Postwar America
advertisement

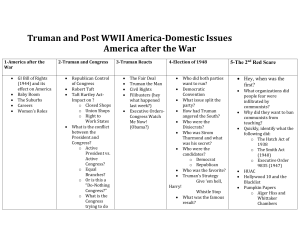
POSTWAR AMERICA Unit 10.7 POSTWAR AMERICA After the war, America’s economy was up as the war had increased the per-capita income of Americans 15 million troops returning home found jobs and housing hard to come by, and many feared the return of hard economic times These fears were not realized- much of America’s income was tucked away in savings because wartime rationing meant there were fewer consumer goods to buy Millions of Americans were wanting to unleash pent-up needs to BUY, BUY, BUY By the 1950’s, the U.S. enjoyed the highest standard of living in history of all societies THE G.I. BILL Formally known as the Servicemen’s Readjustment Act of 1944 Supported the transition of 15 million veterans to a peacetime economy As a part of the GI Bill, the government covered the cost of college expenses for the returning veterans 2 million GI’s attended college, starting a postwar boom in higher education Also provided $16 billion in low-interest loans for veterans to buy homes and farms and to start businesses THE BABY BOOMERS After millions of soldiers returned home, there was an explosion of marriages and births 50 million babies entered the U.S. population between 1945-1960 The baby boomers profoundly affected the nation’s social institutions and economic life RISE OF THE SUNBELT Millions of Americans made moving a habit after the war was over A warmer climate, lower taxes, and economic opportunities in defense-related industries attracted many families to the sunbelt states from Florida to California Represented a huge shift of industry, people, and political power from one region to the other THE SUNBELT STATES SUBURBAN GROWTH Desperate need for housing after the war resulted in a construction boom William J. Levitt and Levittown: 17,000 mass-produced, low-priced family homes on Long Island, New York Low interest rates made moving to the suburb affordable for many families The majority of middle-class Americans became suburbanites– this effect of mass movement was disastrous for the inner cities Major cities were becoming increasingly poor and racially divided LEVITTOWNS ECONOMIC PROGRAMS Employment Act of 1946: Council of Economic Advisers who helped the president and Congress on means of promoting national economic welfare Truman asked Congress to continue the price controls of wartime to keep inflation in check; instead, Congress elected to relax the controls of the Office of Price Administration Inflation was up 25% in the first years of peace 4.5 million workers went on strike for wage increases to combat inflation Truman used former soldiers to fill the jobs of railroad workers and miners Most of the strikes were eventually called off CIVIL RIGHTS Truman was the first modern president to challenge racial discrimination Established the Committee on Civil Rights (1946) 1948: Prohibited racial discrimination in the federal government and ended segregation in the military Fair Employment Practices Commission: Prevent employers from discriminating against the hiring of African Americans Blocked by Southern Democrats REPUBLICAN CONGRESS Unhappy with inflation and strikes, voters were in a conservative mood in 1946 when they elected a Republican majority in both houses of Congress 22nd Amendment (1951): Limited presidential terms to a max of two terms (8 years) Taft-Hartley Act (1947): Main objective was to check the growing power of unions Outlawed closed-shop policies Outlawed secondary boycotts THE ELECTION OF 1948 Several political parties emerged in opposition to Truman Progressives- Liberal Democrats who thought Truman’s aggressive foreign policy threatened world peace Dixiecrats- Southern Democrats who fled from Truman’s support for civil rights Republican candidate Thomas Dewey looked like the winner from the beginning, but Truman confounded the polling experts and won a decisive victory 2 million majority in the popular vote 303-189 electoral vote THE FAIR DEAL (1949) National healthcare insurance Federal aid for education Civil rights legislation Funds for Public housing New farm programs Shot down by the Republican Congress except for an increase in the minimum wage (40 to 75 cents/hour): Political disagreements/Truman’s conflicts with Congress Foreign policy concerns of the Cold War overshadowed domestic issues