Document
advertisement

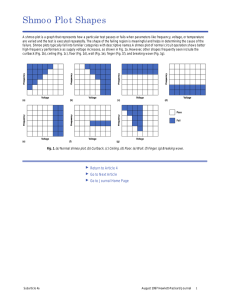
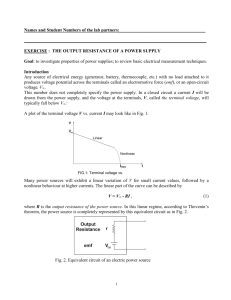
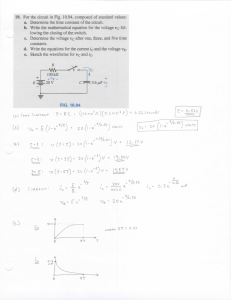
UNIT-1 Basic Concepts 1) For the network shown in fig. determine the voltage V using source shift and / or source transformation techniques only. Then verify by node equations. JAN.2015 Sol.: A) Using source shifting and source transformation technique: The first step in the analysis is to shift voltage source 3V in series with 4Ω and 3Ω resistor branches at the node. it is clear that nodes are connected to each other through a short branches. Hence all the points along these branches are at same potential i.e. at ground with 3Ω. Converting both the voltage sources into their equivalent current sources. Combining 3Ω and 1Ω in series and converting voltage source into current sources. Combining parallel current sources and parallel resistors excluding 2Ω resistor as shown in the fig. 2(g). Hence the equivalent current source value and resistance are given by, Q.2) Distinguish the following with suitable examples. i) Linear and non-linear elements. ii) Unilateral and trilateral elements. iii) Independent and dependent sources. sol : i) Linear and non-linear elements. JUNE 2015 Q.3) Write the mesh equation for the circuit shown in Fig. and determine mesh currents using mesh analysis. JUNE 2014 Ans. : Due to the current source, before applying KVL, analyze the branch consisting of current source and express current source in terms of assumed loop currents. ∴ I1 = 10A …..(1) Q.4) For the network shown in fig. determine the voltage V using source shift and / or source transformation techniques only. Then verify by node equations. Sol. : A) Using source shifting and source transformation technique: JUNE 2015 Q.5) Reduce the network shown in Fig. to a single voltage source in series with a resistance using source shift and source transformations. JUNE 2015,JAN.2015, JAN.2014, JUNE 2013 Q.6) In the circuit shown in Fig. Q. 1(a) determine V2, which results in zero current through the 4Ω resistor. Use mesh analysis. JAN.2014