Theoretical Yield Vs. Actual Yield: Sample Lab Data
advertisement

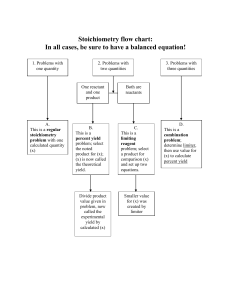
Theoretical Yield Vs. Actual Yield: Sample Lab Data Name:_____________________ Hr:___ Rhee Action was in the chemistry lab when some aluminum metal fell into a container of bluecolored copper(II) nitrate Cu(NO3)2 solution. An immediate reaction occurred producing much heat, the blue color faded, and a shiny, brown product, Cu, was formed. 1. Write the balanced equation for this reaction. 2. What type of reaction is this?_____________________________________ Rhee decided to do this reaction under more controlled conditions. At the end of the experiment there was aluminum remaining, copper product, and a clear, colorless solution. She decanted the solution, removed the aluminum, and dried the copper product. She recorded: Mass of aluminum before reaction Mass of aluminum after reaction Mass of copper and beaker Mass of empty beaker 2.59g 1.35g 52.73g 48.52g SHOW WORK AND UNITS FOR THE FOLLOWING CALCULATIONS: 3. Determine the mass of aluminum that reacted. 4. Use the mass of aluminum and stoichiometry to calculate the expected mass of copper produced from this reaction, also known as "theoretical yield". 5. Determine the experimental mass of copper produced, or "actual yield". 6. Calculate the percent yield using the following formula: 7. Calculate the percent error using the following: % yield = 8. What do you notice about these percentages? 9. Identify the reactant in excess:_________________________ 10. Identify the limiting reactant:_________________________ theoretical yield x 100 theoretical yield−actual yield % error = | [Note the absolute value signs] actual yield theoretical yield |x 100