1st-Nine-Week-Benchmark-Exam-Review-End-of-1st-Nine
advertisement

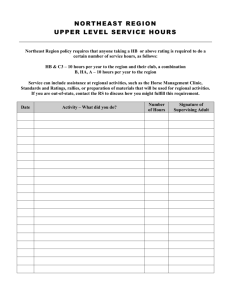
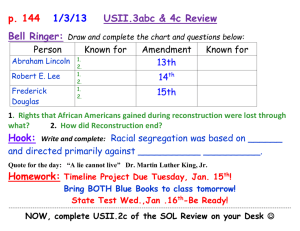
Benchmark Exam st Review 1 Nine Weeks USII.4e-USII.6d 1. What are the negative effects of industrialization? • Child labor • Low wages, long hours • Unsafe working conditions 2. Rise of Organized Labor *Formation of Labor Unions-the American Federation of Labor Supported/fought for higher wages, shorter hours, and better working conditions. *Strikes- The Homestead Strike ended with non-union workers accepting lower wages. 3. What were the Progressive Movement workplace reforms? • Improved safety conditions • Reduced work hours • Restrictions on child labor 4. What opportunities did women gain during women’s suffrage? • Increased educational opportunities • Attained voting rights 4. What amendment gave women these rights? • The nineteenth amendment 4. Who worked for women’s suffrage? • Susan B. Anthony • Elizabeth Cady Stanton 5. The Temperance Movement • Composed of groups opposed to the making and consuming of alcohol • Supported which amendment? The eighteenth amendment th 18 5. What did the amendment do? • Prohibited the manufacture, sale, and transport of alcohol. 6. What were the causes for the Spanish American War? • Protection of American business interests in Cuba • American support of Cuban rebels to gain independence from Spain • Rising tensions as a result of the sinking of the USS Maine • Exaggerated news reports called YELLOW JOURNALISM 7. What were the results of the Spanish American war? • The USA emerged as a world power • Cuba gained independence from Spain • US gained possession of Philippines, Guam, and Puerto Rico 7a. Where did the Spanish American War take place? CUBA 8. Theodore Roosevelt’s Foreign Policies • Theodore Roosevelt expanded the Monroe Doctrine as a way to prevent European involvement in the affairs of Latin American countries. 9. Theodore Roosevelt’s foreign policies and their impact on the United States included the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine which states: • A. Asserted the United States right to interfere in economic matters of nations in the Americas. • B. Claimed the United States’ rights to exercise international police power (use of military) • C. Advocated the “Big Stick” Diplomacy (building of the Panama Canal) 10. Give the 4 reasons the USA got involved in WWI. • Inability to remain neutral • German submarine warfare—sinking of the Lusitania • US economic and political ties to Great Britain • Zimmerman Telegram 11. Who were the WWI Allies? • British Empire (Great Britain) • Serbia • France • Belgium • Russia * USA 11. Who were the Central Powers during WWI? • German Empire • Austria-Hungary • Bulgaria • Ottoman Empire 11a. When the US joined WWI, which side did they join? • The USA joined on the side of the Allies. • 12. At the end of WWI, President Woodrow Wilson prepared a peace plan known as the 14 Points that called for the formation of the League of Nations, a peacekeeping organization. 13. Which country did not join the League of Nations? • The United States 14. Why didn’t the above country join the League of Nations? • The United States Senate failed to ratify the Treaty of Versailles 15. List 4 results of improved transportation. • Greater mobility • Creation of jobs • Movement to suburban areas • Growth of transportation related industries (oil, steel, road construction) 16. Why are the Wright Brothers well known? • Invention of the Airplane 17. Who was known for the use of the assembly line, automobile and rise of mechanization? • Henry Ford 18. List 3 communication changes. • Increased availability of telephones • Development of movies • Development of radio and the broadcast industry 19. List 4 ways electrification changed American life. • Labor saving products (electric stove, water pump, washing machine) • Electric lighting • Entertainment (radio) • Improved communication 20. What is prohibition? • Prohibition made it illegal to manufacture, transport, and sell alcoholic beverages 21. What amendment did Prohibition uphold? • The eighteenth amendment • What amendment repealed st it? The 21 Amendment 22. What are speakeasies? • Places for people to drink illegal alcoholic beverages 23. What (Who) are bootleggers? • People who smuggled illegal alcohol and promoted organized crime. 24. List 4 facts about the Great Migration. • Jobs for African Americans in the South were scarce and low paying. • African Americans faced discrimination and violence in the South. 