Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
advertisement

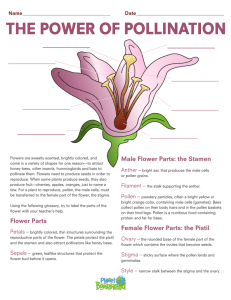
2 Types of Seed Plants • Angiosperms • Gymnosperms Gymnosperms • Have cones for reproduction instead of flowers • 4 Types – – – – Cycad Ginkgo Conifer Gnetophyte Gymnosperms • Cycads: look like ferns except they have seeds • Ginkgo: very large trees found mainly in China Gymnosperms • Conifers: seeds are in cones or berrylike structures • Gnetophytes: shrubs and climbing vines Angiosperms • Largest group of plant in the world • Found in all types of climates • Produce flowers for reproduction Angiosperms • Parts of the flower: – – – – Sepals Petals Stamen Pistil Sepals sepal • The sepals protect the flower before it opens. Petals • The petals attract pollinating insects with their bright color and attractive scent. Male Parts • The stamens are the male structures of the flower. • Made up of two parts: – Anther – Filament Male Parts • Anther: top part of the stamen, that makes pollen. • Filament: this is the stalk of the Anther Female Parts • Pistil is the female structure of flower that has 3 parts: – Stigma – Style – Ovary stigma Female Parts • Stigma: – The pollen from another flower collects on the stigma’s sticky surface. • Style: – raises the stigma away from the Ovary Female Parts • Ovary protects the ovules(egg). • Once fertilization has taken place it will become the fruit. Write the correct words in the boxes: stamens, stigma, petals, ovary, sepals pollen sticks to this 5 where the seeds grow 1 these attract insects 4 These protect the flower before it opens 3 where the pollen is made 2 PLANT REPRODUCTION Plants Reproductive Structures • Cones: Gymnosperms – Female cones contain the ovules which contains the egg cell – Male cones contain pollen which are like sperm cells • Flowers: Angiosperms – Pistil: female part of flower – Stamen: Male part of flower Pollination • Insects visit flowers to search for nectar – their food. • But the flowers use the insects for their own purposes! • As the insect probes for nectar, its body rubs against the stamens. • Pollen gets stuck on the insect’s legs. • You can often see bees with a heavy load of yellow pollen on their hind legs. Pollination When the insect visits another flower of the same type, the pollen will stick to the pistal. This is called pollination. Fertilization The pollen travels to the ovary, where it joins with an ovule. This is called fertilization. Seeds • Seeds: the fertilized egg • Seed Structure: consists of a seed coat, a young plant, and stored food Types of Seeds Types of Seeds Seeds • The seeds develop inside the ovary, which grows to become the seed pod or fruit. Seed Dispersal • The seeds are dispersed; some by animals, some by the wind, some by explosion and some by water.