Test Standards
advertisement

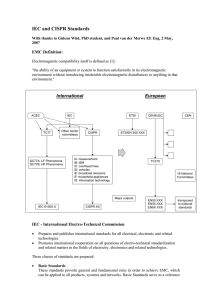
ITU Regional Standardization Forum for Asia-Pacific (Jakarta, Indonesia, 27-28 October 2015) EMC Generals and Testing Technologies Sangho Choi, Ph.D. The Chief of EMTI/Research Fellow Electromagnetic Technology Institute(EMTI), RAPA (shchoi@rapa.or.kr) EMC Concept and Technical Standards 1 EMC Definition EMC : EMC is defined as the ability of electronic and communication equipment to be able to operate satisfactorily in the presence of interference and not be a source of interference to nearby equipment. 2 Electromagnetic Environment (Coupling Path ) Radiation (Nonmetallic Paths) (Source) RE CE Emitter Conduction (Metallic Paths) (Victim) RS CS Susceptor ·Transmitters ·Conduction (current) ·High-speed logic Common impedance ·HF generators + ·Power switchers ·Electromagnetic fields ·Inductive loads Cross-talk/Radiation ·Transients : ESD, lightening ·Receivers ·Analog circuits ·Digital circuits ·Human beings Low susceptibility threshold EMS Regulation High unwanted emissions EMI Regulation 3 The Changes of EM Environment ICT convergence : High speed/quality/definition, wireless Smart grid technology, new and renewable energy development Electric vehicles Energy efficiency, mobility, portability Automatic, social safety and security, intelligent public transportation infrastructure Aerospace & avionics, ships advance Technology Innovation Changes of EM Environment To be required the development of new EMC (testing) technologies in electromagnetic environment 4 EMC Problems Brazil rocket explosion Alcantara launch center killing 21 people, injuring 20 more 2003 Aircraft carrier explosion USS Forrestal Disaster, Vietnam July 29, 1967 5 EMC Controls • The control of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and assurance of EMC comprises a series of related disciplines: – – – – Characterizing the threat. Setting standards for emission and susceptibility levels. Design for standards compliance. Testing for standards compliance. • Characterization of the problem requires understanding of: – The interference source and signal. – The coupling path to the victim. – The nature of the victim both electrically and in terms of the significance of malfunction. 6 EMC Tests for the Compliance Needs testing about 1) Intra-system EMC for stable operation, performance & quality 2) inter-system EMC for the protection of radio service (Radio law) and the safety from danger regulation & certificate EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility EMI Electromagnetic Interference EMS Electromagnetic Susceptibility RE (IEC/CISPR) CE (IEC/CISPR) RS (IEC/TC77, ISO) CE (IEC/TC77, ISO) Radiated Emission Conducted Emission Radiated Susceptibility Conducted Susceptibility ∙ Magnetic Fields ∙ Electric Fields ∙ HF/LF ∙ Surge, EFT Burst ∙ ESD ∙ Magnetic Fields ∙ Electric Fields ∙ Conducted Power Disturbance ∙ Voltage ∙ Current 7 Technical Standards for EMC(1) Basic Standard - Basic standards for the measurement of radio disturbance in the frequency range 9kHz - 18GHz ex: CISPR 16 Series, IEC/EN/K 61000-4 Series for ESD, RS/CS, Surge, EFT burst tests Generic Standard - Generic standards – Immunity(EMS) and emission(EMI) for residential, commercial and light-industrial environments ex: IEC/EN/K 61000-6-1 & IEC/EN/K 61000-6-2 for EMS IEC/EN/K 61000-6-3 & IEC/EN/K 61000-6-4 for EMI 8 Technical Standards for EMC(2) Product Family Standard ex: CISPR 11(ISM), CISPR 12(vehicles, boats, combustion engine), CISPR 13(EMI for broadcasting receiver), CISPR 14-1(EMI for home appliances), CISPR 14-2(EMS for home appliances), CISPR 15(lightening equipment), CISPR 2013(EMS for broadcasting receiver), CISPR 22(EMI for ITE), CISPR 24(EMS for ITE), CISPR 25(vehicles, boats, combustion engine), CISPR 32 and CISPR 35(multimedia), etc. Product Standard ex: IEC 60945(Maritime Navigation and Radiocommunication Equipment and Systems) , IEC 60533(Electrical and electronics installation in ships), IEC 61326(Electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use), IEC 61131-2(Programmable controllers ), IEC 61204-3(Low voltage power supplies), etc. 9 EMC