Drug Identification for School Counselors
advertisement

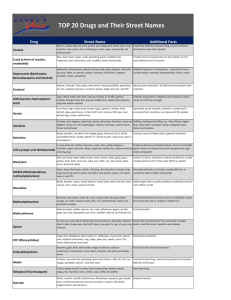
Drug Endangered Children and Drug Identification What is a drug endangered child? A child who lives in a place with no heat A child who smokes pot with his parents A child left alone with no supervision A child in need of medical attention Drug Endangered Children Children who suffer physical or psychological harm or neglect resulting from exposure to an environment where adults are manufacturing, selling, or using drugs. Neglected & Abused Children 50% more likely to be arrested as juveniles 40% more likely to be arrested for a violent crime as adults 33% more likely to become substance abusers US Department of Justice Drugs of Abuse Most Commonly Abused Drug Legal Drug Commonly Abused Drugs Marijuana Commonly Abused Drugs Methamphetamine Commonly Abused Drugs Prescription Drugs Commonly Abused Drugs Cocaine Drugs Of Abuse Heroin Drugs Of Abuse MDMA (Ecstasy) Drugs Of Abuse GHB Drugs Of Abuse LSD Drugs Of Abuse Inhalants Drugs Of Abuse Dextromathorithan Drugs of Abuse Fentanyl Drug Schedules Schedule I Heroin, Ecstasy, Marijuana , LSD, Rohypnol Schedule II Cocaine, Ritalin, PCP, Fentanyl, OxyContin, Percocet, Morphine, Methamphetamine Schedule III Ketamine, Vicodine, Loritab, Tylenol 3 Schedule IV Xanax, Librium, Valium, Phenobarbital, Darvocet Schedule V Cough suppressants Marijuana The most commonly abused illicit drug in the U.S. A dry, shredded green/brown mix of flowers, stems, seeds, and leaves. Is a schedule I drug under the controlled substance act. Smuggled in from Mexico and Canada. Domestically grown. Grass, Pot, Weed, Bud, Reefer, Cannabis Marijuana Short term effects – Increased heart rate – Loss of coordination – Difficulty in thinking and problem solving – Distorted perception – Time passes slowly – Anxiety and panic attacks – Dry mouth Long term effects – Respiratory problems (cough and phlegm) – Symptoms of chronic bronchitis – Difficulty in registering, processing and using information – Difficulty sustaining attention What to look for . . . Prescription Drug Abuse How is it done? The DEA calls this pharmaceutical diversion 20% of the U.S. population have used prescription drugs for non-medical reasons in their lifetime. 1. Illegal sale and distribution by health care professionals and worker 2. “Doctor shopping” 3. Employee theft 4. Forged prescriptions 5. Internet Three classes of most commonly abused prescription drugs Opioids are prescribed to treat pain (OxyContin) CNS depressants are prescribed to treat anxiety and sleep disorders (Valium) Stimulants – are prescribed to treat narcolepsy and ADHD (Ritalin) Prescription Drug Abuse What are the brand names of some of these drugs? Painkillers: Vicodin, Tylenol w/ Codeine, OxyContin, Percocet Depressants: Klonopin Nembutal, Soma, Valium, Xanax Stimulants: Adderall, Concerta, Dexedrine, Ritalin OTC’s Coricidin HBP Cough and Cold, Robitussin, Vicks Formula 44 Cough Relief Pharm Party At a “pharm party,” teens share and mix various prescription medications, especially painkillers (OxyContin and Vicodin); tranquilizers (Xanax and Valium), stimulants (Ritalin and adderall); and sedatives. Alcohol is often added to the “cocktail,” increasing the danger. What to look for . . . . Constricted pupils, slurred speech, flushed skin, sweating, and loss of appetite Personality changes, moods swings, irritability, sleepiness or avoiding sleep, forgetfulness Increasingly secretive, losing interest in personal appearance, changes at school Cocaine Cocaine is a naturally derived central nervous system stimulant extracted and refined from the Coca plant It is an intense euphoric drug with strong addictive potential Cocaine is typically a white-ish powder with a bitter, numbing taste. Is a schedule II drug under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. Coke, Flake, Snow, Crack, Nose Candy Cocaine The powdered, hydrochloride salt form of cocaine can be snorted or dissolved in water and injected. Crack is the free base form of cocaine. It is not water soluble, but volatile. This form comes in a rock crystal that can be heated and its vapors smoked. Cocaine Initial effects: Hyperactivity Restlessness Increased blood pressure Increased heart rate Short term effects: Increased focus Excitation Euphoria Sexual arousal Insomnia Decreased appetite Negative effects: Increased body temperature and heart rate Agitation and anxiety Paranoia Dizziness Nausea/vomiting Violent behavior Increased risk for heart attacks Strokes Respiratory problems What to look for . . . Heroin Heroin is processed from morphine, a naturally occurring substance extracted from the seedpod of the Asian poppy plant. Heroin usually appears as a white or a brown powder Is a schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. Smack, Thunder, Junk, Mexican black tar Heroin withdrawal Drug craving Restlessness Muscle and bone pain Insomnia Diarrhea Vomiting Cold flashes with goose bumps (cold turkey) Kicking movements (kicking the habit) Heroin Treatment Methadone maintenance treatment programs Substance abuse counseling Psychosocial therapies Supportive services What is inhalant abuse? Deliberate inhalation of fumes, vapors or gases to “get high” Inhalants are poisons to the body Quick intoxication with serious health consequences. It’s like a quick drunk. It