Properties of Light
advertisement

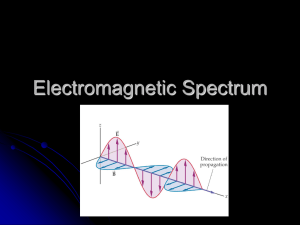
DO STOP WORK Finish Begin collecting lab data. to explain the observations you made during the lab. Physics SLC Club today Thursday Answer Sheets Missing Polarization Lens Let’s Go finish collecting our lab data. to your last station. Take out your “What is light” lab Emission Transmission Reflecting/Scattering Absorption Dispersion Polarization Diffraction A light bulb emits visible light; the energy of the light comes from electrical potential energy supplied to the light bulb. Some forms of matter, such as glass or air, transmit light, which means allowing it to pass through. Light can bounce off matter leading to what we call reflection (when the bouncing is all in the same general direction) or scattering (when the bouncing is more random). When you place your hand near an incandescent light bulb, your hand absorbs some of the light, and this absorbed energy warms your hand. These bananas absorb all colors of light except yellow. Instead yellow is scattered, so the bananas appear yellow! What is emission? What is transmission? What is reflecting/scattering? What is absorption? When white light travels through a prism it disperses into a rainbow, showing that white light is made up of all the color we can see. When light passes through a polarizing filter it is only allowed to vibrate in one direction. Light cannot pass through two polarizing filters that are set 90 degrees from one another. When a wave encounters an obstacle, or a slit is diffracts and a pattern is produced on a screen. What is dispersion? What is polarization? What is diffraction? Jump to “Details of light properties” PowerPoint How does light behave like a particle? How does light behave like a wave? Wave-Particle Duality says that light exhibits both wave and particle properties. This duality addresses the inability of classical concepts like “particle” and “wave” to fully describe the behavior of light. This is a central concept in quantum mechanics. A photon is one particle of light that obeys the wave-particle duality of light. Wave-particle duality Photons always want to travel at the speed of light in a vacuum: Every photon has a specific frequency and wavelength that obey the equation: f is the frequency of the photon (Hz) Lambda is the wavelength of the photon (m) Photons have energy that obey the equation: h is Planck’s constant: E is the energy measured in Joules (J) Note: Not every photon has the same energy Explain Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. DO STOP WORK Solve for the velocity, wavelength, frequency, energy, and type of light. Remember your long answers are due tomorrow. I’ll be collecting the them so write your answers in the question packet too. Does anyone have the completed letter slip? For a photon that has wavelength of 650nm find its velocity, frequency, energy, and color. Velocity: The velocity of a photon is always the same in a vacuum. Frequency of the photon: Energy Or: of the photon: Color of the photon RED! Which has a larger wavelength, red or blue light? Red Which has a greater frequency, red or blue light? Blue Which has more energy, red of blue light? Blue What color light has a wavelength of 200nm? Gamma Rays, X-Rays, Ultraviolet, Visible, Infrared, Microwaves, and Radio Waves are all part of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are all electromagnetic rays We can only detect visible electromagnetic waves with our eyes, but this doesn’t mean the visible waves are a different type of wave than the ones we can’t see. How can chicken wings be used as an analogy for the electromagnetic spectrum? Spicy Cajun Style Spicy Glazed Baked Buffalo Sesame Maple Broiled Barbecued Inferno Plain TV, FM, AM, Wifi, cell phones Wavelength – Football field to a baseball Can you hear radio waves? “Most people associate the term radio with sound, but radio waves are a form of light with long wavelength-too long for our eyes to see. Radio stations encode sounds as electrical signals and broadcast the signals as radio waves. What we call “a radio” in daily life is an electronic device that receives these radio waves and decodes them to recreate the sounds played at the radio stations.”-The Cosmic Perspective Microwaves Microwave oven, Radar Wavelength – Lacrosse ball to a small dot Infrared People, light bulbs Wavelength – Cell to bacteria Visible The only electromagnetic waves we can see Wavelength – 780nm to 380nm Ultraviolet The cause of sunburn Wavelength – Virus to a protein X-Ray machines Wavelength – Protein to a water molecule What could you see with X-ray vision? “The “X-rays” that the doctor or dentist holds up are not a form of light; they are just pieces of film. The images of your bones and teeth are made with the help of a special machine that works somewhat like the flash on an ordinary camera but emits x rays instead of visible light. This machine flashes the x rays instead of visible light, and the x rays that are transmitted through your body are recorded on film. Thus, what you see is the image left by these x rays, not the x rays themselves” The Cosmic Perspective Radioactive elements Wavelength – Water molecule to even smaller Is all radiation dangerous? Many people associate the word radiation with danger. However, the word radiate simply means “to spread out from a center” (radius-radiation). Radiation is energy being transmitted through space. High-energy forms of radiation, such as particles from radioactive materials or x rays, are dangerous because they can penetrate body tissues and cause cell damage. Low energy forms of radiation, such as radio waves, are usually harmless. How much more do you think we could learn about the universe if we could see the full electromagnetic spectrum? Find the wavelength, energy, and type of radiation of a EM wave that has a frequency of 13x10^13Hz. DO STOP WORK Better your understanding of the proper way to answer Regents long answer questions. Practice your skills of the electromagnetic spectrum. Index of Refraction Lab Ryan Matt O Caleb Cody What is Light? Lab – Lab quality! Ryan Matt O Caleb Meghann, and Annika Please pass up your signed slips. Please pass up your completed answer packet. Let’s go over the packet. One worksheet, front and back Electromagnetic spectrum practice