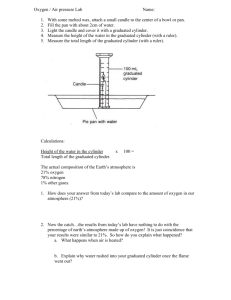
Celsius and Kelvin Temperature
advertisement
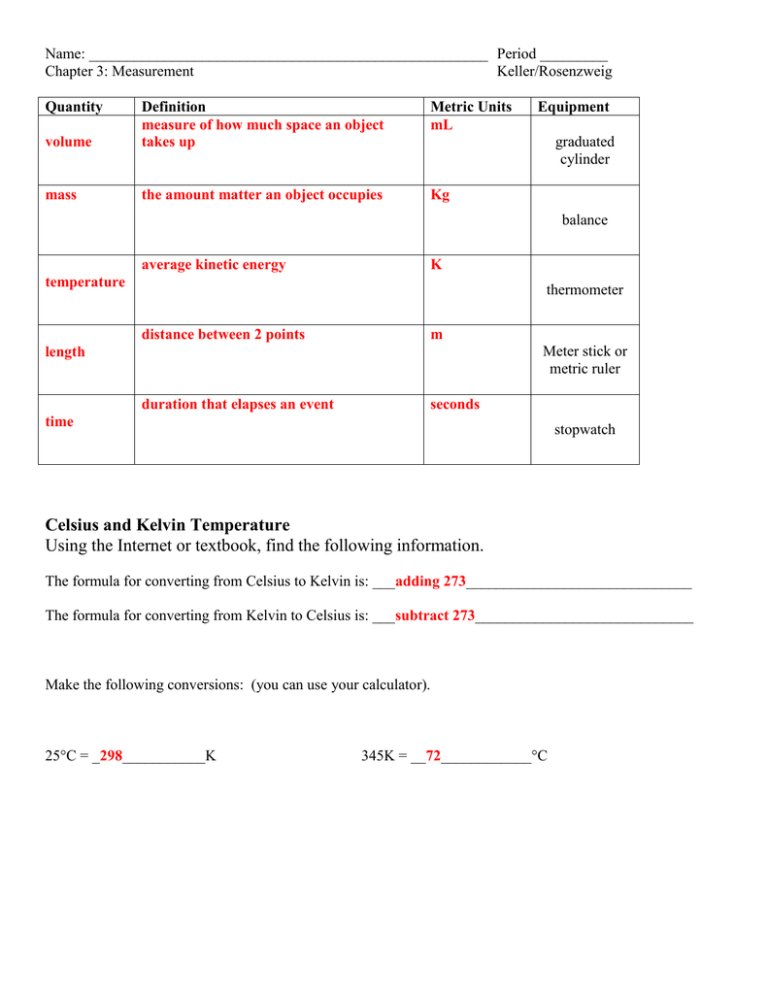
Name: _____________________________________________________ Period _________ Chapter 3: Measurement Keller/Rosenzweig Quantity Metric Units mL volume Definition measure of how much space an object takes up mass the amount matter an object occupies Kg Equipment graduated cylinder balance average kinetic energy K temperature thermometer distance between 2 points m Meter stick or metric ruler length duration that elapses an event seconds time stopwatch Celsius and Kelvin Temperature Using the Internet or textbook, find the following information. The formula for converting from Celsius to Kelvin is: ___adding 273______________________________ The formula for converting from Kelvin to Celsius is: ___subtract 273_____________________________ Make the following conversions: (you can use your calculator). 25C = _298___________K 345K = __72____________C READING LAB EQUIPMENT RULE: Always read lab equipment one place value past the decimal value that you see! EXAMPLE 1: Ruler A: you can read to the tenths, so you estimate the hundredths Length of nail when measured with Ruler A: _____4.35cm____5 is your guess digit______ Ruler B: you can read to the ones, so you estimate to the tenths Length of nail when measured with Ruler B: _____4.4cm _____4 is your guess digit ___ EXAMPLE 2: Ruler A: 40 cm Ruler B: 50 cm 40 cm 41 cm Ruler A: you can read to the ___tens_________, so you estimate to the ____ones__________ Length of the line when measured with Ruler A: _______48cm ________________________ Ruler B: you can read to the ___ones_________, so you estimate to the __tenths____________ Length of the line when measured with Ruler B: _______40.8cm _______________________ 115.5mL 0.40mL 555mL 57.3mL 1.61mL 57mL 66.0mL 8.21mL 660mL 39.6mL 4.80mL 3700mL Station 1 Read the volumes in different graduated cylinders to the correct place value: a) 10mL graduated cylinder __________ b) 25mL graduated cylinder __________ c) 100mL graduated cylinder __________ Station 2 Read the length to the correct place value of the following items. Make sure to use the cm side of the ruler! a) Stirring rod: __________ b) Length of index card: __________ c) Width of index card: __________ Station 3 a) The volume of water given in the beaker is: __________ b) Carefully pour the water from the beaker into the graduated cylinder. c) Now measure the volume of water in the graduated cylinder: d) Pour the water back to the original beaker. __________ Station 4 A. MASS 1. Bring a pencil and a calculator to the table. 2. Predict the masses of each object in grams. 3. Use the electronic balance to determine the mass of each object. Record the mass in the data table below. OBJECT pencil PROJECTED MASS (g) MASS (g) calculator B: VOLUME 1. Take the empty cup. Using the cup, try to obtain 75mL of water from the sink. 2. Transfer the water to the graduated cylinder. How did you do? Record the results in the data table. 3. Try obtaining 200 mL of water from the sink and record results. TARGET VOLUME ACTUAL (MEASURED VOLUME) 75mL 200mL Station 5 1. There are three cups of water – one dyed blue, one dyed green and one dyed red – on the lab table. Transfer each sample of liquid to the smallest graduated cylinder on the table that will hold all of the water. 2. Read the graduated cylinder. Record the volume of water in each cup in the data table. Then return the water to the cup. COLOR OF WATER blue green red VOLUME (mL)