AP Biology, Ecology Unit, Week 1 - APBiology2010-2011
advertisement
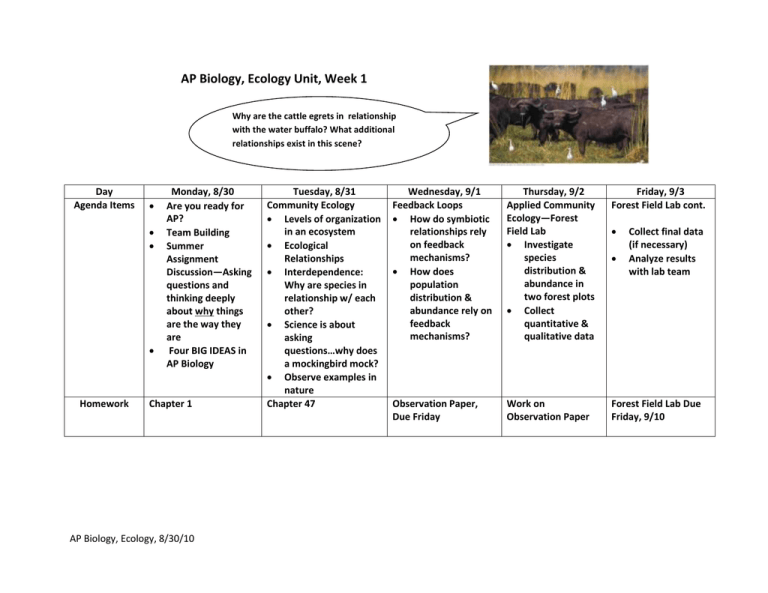
AP Biology, Ecology Unit, Week 1 Why are the cattle egrets in relationship with the water buffalo? What additional relationships exist in this scene? Day Agenda Items Homework Monday, 8/30 Are you ready for AP? Team Building Summer Assignment Discussion—Asking questions and thinking deeply about why things are the way they are Four BIG IDEAS in AP Biology Chapter 1 AP Biology, Ecology, 8/30/10 Tuesday, 8/31 Community Ecology Levels of organization in an ecosystem Ecological Relationships Interdependence: Why are species in relationship w/ each other? Science is about asking questions…why does a mockingbird mock? Observe examples in nature Chapter 47 Wednesday, 9/1 Feedback Loops How do symbiotic relationships rely on feedback mechanisms? How does population distribution & abundance rely on feedback mechanisms? Thursday, 9/2 Applied Community Ecology—Forest Field Lab Investigate species distribution & abundance in two forest plots Collect quantitative & qualitative data Friday, 9/3 Forest Field Lab cont. Observation Paper, Due Friday Work on Observation Paper Forest Field Lab Due Friday, 9/10 Collect final data (if necessary) Analyze results with lab team AP Biology Curriculum Details, Community Ecology Review this page to get a sense of the key concepts and main ideas each week. These are (mostly) derived directly from the official AP Biology Curriculum. http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/apc/public/courses/teachers_corner/2117.html Enduring Understanding: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems (Community Ecology) Essential Questions: Why do species interact in the ways they do? What is the purpose of relationships? Is interdependence always a necessity, or can life survive independently? Key Concepts Interactions between and within populations influence patterns of species distribution and abundance Global distribution of ecosystems changes substantially over time. POSITIVE & NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOPS What will you need to know? Symbiotic & antagonistic interactions affect the distributions and abundance of populations Competition, parasitism, predation, mutualism, commensalism affect population dynamics Each relationship can be characterized to have positive and negative effects on interacting populations Many complex symbiotic relationships exist in an ecosystem and feedback control systems play a role in the functioning of these ecosystems A population of an organism has different properties than the individual organisms that make up the population. The cooperation and competition b/w individuals contributes to these different properties AP Biology, Ecology, 8/30/10 What will you need to DO? Refine observations and measurements on the effect of population interactions on patterns of species distribution and abundance based on data analysis Observe symbiotic relationships in nature Collect data on species distribution (forest plot analysis) Write an observation paper to explore concepts Read chapter 47 Connect science concepts to problems or scenarios in nature (observed or otherwise) AP Biology, Ecology, 8/30/10