effects the same receptors that alcohol does. Who knows about Inhalant Abuse? Who doesn't know about Inhalant Abuse? Why do kids abuse inhalants? Because they can Because they’re bored Because they’re upset In short, for any reason or no reason They don’t have to have money They don’t have to have transportation They don’t have to have the ability to get the drugs In short, they have access How it’s Done Sniffing from a container, bag, cans or clothing Huffing - Inhaling from a chemical soaked rag, open container or balloon Bagging - Putting a bag over one’s head and huffing For maximum effect, children inhale deeply and then take several more short breaths Commonly Product/Potential Inhalants Gases Nitrous oxide, helium, refrigerants, propane Solvents and Fuels Butane, nail polish remover, paint thinner, correction fluid, permanent markers, gasoline Aerosols Spray paint, hair spray, air freshener, dust-off Adhesives Model airplane glue, rubber cement, PVC cement Foods Cooking spray, aerosol whipped cream topping Cleaning Agents Spot remover, degreaser Among teens aged 12 to 17, 20.9% used illegal drugs in the past year. (age) 12-13 14-15 45.5% 25.1% 12.4% Painkillers 36.5% 34.2% 35.2% Marijuana 28.4% 66.2% 81.4% Other 9.8% 26.3% 34.2% Inhalants 16-17 The National Inhalant Prevention Coalition & SAMSHA, 2007 Immediate Effects Dizziness Disorientation Emotional volatility Loss of coordination Distortion of perception Cognitive impairment Hallucinations Lightheadedness Diminished sensitivity to pain Slurred speech Loss of inhibitions Medical Consequences Asphyxiation- displacing oxygen in the lungs Suffocation – blocking air from entering the lungs (bag over head) Convulsions or seizures – abnormal electrical discharges in the brain Choking- from inhalation of vomit Fatal injury- accidents while high Death Inhalant Abuse Emergencies Remove the source of chemicals from around the nose and mouth Call 911. Turn person on side to prevent aspiration of vomit If not breathing, administer CPR Ventilate the area Do not excite, scare, shock, upset or chase the person Try to identify the inhalant What to look for: Household cans left in child’s bedroom or going through an item too fast Pain around the mouth or on the tongue Upset stomach or throwing up with no know reason found Change in behavior Passing out A chemical odor Death Methamphetamine Methamphetamine is a synthetic stimulant drug which induces a strong feeling of euphoria (similar to adrenaline) and is highly addictive. Can be injected, snorted, smoked or taken orally Is a schedule II drug under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. Speed, Meth, Ice, Crystal, Chalk, Crank, Go-Fast Meth comes in two forms POWDER The powder form is usually white, odorless and bitter-tasking, and can be snorted, smoked, eaten, dissolved in a drink and ingested, or heated and injected. ROCK The purer form of the drug, called “crystal”, “glass” and “ice” appears as clear, chunky crystals that are usually smoked or injected What meth does for the user Repeated use damages the dopamine producing cells in the brain !!!!!!!!!! What to look for . . . Appearance Mouth: User may develop “meth mouth” – extreme tooth decay Skin: Infected sores or “meth bugs” appear and are slow to heal Body weight: User may experience dramatic weight loss, anorexia, malnutrition What to look for . . . Behavioral May act euphoric – Jittery – Nervous – Confused – Violent Incessant talking Paranoid Erratic sleep patterns Repetitious behavior The meth cycle of abuse High Binge (4–16 hours) (3-15 days) Crash (up to 3 days) Making meth Process to make meth is easy and accessible. There are several ways of making meth, most of which require the use of caustic chemicals such as lye, ether, acetone, and phosphorus The two major methods are the red phosphorous method or the anhydrous ammonia method Hundreds of recipes on the internet Start with extracting the active ingredient, ephedrine or pseudoephedrine, from over the counter drugs Average meth “cook” teaches ten other people how to make meth annually Indicators of a meth manufacturing: Chemicals Ephedrine tablets – cold medicine Acetone – finger nail polish remover Red Phosphorus – match striker plates Iodine – antiseptic (merthiolate) Sulfuric Acid – drain cleaner Hydrochloric acid – concrete cleaner Methyl alcohol/methanol – gas line antifreeze (heet) Coleman/camp fuel used for extraction Indicators of a meth manufacturing: Household equipment Burner plates Coffee filters Glass bottles Plastic jugs Pyrex dishes Funnels Aquarium tubing Chemical Test Tubes If you Suspect a Meth Lab Remain calm. Give yourself time to think. Do NOT approach the suspects. They are often armed and may be dangerous Do NOT enter the lab area. If you are in the lab already, find an excuse to leave immediately. If you are in a lab already, do not touch or turn off anything. Keep a safe distance. Hazardous materials may ignite or the fumes may overcome you. Promptly notify law enforcement Being a good parent is a tough job. Being a good parent on drugs is impossible Andrea Darr WV DEC Coordinator WV Prosecuting Attorneys Institute 90 MacCorkle Ave., SW South Charleston, WV 25303 304-558-3348 phone Andrea.l.darr@wv.gov Many thanks to the Marathon County Sheriff’s Department in Wisconsin for the Making Meth video used in this power point presentation