Regulation Issues 10 EMC Regulation in the World • US – The body responsible for regulation of EMC emissions in the USA is the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). The specific regulations are Part 15 (Radio Frequency Devices) and Part 18 (Industrial, Scientific and Medical Equipment) for the FCC marking. • EU – For the majority of electrical and electronic products, EMC requirements in the European Union are covered by the EMC Directive (2004/108/EC) for the CE marking • Japan – The body responsible for EMC emissions in Japan is the VCCI. Products must comply with CISPR 22. Equipment intended for the domestic environment must comply with the Class B requirements, while other equipment should satisfy the Class A requirements – These requirements are not mandatory regulations. 11 Korea Standard Development System for EMC RRA is the National Committee in EMC Field for CISPR EMC Technical Regulation Body Contribute KCS Establishing KCS Establishing KS KS Standards Sale TTA Standard (TTAS) Standard Draft Version 12 Requesting KS Standards Korea Conformity Assessment System Conformity Certification (Radio Waves Act Article 58-2.2) Technical Regulation : Radio and Telecommunication, SAR, EMC (Low voltage damage) Conformity Registration(Radio Waves Act Article 58-2.3) Technical Regulation : EMC (Low voltage damage) 13 EMC Regulation in Korea • Products Covered – In accordance with the regulations of the South Korean KCC, the following products are covered by the requirements for EMC certification: • • • • • • • • • High Frequency equipment for industrial, scientific and medical use Automobiles and equipment powered by spark ignition engines Radio receiver equipment Domestic electrical appliances and electrical power tools Fluorescent lighting equipment High voltage equipment and accessories Information technology equipment Any other equipment Test Standards – Products must comply with the appropriate South Korean standards, which are based on, but not necessarily identical to, the appropriate CISPR standards. 14 EMC Testing Facilities 15 Typical EMC Test Facilities Shield room RS chamber 3m EMI chamber OATS 30m EMI chamber 10m EMI chamber 16 Typical Semi-Anechoic Chamber (10m) 17 Semi-Anechoic Chamber (10m) configuration Antenna mast 1 to 4 m EUT direct wave turntable Ground plane 18 Semi Anechoic Chamber Information General Information Dimension : 20m(L) x 12m(W) x 8.5m(H) Frequency Range : 30MHz ~ 18GHz Site Attenuation (ANSI C63.4), NSA less than ±4dB Site Attenuation (CISPR 13), CSA less than ±3dB Site Validation (CISPR 16-1-4), SVSWR less than 6dB Test Distance : 3m & 10m Test Items Standards Radiated Emission ANSI C63.4 Conducted Emission CISPR 13 CISPR 16-1-4 19 Cost USD 1.7 million(about) Typical EMC test facilities layout(Top view) 20 EMC test facilities construction procedure(1) 1. Installation of steel structure 2. Installation of shield panel[Floor] 3. Installation of scaffold 4. Installation of shield panel 5. Installation of Door, Filter 6. Performance [SE Test] [Wall & Ceiling] 21 EMC test facilities construction procedure(2) 7. Installation of Ferrite Tile 8. Installation of Absorbers 9. Installation of Raised floor 10. Installation of Groundplane 11. Finishing; Floor, interior 12. Performance [NSA Test] 22 Typical EMS RS Chamber 23 EMS RS Chamber General Information General Information Dimension : 9m(L) x 6m(W) x 6m(H) Frequency Range : 26MHz ~ 18GHz Field Uniformity (IEC 61000-4-3) : (0 ~ 6)dB, over 75% of a surface Polarization : Vertical & Horizontal Uniformity Plane : 1.5m x 1.5m Height of the antenna : 1.55m Test Distance : 3m Test Items Radiated Susceptibility Standards IEC 61000-4-3 24 Cost USD 430 thousand(about) Typical Screen/Shield Rooms 25 Typical Shield Rooms Information General Information Dimension : 10m(L) x 7.5m(W) x 3m(H) Frequency Range : 14kHz ~ 18GHz Shielding Effectiveness (IEEE 299) : more than (60 ~ 100)dB Measurement Point : Door, Filter, Ceiling, walls, and ventilator Test Items Conducted Emission Standards CISPR 14-1/13/22 etc. Disturbance Power ESD/EFT/Surge etc. 26 Cost USD 260 thousand(about) Typical Open-Area Test Sites(OATS) 27 OATS Configuration 28 OATS Information General Information Frequency Range : 30MHz ~ 1GHz Site Attenuation (ANSI C63.4), NSA less than ±4dB Test Distance : 3m, 10m & 30m Test Items Radiated Emission Standards ANSI C63.4 29 Cost USD 86 thousand(about) EMC Testing Instruments Oscilloscope ESD Generator EMI test Receiver LISN Signal Generator Spectrum Analyzer EFT/Surge Generator Antenna Network Analyzer Above equipments are the most commonly used available for performing EMC measurements. 