Vocabulary Review- Cells and Cellular Transport
advertisement

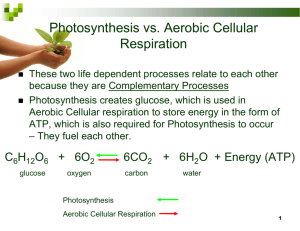
Vocabulary Review Goal 2- Cell and Cellular Transport Cells without a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles Prokaryote Green plant pigment Chlorophyll Control what goes in and out of the cell ; “gatekeeper” Plasma Membrane Found in plants; supports and protects the plant. Cell Wall Membrane bound structures in the cell“little organs” Organelles Control center of a cell. Nucleus Cells that have a true nucleus and has membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotes All organisms are composed of cells. Cell is the basic structure and function of all living things. All cells come from other cells. Cell Theory Basic unit of life. Cell Site of photosynthesis, where plants make their own food. Chloroplasts Folded membrane that serves as site of cellular reactions, “transport center” Endoplasmic Reticulum Long whip-like projections used for movement. Flagella Short hair like projections for movement. Cilia Found in the nucleus, and is the site where ribosomes are made. Nucleolus Site for protein synthesis“protein factory” Ribosomes “Storehouse” of the cell, large in plants Vacuole “Protein package station of the cell” Golgi Apparatus Site of cellular respiration. “Powerhouse of the Cell” Mitochondria Contain digestive enzymes, “suicide sacs” Lysosomes The act of allowing only certain substances in the cell; window screen Selective Permeability Molecules moving from a high to a low concentration. Diffusion Movement of water thru a selectively permeable membrane from high to low concentration. Osmosis Term that describes a solution where water moves from the cell. “Cell Shrinks” Hypertonic The organelle of photosynthesis. Chloroplast Term that describes a solution where water moves into the cell. “Cell Swells” Hypotonic Movement of water is the same inside and out of the cell Isotonic Organelle found in animal cells involved in cell division Centriole Type of transport that does not require energy. Passive Transport Type of transport that require energy in the form of ATP. Active Transport Moving substances into the cell. Endocytosis Moving substances out of the cell. Exocytosis Coined the term cell. Robert Hooke Invented the first microscope. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek The site of lipid synthesis in the cell. Smooth ER Two organelles within eukaryotic cells that have their own DNA. Mitochondria and the Chloroplast Clear gel-like material that is a medium for all cell organelles. Cytoplasm The model of the plasma membrane. Fluid Mosaic Model Example of a prokaryotic cell. Bacteria Cell Maintaining a constant internal environment. Homeostasis Type of endocytosis that allows the cell to engulf large particles. Phagocytosis Type of endocytosis that allows a cell to take in liquid molecules. Pinocytosis A process in which glucose molecule is broken down and ATP is released. Cellular Respiration The Energy Molecule in the body. ATP Process in which ATP is made using oxygen. Aerobic Respiration Process in which ATP is made in the absence of oxygen? Anaerobic Respiration How many ATP is made per molecule of glucose in anaerobic respiration? Two The respiration that takes place in animal cells when oxygen is absent resulting in sore muscles. Lactic Acid Fermentation The anaerobic respiration that takes place in bacteria and yeast cells making two ATP per molecule of glucose. Alcoholic Fermentation The number of ATP made per molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration? 36 The Organ of Photosynthesis? Leaf What are the reactants of Cellular Respiration? Glucose and Oxygen What are the reactants of Photosynthesis? Water and Carbon Dioxide What are the waste products of Photosynthesis? Glucose and Oxygen What are the waste products of Cellular Respiration? CO2, Water and ATP Organism that is able to make its own food. Autotroph Organism that has to ingest food; not able to make its own food. Heterotroph Alcoholic Fermentation produces what? Ethyl Alcohol and CO2 DNA is located in this organelle in eukaryotic cells. Nucleus