The removal of Native Americans 5-1
advertisement

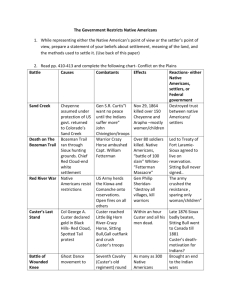
The removal of Native Americans Settlers pushing Westward Different Beliefs • • • • • Native Americans: No one could “own” the land. It belong to no one. They had to be nomadic in order to survive. Led by a group, not one. Learned history, etc. by telling stories. White Settlers: • You can buy and own land. • Making a claim or starting a business would give them a stake in the country. • Natives forfeited their rights when they failed to make improvements to it of “settle it.” How do members of each group earn respect? Read page 203 of your textbook about the importance of Buffalo and complete the notes. The Lure of Silver and Gold • Tens of thousands of miners flocked to the region in search of the gold discovered in Colorado in 1858. • Mining camps and Boomtowns forever changed the pristine landscape. This changed the landscape from this….. • To this… and this.. and this.. and this.. Can they peacefully co-exist? The Government Restricts Native Americans Railroads help to change everything •Before railroad travel in the west, the government passed an act that designated all the Great Plains as one giant reservation. Why? •In the 1850 the government started to divide land between the tribes and define boundaries. However, they didn’t listen and hunted their traditional land anyway. * This created clashed between natives and white settlers. Government’s attempt to remove Native Americans… Eliminate their source of survival Buffalo Skulls Government’s attempt to remove Native Americans… Prairie Dogs Massacre at Sand Creek • The Cheyenne returned to the Sand Creek Reserve in Colorado the winter of 1864 assuming that they were still under the protection of the U.S. government. http://www.kawvalley.k12.ks.us/schools/ rjh/marneyg/03-04_PlainsProjects/goolsby_04_sand-creek.htm Death on the Bozeman Trail •The Bozeman Trail was used a short cut for gold prospectors and then used by the military. •The problem was that it cut through some of the best hunting grounds of the Sioux. •The Sioux chief, Red Cloud, asked to have white settlement stop. He was ignored. •A warrior named Crazy Horse ambushed Captain Fetterman along the trail and killed over 80 soldiers. http://nv.essortment.com/fettermanmassa_rfkt.h tm Treaty of Fort Laramie: The government agrees to close the trail in exchange for the Sioux agreeing to live on reservations along the Missouri river. The tribal leader who signed it still expected to hunt on their traditional hunting grounds. (Sitting Bull didn’t sign.) NPS - The Peace Commissioners in council with Indians at Fort Laramie in 1868. From a photograph by Alexander Gardner in the Newberry Library. The treaty set aside the Black Hill as part of the Great Sioux reservation and for the exclusive use of the Sioux people. However, after Custer reported gold was found miners moved in and demanded protection by the government. Native pleaded their case to Washington to no avail. The government soon ordered wondering troops to be rounded up. One of these actions included Custer’s last stand. Eventually, the government would confiscate the land back in 1877. There is still an ongoing legal dispute about ownership of the Black Hills between the Sioux and the government. Red River War • The Kiowa and Comanche had been raiding for six years. • Army rounded up friendly tribes onto reservations and killed all others. • The tactic of burning villages, and killing warriors and horses crushed the resistance of the southern plains. • This was brought to an end on September 28, 1874 when Colonel Mackenzie surrounded a large group of Kiowa, Comanche, and Cheyenne. There tactic was to kill their horses and they slaughtered more than 1,100. Without any swift means of transportation, the virtually defenseless surrendered and returned to the reservations. Custer’s Last Stand • In June of 1876 the Sioux and Cheyenne held a sun dance. http://library.thinkquest.org/15215/Culture/dance.htm *Sitting Bull saw a vision of soldiers falling off of their horse. They took it as a warning and started to prepare. Crazy Horse, Sitting Bull, and Gull out numbered the coming troops. *Custer and his troops were killed within an hour of arriving at Little Big Horn: After the battle, the Indians came through and stripped the bodies and mutilated all the uniformed soldiers, believing that the soul of a mutilated body would be forced to walk the earth for all eternity and could not ascend to heaven. Inexplicably, they stripped Custer's body and cleaned it, but did not scalp or mutilate it. He had been wearing buckskins instead of a blue uniform, and some believe that the Indians thought he was not a soldier and so, thinking he was an innocent, left him alone. Because his hair was cut short for battle, others think that he did not have enough hair to allow for a very good scalping. Immediately after the battle, the myth emerged that they left him alone out of respect for his fighting ability, but few participating Indians knew who he was to have been so respectful. To this day, no one knows the real reason. (Source: www.axel-jacob.de/ little_bighorn2.html ) * The victory was short term. The Sioux were defeated by late 1876. Sitting Bull escaped to Canada for awhile, but to avoid starvation, surrendered and was put on a reservation. He later joined the “Buffalo Bill” show. 6.15 "Scene of Gen. Custer's last stand, looking in the direction of the ford and the Indian village." The skeletal remains of horses still litter the battlefield in this photograph taken one year later, in 1877. The Sun Dance Chief Sitting Bull http://www.pbs.org/weta/thewest/people/s_z/sittingbull.htm Assimilation 1. Native Americans should give up their way of life and beliefs to become part of the white culture. -Many children sent away to white schools to learn white ways. Punished for speaking or acting Native American. -Failed because it isolated Americanized Natives from family and friends who were not. 2. Dawes Act: Broke up reservations and was supposed to give land to individual Native American families. White settlers took most and natives received nothing. The Battle of Wounded Knee • The Seventh Cavalry, Custer’s old regiment, took about 350 starving and freezing Sioux to the Wounded Knee reservation in South Dakota. • Soldiers demanded that the tribal people give up their weapons. After a shoot was fired by an unknown source, the soldiers opened fire and killed 300 unarmed Native Americans, including many children. • The soldiers then left the bodies where they lay to freeze on the ground. • The event brought the Indian wars to a “bitter end.” The Battle of Wounded Knee Sitting Bull's half-brother, Big Foot, was chosen as the new leader of the tribe. On the way to help fellow chief Red Cloud make peace with the Whites, Big Foot was intercepted by Major Samuel Whitside of the 7th Cavalry. Whitside transferred Big Foot to an army ambulance due to his severe pneumonia and escorted the Native Americans to their camp for the night at Wounded Knee Creek. The army supplied the Native Americans with some tents and rations, and then conducted a census, determining that there were 120 males and 230 women and children. -Wikipedia encyclopedia Miniconjou Chief Big Foot lies dead in the snow • Fill out your graphic organizer about Native Americans now. Why did they go out West? What hardships did they face? What accomplishments did they have?