Prefixes - Read & Write with Albright
advertisement

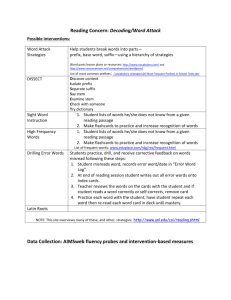
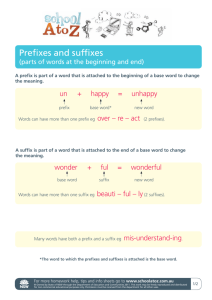
Prefixes, Suffix Root The Automobile of the WORD They are our friend. Definition of Prefix A prefix is a group of letters that appears at the front of a word. A prefix affects the meaning of the root (base) word to which it is attached. To determine whether or not a group of letters is a prefix, remove them from the word. The letters are a prefix if a known word remains. For exam- ple, remove the letters un from the following words: unhappy, untie, uncle, uninterested. In which word are the letters un not a prefix? Yes, these let- ters are not a prefix in the word uncle. Be AWARE 1. Most prefixes have more than one meaning. For example, the prefix un can mean “not” as in unhappy, or “do the opposite of” as in untie. Teach the multiple meanings of the most com- mon prefixes, and use careful language during lessons such as, “the prefix un sometimes means not.” 2. Be careful of letter clusters that look like pre- fixes, but aren’t. For example, when the letters un are removed from uncle, no recognizable root word is left. In addition, when the letters in are removed from invented, the word that remains has no relation to the whole word. The prefixes that cause the most difficulty are re, in, and dis. One more thing 3. Don’t rely solely on word-part clues to determine meaning. Use context clues as well to verify a word’s meaning. For example, you might think the word unassuming means “not assuming/not supposing” instead of its actual meaning “modest.” It is estimated that about 15 to 20% of the prefixed words stu- dents will encounter share this complexity (White et al., 1989). Most used prefixeswrite in GRAMMAR FIND PREFIXES Go to your novel and find prefixes Write a list or words that you find with prefixes under the definition list or table you copied, FIND at least 6… Write down what you think the word means based on the prefix definition table you wrote SPOKES Take the wheel copy that Mrs. Albright gave you. Divide it into 6 sections. Each person in class will pick a different prefix which will go in the middle circle on your wheel. Each spoke will have a word that is from that prefix Watch out for words that might contain your prefix but it is a word and not a prefix-root word situation. Mrs. Albright will model the prefix un. This is due tomorrow. If you don’t get done- it is homework. Continue another wheel Write the most common suffix in your notebook along with prefix list. After you are done with your list, make another wheel with suffix That is the part of the word that is on the end. Like the word teacher. ER is the suffix. Er means “one who” so teacher is one who teaches. Suffix Suffix -acy -al -ance, -ence -dom -er, -or -ism -ist -ity, -ty -ment -ness -ship -sion, -tion Noun Suffixes Meaning Example state or quality privacy act or process of refusal state or quality of maintenance, eminence place or state of being freedom, kingdom one who trainer, protector doctrine, belief communism one who chemist quality of veracity condition of argument state of being heaviness position held fellowship state of being concession, transition -ate -en -ify, -fy -ize, -ise become become make or become become -able, -ible -al -esque -ful -ic, -ical -ious, -ous -ish -ive -less -y Adjective Suffixes capable of being edible, presentable pertaining to regional reminiscent of picturesque notable for fanciful pertaining to musical, mythic characterized by nutritious, portentous having the quality of fiendish having the nature of creative without endless characterized by sleazy Verb Suffixes eradicate enlighten terrify civilize ROOTS Root words are the base of the word. A root word is the main part of a word that contains its core meaning. Sometimes it is a word on its own, as in unbelievable (believe is the root word), and sometimes it cannot stand alone, as in relocation (loc is the root word). In either case, prefixes and suffixes can be added to root words, which might change either the meaning of the word (reactivate, deactivate) or its grammatical function (transports = present tense, transported = past tense, transportation = noun). Sometimes spelling changes when suffixes are added to root words (noise, noisy). The base of your car is your root word Put 6 root words as the base of the car The wheels are the prefix and suffix This makes up your car named WORD