BONE TISSUE
advertisement

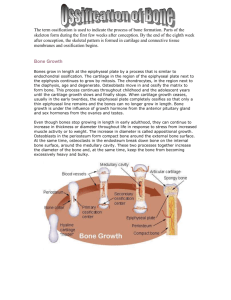
BONE TISSUE DEVELOPMENT and GROWTH FUNCTIONS • • • • Support/Movement Protection Mineral reservoir Site of blood cell production • Storage of fat Skeletal Cartilage • Consists primarily of water • Contains no nerves or blood vessels • Surrounded by perichondrium – Dense irregular connective tissue – Maintains shape Skeletal Cartilage • Basic components – Chondrocytes in lacunae – Extracellular matrix with jellylike ground substance • 3 Types – Hyaline – Elastic – Fibrocartilage Hyaline Cartilage • Most abundant • Fiber not detectable • Locations • Articular cartilage • Costal cartilage • Respiratory cartilage • Nasal cartilage Elastic Cartilage • Contains more elastic fibers; more flexible • Found in ear and epiglottis Fibrocartilage • Highly compressible • Great strength • Locations – Knee – Vertebral disks Cartilage Growth • Two methods – Appositional – adds to outside – Interstitial – growth from inside • Growth stops during adolescence Bone Histology - Cell Types • Osteocytes – mature bone cells – Osteoblasts – bone forming cells – Osteoclasts – bone destroyers BONE OSSIFICATION Process by which tissue becomes bone Also called osteogenesis Bone Formation • Bone formation begins approx. 8 weeks into fetal development from a skeleton that is mostly fibrous membranes and cartilage • Intramembranous ossification – bone forms from the fibrous membranes • Endochondral ossification – bone forms from hyaline cartilage Intramembranous Ossification • Osteoprogenitor (mesenchymal) cells in fibrous C.T. develop into osteoblasts • Osteoblasts secrete collagen matrix • Calcification occurs in ossification centers; forming a network of bone rather than layers • Bony plates form which are later converted into compact bone • Flat bones only; skull & clavicles • Fontanelles are areas not ossified at birth ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION • Forms most bones • Hyaline cartilage model in shape of the bone initially; a pH change causes cartilage to calcify and the cells to die • Primary ossification center forms as blood vessels from periosteum and osteoblasts invade calcified cartilage • Matrix formed (osteoid= unmineralized bone matrix) • Ossification occurs = calcium salts deposited • Primary centers form before birth; Secondary centers form 8th month dev. Epiphyseal Plate • Cartilage region between primary and secondary ossification centers • Responsible for postnatal bone growth • Zone of resting cartilage • Growth Zone – mitosis occurs • Transformation Zone – cartilage matrix deteriorates • Osteogenic Zone - bone salts deposited Calcium regulation • Calcium is most abundant mineral in the body; 99% located in the bone • Regulated by two hormones: PTH (parathyroid hormone) and calcitonin • PTH - raises blood calcium levels • Calcitonin - lowers blood calcium levels Hormones and Vitamin Effect on Bone Growth • • • • • Testosterone Estrogen Growth Hormone Throxine Vitamin D – calcium absorption Bone Types • Compact Bone – also called dense bone – hard, strong and solid bone that forms the outer layer of all bone – provides support, protection and resists stress • Contains osteons • Cancellous – also called spongy bone – found more toward the inner portion of bone – open lattice-work of struts and plates that serves to store bone marrow • Trabeculae Osteons = Haversian System • Haversian canal • Volkmann’s canals • Lamellae • Lacunae • Canaliculi Bone Types • Long – arms and legs • Short – wrist and ankle – Sesamoid – forms within a tendon (patella) • Flat – sternum, scapula, ribs, skull • Irregular – vertebrae & coxal bones Structure of a Long Bone • • • • Diaphysis Epiphysis Articular cartilage Periosteum – connective tissue covering bone • Medullary cavity • Endosteum – connective tissue; lines inside Bone Fractures • Open ( Compound) – penetrates skin • Closed (Simple) • Partial/Complete - Greenstick • Comminuted – broken into 3 or more pieces Bone Repair • Formation of clot ( hematoma) • Callus ( soft followed by hard) • Mineralization of callus by calcium & phosphorus • Remodeling