The Roman Republic
advertisement

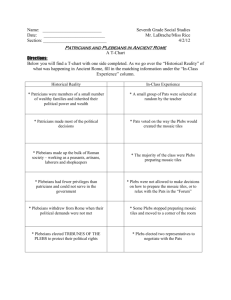
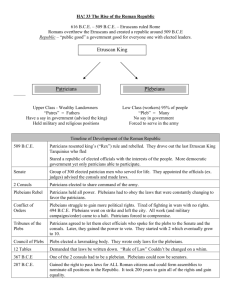
THE ROMAN REPUBLIC REPUBLIC Republic: A type of government with elected officials ROMAN CLASSES Patricians: Wealthy Romans who ran the government Means Father Wealthy Landowners Could be elected to the Senate Held High Military Positions Held High Religious Positions ROMAN CLASSES Plebeians: The Common people of Rome, majority of the Population Means Many Peasants– Laborers, Craftsmen, Shopkeepers Could Not Be Elected To Senate Could Not Be Priests Forced to Serve in Army ELECTED OFFICIALS Senate: 300 men elected by Patricians to advise Roman leaders Term of Office: Life Powers: A. Appoint other government officials B. Serve as judges ELECTED OFFICIALS Consuls: Two executives elected to run the government Term of Office: One year Powers: A. Direct the government B. Command the army Veto Power: Each consul could overrule the other REVOLT OF THE PLEBEIANS What Happened: Plebs rebelled and left the city, refused to work on farms Why: Plebs wanted more rights in the government Results: Tribune of the Plebs was created REVOLT OF THE PLEBEIANS “There was great panic in the city, and everyone was afraid. Many of the common people were leaving the city. The rich and powerful wondered how long the crowds who stayed in Rome would remain peaceful. And what would happen if an army was needed to fight foreign invaders?... The patricians had little choice but to compromise.” PLEBEIAN GOVERNMENT OFFICIALS Tribunes of the Plebs: Leaders elected to represent the Plebeians Powers: A. Speak for the Plebeians to Senate and Consuls B. Veto actions by the Senate PLEBEIAN GOVERNMENT OFFICIALS Council of the Plebs (Assembly): Law-making body of the Plebeians Power: Make laws (for Plebeians only, not Patricians) GOVERNMENT REFORMS The Twelve Tables: The laws of Rome written on 12 bronze tablets and displayed in the Forum in 451 B.C. Why did Plebs like this? Everyone can see the laws Prevents government from applying laws differently to rich and poor GOVERNMENT REFORMS New Law in 367 B.C. A. Required one Consul to be a Plebeian B. Former Consuls became Senators, so Plebs were allowed in the Senate New Law in 268 B.C. A. Council of the Plebs could now make laws for all Romans B. Council of the Plebs nominated Consuls, Tribunes, and Senators Significance: Provides more rights and equality to Plebs GOVERNMENT TERMS Tripartite Government: Government is divided into three parts Rome United States Legislative 300 Senators 100 Senators, 435 Representatives Executive Two Consuls One President Judicial Eight judges served for one year Nine Supreme Court justices serve for life GOVERNMENT TERMS Roman Citizen: Person who was allowed to participate in the government Rights of Citizens Duties of Citizens 1. Vote 1. Pay taxes 2. Hold political office 2. Serve in army GOVERNMENT TERMS Civic Duty: Actions expected of responsible citizens A. Paying taxes B. Serving in the military C. Holding public office D. Voting GOVERNMENT TERMS Checks and Balances: Each part of the government balances the others so no one branch becomes to powerful A. Consuls and Tribunes could veto laws passed by the Senate B. Consuls only served for one year