Cell membrane
advertisement

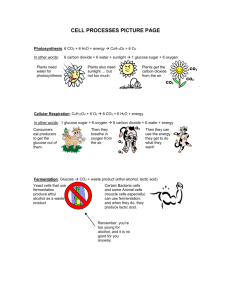
Chapter 2 Benchmark Review 26. What are the 3 parts of the Cell Theory? 1. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living things. 2. All known living things are made up of cells. 3. All cells come from other living cells. hypertonic solution a solution in which the concentration of dissolved substances is greater outside the cell (in the solution) than inside the cell 27. What happens to red blood cells in a hypertonic solution? They shrink. hypotonic solution a solution in which the concentration of dissolved substances is greater inside the cell than outside the cell 28. What happens to red blood cells in a hypotonic solution? They swell. isotonic solution a a solution in which the concentration of dissolved substances is the same inside and outside the cell 29. What happens to red blood cells in an isotonic solution? Water will continue to move into and out of the cell at the same rate. Cells in Solutions animation 30. What is required for photosynthesis to happen? PROCESS REQUIRED Photosynthesis sunlight (plants, plant-like protists, Carbon dioxide plant-like bacteria) water 31. What is produced during photosynthesis? PROCESS PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) Photosynthesis GLUCOSE (plants, plant-like protists, plant-like bacteria) Oxygen Photosynthesis PROCESS REQUIRED PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) Photosynthesis sunlight GLUCOSE (plants, plant-like protists, plant-like bacteria) Carbon dioxide Oxygen water 32. What is required for cellular respiration to happen? PROCESS Cellular Respiration REQUIRED glucose (mitochondira of all multicellular organisms) Oxygen 33. What is produced during cellular respiration? PROCESS PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) Cellular Respiration ENERGY (mitochondira of all multicellular organisms) Carbon dioxide water (vapor) Cellular Respiration PROCESS REQUIRED PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) Cellular Respiration glucose ENERGY (mitochondira of all multicellular organisms) Oxygen Carbon dioxide water (vapor) 34. What is required for lactic acid fermentation to happen? PROCESS Lactic Acid Fermentation REQUIRED GLUCOSE NO Oxygen (mitochondria of muscle cells) 35. What is produced from lactic acid fermentation? PROCESS Lactic Acid Fermentation PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) ENERGY Carbon dioxide (mitochondria of muscle cells) Lactic acid Lactic Acid Fermentation PROCESS REQUIRED Lactic Acid Fermentation GLUCOSE PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) ENERGY NO Oxygen Carbon dioxide (mitochondria of muscle cells) Lactic acid 36. What is required for alcoholic fermentation to happen? PROCESS REQUIRED Alcoholic Fermentation GLUCOSE NO Oxygen (mitochondria of yeast cells) 37. What is produced from alcoholic fermentation? PROCESS PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) Alcoholic Fermentation ENERGY Carbon dioxide (mitochondria of yeast cells) Alcohol Alcoholic Fermentation PROCESS REQUIRED Alcoholic Fermentation GLUCOSE PRODUCED (underline the waste products or by-products) ENERGY NO Oxygen Carbon dioxide (mitochondria of yeast cells) Alcohol diffusion cell membrane high concentration low concentration diffusion Cell membrane Inside cell Outside cell facilitated diffusion Cell membrane Protein channel Inside cell Outside cell facilitated diffusion high concentration low concentration active transport by transport proteins low concentration high concentration active transport Cell membrane Inside cell Outside cell exocytosis endocytosis chloroplast organelles which use the energy from the sun to make food for plants nucleus control center of the cell DNA and chromosomes structures inside the nucleus that store genetic information, which is information passed on from one generation to the next chromosomes are make up of DNA DNA is made up of genes. ribosomes organelles that produce proteins endoplasmic reticulum (ER) a system of membranes and sacs that can move materials from one part of the cell to another Golgi bodies/apparatus/complex a system of membranes which changes, supports, and packages the proteins to be stored in the cell or secreted out of the cell lysosomes an organelle filled with enzymes that can digest organic compounds mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell which releases energy from food vacuole a saclike structure that stores water or wastes cellular respiration a process in which oxygen (O2) is combined with food (glucose) to release energy fermentation • the process where cells obtain energy from glucose without oxygen photosynthesis • a process in which light energy is used to make food (glucose) by joining carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) Why do things move into or out of cells? In order to survive and function properly, cells must take in nutrients and get rid of wastes. passive transport • a process in which materials are transported across the cell membrane without using energy Three types of passive transport 1. diffusion (O2 and CO2) 2. osmosis (diffusion of H2O) 3. facilitated diffusion active transport • when a cell uses energy to move materials into areas where they are more concentrated Active transport by transport proteins • When molecules move from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. exocytosis when a cell removes large materials by vesicles that carry the materials to the cell membrane facilitated diffusion • when transport proteins (in the cell membrane) help molecules that are too large to diffuse normally pass through the cell membrane diffusion • when particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration endocytosis when the cell membrane forms a fold or a pocket called a vesicle around large particles to get them into a cell osmosis • the diffusion of water through a cell membrane water (vapor) water energy energy from the Sun carbon dioxide oxygen glucose (sugar) glucose (sugar) lactic acid fermentation • The type of fermentation that occurs in muscle cells after strenuous activity. alcoholic fermentation • a type of fermentation that occurs in yeast and some other unicellular organisms that break down sugars