Title of Presentation
advertisement

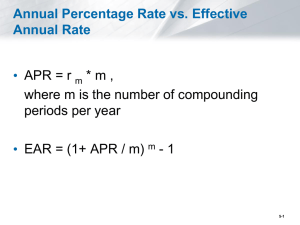
FIN 614: Financial Management Larry Schrenk, Instructor 1. What is an Interest Rate? 2. Types of Interest Rates 3. Conversions between Types of Interest Rates Compensation for the Lending of Money Loss of the Use of an Asset Stated in Percentage Terms (Relative to the Principal) Similar to a Rental or Leasing Charge Holding Period Return, HPR Annual Percentage Rate, APR, NOM% Period Rates, rmonthly, rquarterly, etc. Effective (or Equivalent) Annual Rate, EAR, EFF% Most Basic Rate Calculation Change from one point of time (t = 0) to another (t = 1): V1 V0 HPR V0 HPR = Holding Period Return V1 = Value at t = 1 V0 = Value at t = 0 NOTE: The time from t0 to t1 need not be a year. My portfolio was worth $123,000 5 years ago and it is now worth $131,000: 131,000 123,000 HPR 0.065 6.5% 123,000 REMEMBER: The earlier value always goes in the denominator! Problem: Comparing assets with different holding periods. Which is better? 7.8% over 7 years 10.5% over 10 year Need a common time period Convert all rates to an annual basis ‘Annualize’ them Annual Cost of Borrowing Including Fees and Transaction Costs Legal Standard–Consumer Credit Protection Act (1968) Does not Incorporate Compound Interest Formula: APR ri m APR = Annual Percentage Rate ri = Return for Period i m = Periods per Year What is my APR is my weekly return is 0.25%? rweekly x m = 0.25% x 52 = 13.00% APR = 13.00% Period Rate is the Rate over a Certain Period It is the HPR for the Period If your stock was at $110 at the end of last month and $108 at the end of this month: HPRmonthly rmonthly 108 110 0.0181 1.81% 110 EAR Incorporates Compound Interest Accurate Calculation of Return Formula: EAR 1 ri 1 m EAR = Effective Annual Return ri = Return for Period i m = Periods per Year If your monthly return is 2%, what is your EAR? EAR 1.02 1 26.82% 12 EAR → APR 1 m APR EAR 1 1 m EAR = Effective Annual Return APR = Annual Percentage Rate m = Periods per Year (for APR) APR → EAR m APR EAR 1 1 m Also, a calculator function is available. If you get 1% return each month: EAR 1.01 1 12.68% 12 APR 0.01 12 12.00% If I invested $1.00, I would have $12.68. EAR accurately calculates the actual return. ARP underestimates your return, since it does not incorporate compound interest. My investment portfiolo increased from $125,500 to $275,100 in 5 years, find my EAR? N=5 I%=0 ◄ Select I%, then [ALPHA] [ENTER] PV=-125500 PMT=0 FV=275100 P/Y=1 C/Y=1 PMT: END BEGIN I% = 17.00% 1. [ON] 2. [APPS] [ENTER] 3. CALC VARS 1: TVM Solver... 2: tvm_Pmt 3: tvm_I% 4: tvm_PV 5: tvm_N 6: tvm_FV 7↓npv( 4. Scroll Down to ‘B:►Nom(’ or ‘C:►Eff(’ ENTER NOTE: EAR = (Eff)ective Rate and APR = (Nom)inal Rate ►Nom( Function Syntax: ►Nom(EAR, m) What is the APR (Nom) based on quarterly periods, if the EAR (Eff) is 13%? ►Nom(13, 4 APR = 12.41% ENTER ►Eff( Function Syntax: ►Eff(APR, m) What is the EAR (Eff), if the APR (Nom) based on weekly periods is 15%? ►Eff(15, 52 EAR = 16.16% ENTER FIN 614: Financial Management Larry Schrenk, Instructor