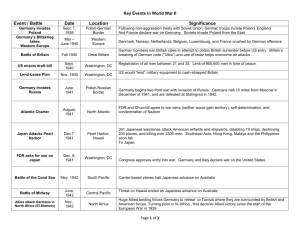
World War II: 1942-1945
advertisement

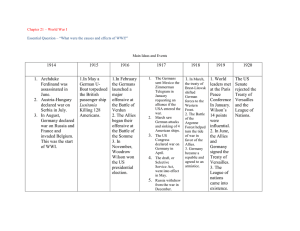
Bellringer • SOL Challenge • Have out your timeline and map from last class! • Review Questions (we’ll do them together) – – – – When did the Germans invade Poland? What was the significance of the Battle of Britain? What was Operation Barbarossa? What was the significance of the bombing of Pearl Harbor? • BJOTD: What do you call Robin Hood’s mom? Agenda • • • • • • SOL Challenge Review Notes Timeline/Map SOL Wrap-Up Cake Project! World War II: 1942-1945 European Theatre North Africa • After Pearl Harbor, Allies decide to open a 2nd front in Africa, not France against the Axis Powers – Angers Stalin • Nazis push the Allies back in August of 1942 • Battle of El-Alamein, 23 October – 5 November 1942 – Allied victory against Rommel’s Axis forces • Operation Torch – November 8th, 1942: Allied forces land behind Rommel’s troops and wipe out the Afrika Korps – Allies led by General Dwight D. Eisenhower Battle of Stalingrad • Hitler wanted to control the industrial center at Stalingrad • Began August 23, 1942 – By early November, the Germans controlled 90% of the city • Soviets counterattack, cutting the Germans off from their supplies and starving them through the winter • February 2, 1943: 90,000 frostbitten and starved Germans out of the original 300,000 surrender to the Soviets Battle of the Atlantic • On-going from 1941-1943 • German U-boats vs. Allied shipping convoys • Goal for Germany: cut off Great Britain from its supplies • After 2 convoys are sunk, Allies respond by having planes fly escort for convoys • Allies win, but at a cost: – 3,500 merchant ships, 175 warships lost – Germans only lost 783 U-boats Operation Overlord • Plan: to invade Normandy, France from across the English Channel on June 6, 1944 (D-Day) – Largest land and sea attack in history – Commander: General Dwight Eisenhower • Allied forces landed on 5 different beaches along the coast of France – Utah, Juno, Sword, Gold, Omaha • Allies took heavy casualties (10,000), but held the beaches • This victory gave the Allies a base from which to continue marching towards Germany Battle of the Bulge • As the Allies moved in from France, the Soviets moved in from the East and the Germans were getting desperate • Hitler decided to counterattack in the West • December 16, 1944: Hitler sent his German tanks through a weak spot in the American defense in the Ardennes • Allies eventually pushed back and won, forcing the Germans into retreat Germany Surrenders Unconditionally • By late March of 1945: Allies crossed the Rhine River into Germany • By April 25, 1945: Soviets surrounded the capital city of Berlin from the East • Hitler committed suicide on May 1, 1945 • May 7, 1945: General Eisenhower accepted the unconditional surrender of Germany – Unconditional surrender: surrendering without making any demands or pleas – President Roosevelt had died on April 12; President Truman received the news of the surrender Pacific Theatre Battle of the Coral Sea • Fought in May, 1942 when an American fleet intercepted a Japanese strike force on its way to Australia • Both fleets of ships faced each other and fought without firing a single shot – Battle fought by air • Battle was a draw – Allies lost more ships than the Japanese, BUT – Allies STOPPED Japanese southward expansion Battle of Midway • Japan’s next target was the island of Midway – Americans had broken the Japanese intelligence code, and knew they were coming • June 4, 1942: Allies launched a surprise attack, destroying over 300 Japanese planes as they waited to take off from carriers • Battle ended by June 6, 1942 with a Japanese retreat – Marked the turning of the tide of the war in the Pacific Battle of Guadalcanal • Commander of the Pacific: General Douglas MacArthur – Strategy: to “island-hop” past the strong Japanese bases to get himself closer to Japan itself, then cut supply lines • Battle of Guadalcanal: August 7, 1942-February 1943 – Fight over the Soloman Islands in the Pacific – Japanese stayed until they lost 23,000 out of 36,000 men, then retreated from the islands The Dropping of the Atomic Bomb • Island-hopping continued through 1945 – Japanese lost the battle of Leyte Gulf and Iwo Jima – Next stop for the Allied forces: Japan • Truman had a choice: Invade Japan or Bomb Japan – Invading might cost .5 million Allied lives while atomic bombing would lose only Japanese lives – Truman decides to drop the bomb • First Bomb: Little Boy – Dropped on Hiroshima, Japan on August 6, 1945 – 73,000 perished in attack • Second Bomb: Fat Man – Dropped on Nagasaki, Japan on August 9, 1945 – 37,500 died in attack Japan Surrenders • September 2, 1945: Japanese surrender to General Douglas MacArthur • WWII officially over Directions for Timeline • Place the events from today on the timeline given to you • Recommendation: put the events from Europe on one side, and from the Pacific on the other – Label the event, date it, and write 1 sentence with its importance/significance • If you finish early, have me check it, then try and place the events on the map from last class