H 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 4 2 2 2 2