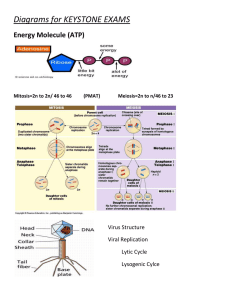
cellular respiration
advertisement
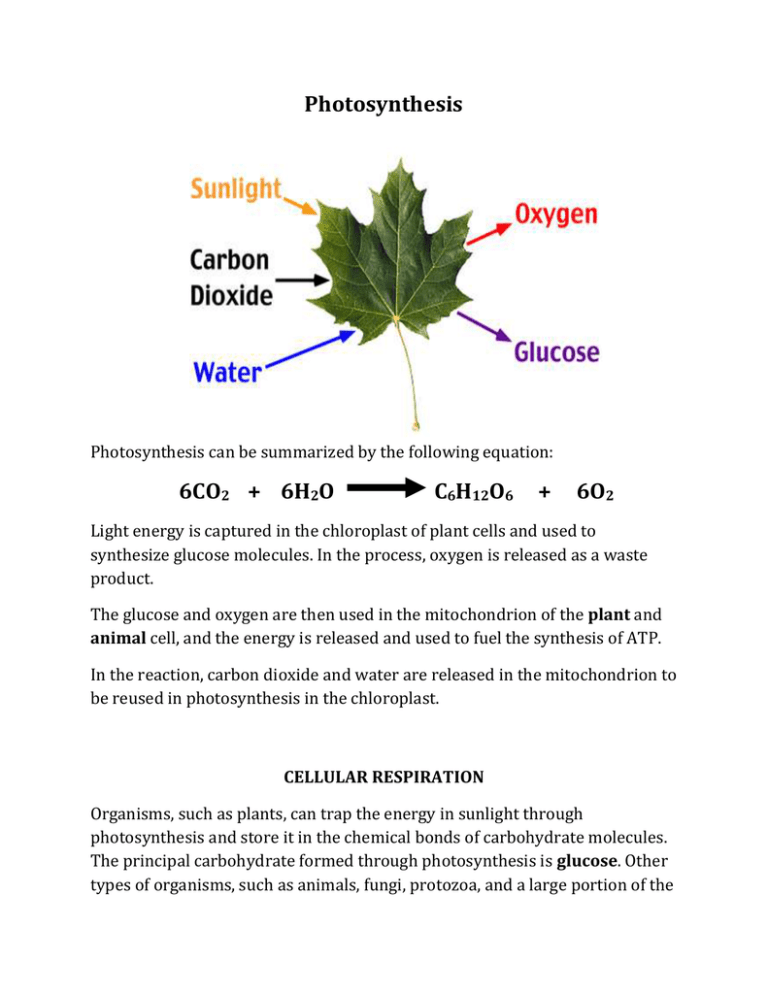
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis can be summarized by the following equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Light energy is captured in the chloroplast of plant cells and used to synthesize glucose molecules. In the process, oxygen is released as a waste product. The glucose and oxygen are then used in the mitochondrion of the plant and animal cell, and the energy is released and used to fuel the synthesis of ATP. In the reaction, carbon dioxide and water are released in the mitochondrion to be reused in photosynthesis in the chloroplast. CELLULAR RESPIRATION Organisms, such as plants, can trap the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis and store it in the chemical bonds of carbohydrate molecules. The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose. Other types of organisms, such as animals, fungi, protozoa, and a large portion of the bacteria, are unable to perform this process. Therefore, these organisms must rely on the carbohydrates formed in plants to obtain the energy necessary for their metabolic processes. Animals and other organisms obtain the energy available in carbohydrates through the process of cellular respiration. Cells take the carbohydrates into their cytoplasm, and through a complex series of metabolic processes, they break down the carbohydrates and release the energy. The energy is generally not needed immediately; rather it is used to combine adenosine diphosphate (ADP) with phosphate ions to form adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules. Remember that ATP is the energy currency of the cell. During the process of cellular respiration, carbon dioxide is given off. This carbon dioxide can be used by plant cells during photosynthesis to form new carbohydrates. Also in the process of cellular respiration, oxygen gas is required to serve as an acceptor of electrons. This oxygen is identical to the oxygen gas given off during photosynthesis. Cellular respiration can be summarized as follows: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O From the diagram you can see that there is an interrelationship between the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, namely the trapping of energy from the sun and providing energy for cellular processes in the form of ATP. Below is a diagram showing the structure of a mitochondrion, the site of cellular respiration.