Station #1
advertisement

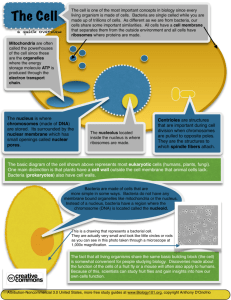
Station #1 • Animal cells are found in all members of the animal kingdom, including humans. • All animal cells are eukaryotic, meaning that they have a nucleus. They also have membranebound organelles. Animals are multicellular. • Animal cells have a cell membrane, made of phospholipids. However, they do NOT have a cell wall of any kind. Animal skin is often soft and pliant due to the lack of a cell wall. • Animal cells do NOT have chloroplasts, an organelle needed for photosynthesis. Station #1 • Answer these questions. 1. Do animal cells have a nucleus? 2. Do animal cells have chloroplasts? Can animals make their own food? 3. Do animal cells have a cell membrane? 4. Do animal cells have a cell wall? 5. Are animal cells soft and fleshy or hard and firm? Station #2 • Plant cells are found in all members of the plant kingdom. • All plant cells are eukaryotic, meaning that they have a nucleus. They also have membrane-bound organelles. Plants are multicellular. • Plant cells have a cell membrane, made of phospholipids. They also have a cell wall, which helps the cell keep its shape. The presence of a cell wall makes plants firm and tough. • Plant cells have chloroplasts, an organelle needed for photosynthesis. They also have a central vacuole, a large sac used for storing and processing materials. Station #2 • Answer these questions. 1. Do plant cells have a nucleus? 2. Do plant cells have chloroplasts? Can they make their own food? 3. Do plant cells have a cell membrane? 4. Do plant cells have a cell wall? 5. What two organelles do plants cells have that animal cells don’t? Station #3 • Bacterial cells are a very common type of prokaryotic cell. Prokaryotic cells do NOT have a nucleus. Bacteria are unicellular. – However, bacteria DO have DNA. • Bacteria also do NOT have any membrane-bound organelles. However, they DO have ribosomes. Bacteria often have cilia (short hairs) and flagella (whip-like tails), which are used for locomotion. • Finally, bacteria HAVE both a cell wall and a cell membrane. Station #3 • Answer these questions. 1. Do bacterial cells have a nucleus? 2. Do bacterial cells have ribosomes? Do they have other organelles? 3. Do bacterial cells have a cell membrane? 4. Do bacterial cells have a cell wall? 5. What two structures do bacteria use for locomotion? Station #4 • Look at the following list of cellular structures. Identify what kind of cells contain those structures. (There may be more than one answer!) • Call your instructor when you are finished. 1. Ribosomes 2. Nucleus 3. Cell Wall 4. Mitochondria 5. Cilia 6. Chloroplasts 7. DNA 8. Cell Membrane 9. Golgi Bodies 10. Central Vacuole