24. List 4 facts about the Great Migration(continued). • African Americans moved to northern cities for employment opportunities (jobs) • African Americans also faced discrimination and violence in the North. 25. Georgia O’Keeffe • Art—artist known for urban and later southwest scenes 25. F Scott Fitzgerald • Literature—novelist who wrote about the 1920’s 25. John Steinbeck • Literature—novelist who wrote about migrant workers in the 1930’s 25. Aaron Copland • Music: Uniquely American Music 25. George Gershwin • Music: Uniquely American Music 25. Jacob Lawrence • Art: painter who chronicled the Great Migration 25. Langston Hughes • Literature: poet who combined African and American cultural roots 25. Duke Ellington • Music: Jazz composer 25. Louis Armstrong • Music: Jazz composer 25. Bessie Smith • Music: Blues singer 26. List the causes of the Great Depression. • People overspeculated on stocks using borrowed money they couldn’t repay when stock prices crashed • The Federal Reserve failed to prevent the collapse of the banking system • High tariffs strangled international trade 27. List 4 ways the Great Depression impacted Americans • A large number of banks and businesses failed • ¼ or 25% of workers were without jobs • Large numbers of people were hungry and homeless • Farmers’ incomes fell to low levels 28. List 5 major features of the New Deal. • Social Security • Federal Work Programs • Environmental Improvement Plans • Farms Assistance Programs • Increased Rights for Labor First Quarter Benchmark SOL’s on the First Nine Weeks Test USII.3b, 4c-USII.4d 1. Reconstruction Policies and Problems included: • A. Southern military leaders could not old office • B. African Americans could hold public office • C. African Americans gained equal rights as a result of the Civil Rights Act of 1866, which also authorized the use of Federal troops for its enforcement Reconstruction Policies and Problems Cont: • D. Northern soldiers supervised the South • E. The Freedmen’s Bureau was established to aid former enslaved African Americans in the South • F. Southerners resented Northern “carpetbaggers”, who took advantage of the South during Reconstruction • G. Southern states adopted Black Codes to limit the economic and physical freedoms of former slaves. 2. The End of Reconstruction • A. Reconstruction ended in 1877 as a result of a compromise over the outcome of the election of 1876. • B. Federal troops were removed from the South. • C. Rights that African Americans had gained were lost through “Jim Crow” laws. 3. Discrimination against African American continued after: • Reconstruction or The Civil War 4. What is racial segregation? *Based upon race *Directed primarily against African Americans, but other groups were also kept segregated. 5. “Jim Crow” laws were passed to discriminate against African Americans. • Although these laws were legal in many communities and states, they were enforced primarily in the South/Southeast region. 6. “Jim Crow” laws were characterized by unequal treatment in what 4 areas? • Housing • Work • Education • Government 7. African American responses included: *Booker T. Washington Believed equality could be achieved through vocational education; accepted social separation. 7. *W.E.B. Dubois Believed in full political, civil, social rights for African Americans 8. Make sure you have colored your map correctly! USII.2c Regions Review • • • • • • • 9. Meatpacking- Midwest 10. New York City- Northeast 11. Automobile industry- Midwest 12. Jim Crow Laws- Southeast 13. San Francisco- Pacific 14. Textile industry- Northeast 15. Denver- Western/Rocky Mountains Regions Review • • • • • • • • • • 16. Harlem Renaissance- Northeast 17. Atlanta- Southeast 18. Great Plains- Midwest 19. Ellis Island (NY)- Northeast 20. Hull House (Chicago)- Midwest 21. Steel industry- Northeast 22. Homestead Strike (PA)- Northeast 23. New Orleans- Southeast 24. Juneau- Non-contiguous 25. New England- Northeast Regions Review • • • • • • • • • • 26. Boston- Northeast 27. Pittsburgh- Northeast 28. Detroit- Midwest 29. Santa Fe- Southwest 30. Salt Lake City- Western/Rocky Mountains 31. Los Angeles- Pacific 32. Honolulu- Non-contiguous 33. Philadelphia- Northeast 34. Angel Island, CA- Pacific 35. Washington D.C.- Southeast Regions Review • • • • • • • • • • 36. St. Louis- Midwest 37. San Antonio- Southwest 38. Seattle- Pacific 39. Chicago- Midwest 40. Nebraska- Midwest 41. Ohio- Midwest 42. Maine- Northeast 43. Florida- Southeast 44. North Dakota- Midwest 45. Oklahoma- Southwest 46. Suffolk, Virginia • Southeast! Congratulations! • Get your parents to sign the study guide! • Study hard so you can make a good grade and make your parents smile!