epithelial tissue
advertisement

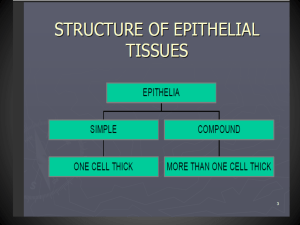
Epithelia Epithelia are tissues consisting of closely apposed cells with very little intercellular substances. They Epithelia are avascular but all epithelia grow on vascular connective tissue. Epithelia and underlying connective tissue are seperated by basement membrane Functions Covering (eg: skin) Lining of all the body cavities (eg : intestines) Secretory(eg: glands) Epithelia covers all free surface of the body, where it is called mesothelium and The internal surfaces of blood and lymph vessels are lined by epithelium, here they are called endothelium The cells on the free surface are called apical cells Classification of epithelia Covering epithelia Glandular epithelia(with secretory function) Classification of covering epithelium Epithelial tissue is classified based on the number of cell layers and the shape of cells in apical layer Based on number of cells: 1. Simple epithelium: there is one layer of cells 2. Stratified epithelium:two or more layers of cells, it is termed stratified Based on the shape of cells in the surface layer: 1. Squamous : flattened scale or plate like cells 2. Cuboidal : Cube shaped cells 3. Columnar : cells are taller than wide Nucleus of the cells corresponds to the shape of the cells and also the long axis of the nucleus is always parallel to the main axis of the cell. Simple Squamous Epithelium One layer of flattened, scale or plate like cells. It lines all serous lining of body cavities; pericardium, pleura, peritonium ; blood vessels and lymph vessels(endothelium) The nuclei are often flattened or ovoid, ie egg shaped, and they are located close to the centre of cells Diffusion and filtration takes place across the single layer of cells Simple Cuboidal Cells One layer of cube shaped cells It occurs in, small excretory ducts of many glands(eg salivary glands), follicles of thyroid gland, tubules of kidney and on the surface of ovaries. Nuclei are spherical and are at the centre Helps in secretion and absorption Simple Columnar Epithelium One layer of tall,rectangular shaped cells;cells are taller than they are wide Lines the internal surface of GI tract from cardia of the stomach to the rectum Lining of gall bladder The nucleus is located at the same height within the cells,often close to the base of the cells Helps in secretion and absorption Pseudo-stratified Columnar epithelium One layer of columnar or irregularly shaped cells. Some kinds have cilia(pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium) and goblet cells. Lines trachea,bronchi and nasal cavity Helps in protection and secretion Stratified Squamous Epithelia Basal cells are present in the basal layer which are in contact with basement membrane Mitotically active and renew the cells These basal cells are either columnar or cuboidal in shape. The apical layer cells of the epithelium become more flattened. Present in the places subjected to wear and tear like skin, mouth, esophagus and vagina Classification of stratified squamous epithelium Keratinized: dry surfaces such as the epidermis of the skin Contains keratin, most superficial layer consisting of dead cells Functions in protection Non-Keratinized: most superficial cells are alive kept moist Linings of nasal cavity, oral cavity,pharynx, vagina and the lower anal canal. Functions in protection Stratified Cuboidal and Columnar Stratified cuboidal epithelium, for example is seen in the ducts of the sweat glands. For example found in the excretory ducts of the mammary glands and the main excretory ducts of the large salivary glands Transitional epithelium Dome shaped cells which are neither squamous nor columnar. Some cells are binucleated Found in ureter,urinary bladder and upper part of urethra Withstands distention and relaxing of bladder. Glandular Epithelium All glands of the body arise from covering epithelium by means of proliferation and invasion of the epithelial cells. Glands further differentiate into exocrine and endocrine glands Exocrine glands retain their connection with the surface epithelium from which they originated. Their connection is transformed into tubular ducts lined with epithelial cells through which the glandular secretions pass to reach the surface Endocrine glands are the ones which lose their connection during development process Releases their secretory products (typically hormones) into spaces between secretory cells from which it enters the bloodstream Exocrine glands According to the # of cells the glands are classified into unicellular and multicellular glands Multicellular glands are further classified into merocrine, apocrine, holocrine glands based on the secretory mechanisms Unicellular Glands Goblet cells are the only unicellular glands secreting mucus Respiratory and Digestive system and other mucus membranses Goblet cells secretes glycoprotin mucin which after combination with water is secreted as mucus Merocrine glands Merocrine secretion: corresponds to the process of exocytosis. Vesicles open onto the surface of the cell and the secretory product is discharged from the cell without any further loss of cell substance. Secretes a watery fluid through cell membrane Eg:salivary glands Apocrine glands Mechanism in which part of apical cytoplasm of the cells is lost together with the secretory product. Apocrine sweat glands, the mammary glands, and the prostate. Halocrine glands Designates the break down and discharge of the entire secretory cell Entire cell is released and it ruptures and dies Eg:sebaceous glands Multicellular exocrine glands Simple columnar B. Simple columnar epithelium with cilia C. Stratified squamous D. Simple squamous E. Transitional F. Pseudostratified G. Cuboidal epithelium H. Choanocytes I. Stratified columnar epithelium with cilia A. Simple columnar epithelium Simple columnar epithelium with cilia Stratified squamous epithelium Simple squamous epithelium Transitional epithelium Pseudostratified epithelium Cuboidal epithelium Choanocytes Stratified columnar epithelium with cilia