Chapters 2&3 Notes
advertisement
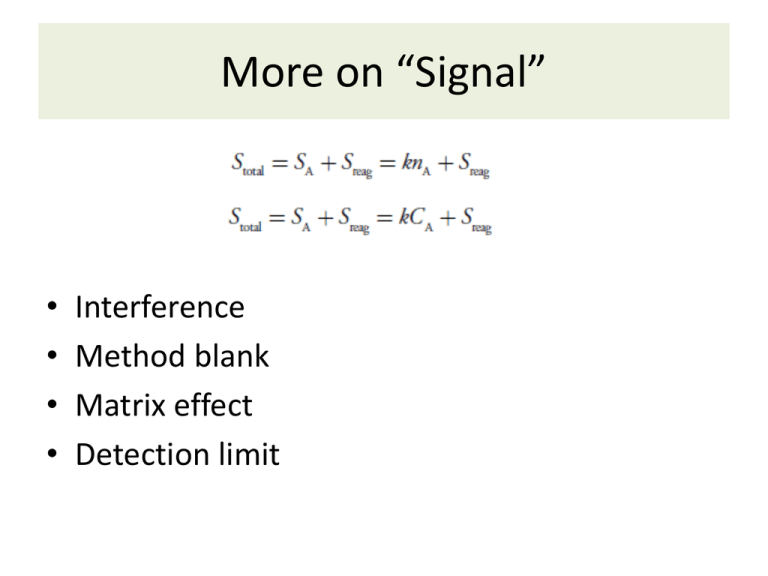
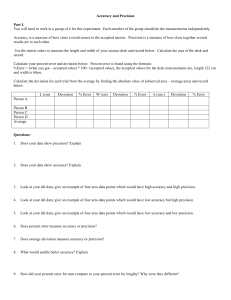
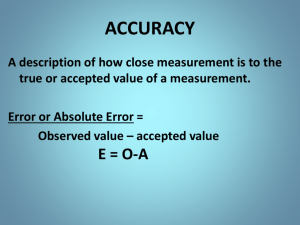
More on “Signal” • • • • Interference Method blank Matrix effect Detection limit The “Scales” of Analytical Chemistry Review Significant Figures • What are sig figs? • Rules: Addition/subtraction Multiplication/division Log/antilog Exact numbers • When to round? Significant Figures Examples • Add the numbers 1.0556, 7.113*10-2, and 0.81 • How many kilometers is 9.3 miles? (Use the conversion factor 1 km = 0.62137 mi.) • A student measures the mass and volume of a liquid to determine its density. The volume is 25.00 mL. An empty beaker has a mass of 74.881 g, and the beaker with liquid is 99.437 g. What is the density? • What is the pH of a 1.56*10-3 M hydrochloric acid solution? Accuracy • What is accuracy? • Quantifying accuracy • Assessing accuracy • No true value? Precision • What is precision? • Quantifying precision • Assessing precision Characterizing Data Example Calculate the average, mode, standard deviation, relative standard deviation, and percent relative error for the following data set (density of pennies, post 1982 = 7.18 g/mL). (By hand first, then use your calculator’s stat mode…) 1. 2. 3. 4. 7.22 g/ml 6.87 g/ml 7.03 g/ml 7.30 g/ml Two Types of Error 1. Determinate error – Sampling – Method – Measurement – Personal **can be constant or proportional** Class A Tolerances Two Types of Error 2. Indeterminate/random Visualizing these: Determinate Indeterminate Uncertainty • What is uncertainty? • DUI example If you don’t learn anything else in this class…