Before cell division
advertisement
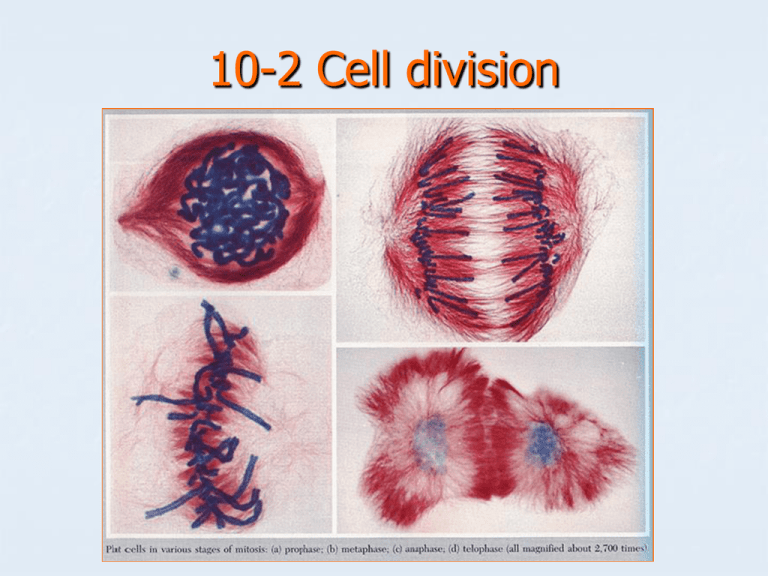
10-2 Cell division 2 phases of cell division Mitosis: division of the cell nucleus, including DNA replication. Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm and organelles cytokinesis Pair share: how is cytokinesis different from mitosis? Chromosomes Genetic material (DNA) is usually in thin strands. Before cell division, it thickens into chromosomes Each chromosome makes a copy of itself , and attaches to a centromere. Nucleolus disappears. Nuclear envelope breaks down. WB: how many copies of DNA are present before cell division? Cell cycle A series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. The cell grows, prepares to divide, then divides into 2 daughter cells. The cycle resumes with each daughter cell. Events of the cell cycle G1: cells grow S: DNA replicates G2: preparation for mitosis M: mitosis and cytokinesis P/S: how long is interphase compared to mitotic phase? Prophase First and longest phase Chromosomes become visible Centrioles separate to opposite sides of the nucleus, forming a spindle of microtubules Metaphase Lasts only a few minutes Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell, held by fibers of the spindle. WB: where are the chromosomes in this phase? Anaphase Sister chromatids split apart Each moves to a different pole of the spindle as the spindle fibers contract. Telophase Frog cell telophase 4th and last phase of mitosis Chromosomes uncoil Nuclear envelope re-forms around each cluster of chromosomes Spindle breaks apart Nucleolus is visible in each daughter nucleus P/S: how is telophase like the reverse of prophase? Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm Animal cell Plant cell In animal cells, the cell membrane pinches in. In plants, a cell plate forms midway between the divided nuclei. The cell plate becomes a membrane, Later, a cell wall forms in the cell plate. Summary 4 5 3 Name the stages of the cell cycle: 6 2 7 1