30 EMC Tests 31 Test for Radiated Emission(RE) • RE Test for EUT • Frequency Range : 30MHz to 1GHz(Up to 18GHz) • Standard : CISPR 11, 12, 13, 25, 22… (EN 550XX) EEC 95/54, SAE J 1113-41 • Major Testing System (Refer to CISPR 16) – Test Facility : OATS, ALSE, FAR, SAR Open area test site or alternate test (anechoic chamber) – Test Equipment : EMI Receiver(Field strength meter with quasi-peak detector or EMI test receiver), Spectrum Analyzer – Test Antenna : Loop, Dipole, Log-periodic, Bi-conical Horn (depending on Frequency & Regulation) – Other : Turntable, Antenna Master, etc. 32 Limit of RE 33 Test for Conducted Emission(CE) • • • • CE Measurement emitting from cable of EUT Frequency Range : 150kHz to 30MHz Standards : CISPR 11, 13, 14, 15, 25, 22.. (EN 550XX) Testing System (Refer to CISPR 16) – Test Facility : Shielded Room or adequate ground planes – Test Equipment : EMI Receiver, Spectrum Analyzer(Quasi-peak Average detector available) – Other : LISN, etc. * LISN (Line Impedance Stabilization Network) : to create a known impedance on power lines of electrical equipment during electromagnetic interference testing. A LISN is typically designed to allow for measurements of the electromagnetic interference existing on the power line. 34 Limit of CE Conducted Disturbance at the Mains Ports Table 1 , 2 Frequency Range MHz dBuV Class A Class B 80 Limits dB (uV) Limits dB (uV) 76 Q.P Average Q.P Average Disturbance Voltage Injected into the Mains 79 Calss A (Q.P) 72 73 68 66 0.15 ~ 0.5 79 66 66 ~ 56 * 56 ~ 46 64 0.5 ~ 5 73 60 56 46 60 Calss A (Average) 5 ~ 30 73 60 60 50 56 Calss B (Q.P) 52 * Decreasing Linearly with the Logarithm of the Frequency 50 48 - The lower limit shall apply at the transition frequencies. - Telecommunication Ports 에 대한 Limit 는 고려중임. 46 44 0.1 Calss B (Average) 0.5 1 5 10 30 100 MHz 35 Test for Radiated Susceptibility(RS) • Radiated field susceptibility testing typically involves a highpowered source of RF or EM pulse energy and a radiating antenna to direct the energy at the potential victim or device under test (DUT). • Frequency Range : 80 MHz to 1000 MHz • Test condition : 1-30 V/m (1 kHz CW, 80% AM) , 100 V/m • Standards : IEC 61000-4-3 (EN 61000-4-3), ISO 11452-2 • Test Facility : FAR – Test Equipment : Power Amplifier system, Antenna, Field Probe Sensor, Signal Generator, Directional Coupler, power meter, – Other : Test software, etc 36 Test for Conducted Susceptibility(CS) • Conducted voltage and current susceptibility testing typically involves a high-powered signal or pulse generator, and a current clamp or other type of transformer to inject the test signal • • • • Frequency Range : 150kHz to 80MHz Test Condition : 1-10V (1kHz CW, 80% AM) Standards : IEC 61000-4-6 (EN 61000-4-6), ISO 7637 Test System – Test Facility : Shield Room – Test Equipment : Power Amplifier system, Signal Generator, Directional Coupler, power meter, CDN, Current Clamp – Other : Test software, etc 37 Test for Electrostatic Discharge(ESD) • ESD is a serious issue in solid state electronics, such as integrated circuits. Integrated circuits are made from semiconductor materials such as silicon and insulating materials such as silicon dioxide. Either of these materials can suffer permanent damage when subjected to high voltages; as a result, there are now a number of antistatic devices that help prevent static build up. • Test Condition(input voltage) : 8kV(Air Discharge), 4kV(Contact Discharge), Max 25kV • Standard : IEC 61000-4-2 (EN 61000-4-2), ISO 10605 • Test System – Test Facility : Shield Room – Test Equipment : ESD Simulator, Coupling Plane – Other : Capacitors, Resistors, etc 38 Thank You So Much !!! 39