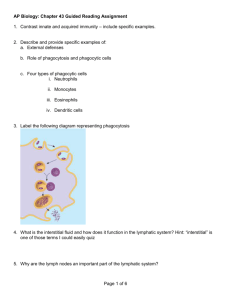
CELLULAR IMMUNE RESPONSE
advertisement

ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immune response to infections – 1. Innate response • Neutrophils, macrophages, NK cells at site of infection – 2. Initiation of adaptive response • iDCs phagocytose Ag and take to nodes • DCs present Ag to T cells – Get specific helper (CD4) T cells » “help” B cell activation = humoral immunity » Activate macrophages = CMI – Get specific cytotoxic (CD8) T cells » Kill virally infected cells = CMI ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE T CELLS • Development: in thymus – Immunogenetic events produce multiple TCRs • Similar to B cells • TCR gene with multiple V, D, and J segments • Recognize 1015 epitopes – T cells with TCRs that react with self antigens deleted • • • • • Start with double negative cells: no TCR, CD4 or CD8 Next get double positive cells: TCR, CD4, CD8 Positive selection = weak recognition of MHCI or MHCII Negative selection = if reaction is strong – apoptosis ~2% of cells survive ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE T CELLS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE T CELLS • TCR complex – T cell receptor – similar to Fab of antibodies • Alpha and beta Ig-like chains with variable and constant domains • Hydrophobic transmembrane regions – CD3 proteins • Gamma + epsilon; delta + epsilon, each with one Ig-like domain • Transmembrane segment binds to TCR • Cytoplasmic domain of each has one ITAM – ITAM = immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation notif; for signaling – Zeta chains = disulfide-liked homodimer, each protein has 3 ITAM • Transmembrane region with aspartate ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE T CELLS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE T CELLS • Co-receptors – CD4 protein binds to MHC-II on APC • CD4 T cells = helper T cells • MHC-II only on APCs – CD8 protein binds to MHC-I on target cells • CD8 T cells = cytotoxic T cells • MHC-I on all nucleated cells ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE T CELLS • Accessory molecules = lymphocyte surface molecule distinct from Ag receptor complex; adhesion or signaling – CD45R, CD28, CD40L • Adhesion molecules = tighten interaction with APC – LFA (leukocyte function-associated antigen)-1, CD2 • Cytokine receptors: IL-1R, IL-2R, others ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Antigen Presentation to T cells – MHC (major histocompatibility complex) 1 • all nucleated cells • MHC-encoded alpha (hvy) chain and beta 2 (lt) microglobulin • Polymorphic alpha 1 and alpha 2 domains for closed binding cleft – agretope • Conserved alpha 3 domains = binding site for CD8 • Beta 2 interacts noncovalently with alpha 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Abbas Fig 4-4 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells – MHC-II = dimer of alpha and beta subunits • APCs • Both chains MHC encoded • Alpha 1 and beta 1 domains variable and form open binding cleft – Most of variability on beta chain – Agretope • Alpha 2 and beta 2 folded into Ig domains – B2 Ig domain binds to CD4 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Abbas Fig 4-6 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Peptide presentation by MHC I molecules – MHC I molecule synthesized in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – Cytoplasmic protein (including microbial) degraded by proteosome • Usually dealing with degraded (misfolded etc) normal proteins – Degraded proteins marked by ubiquitin – To ER via TAP (transporter assoc w Ag processing) – Ag peptide binds to cleft in hvy chain of MHC-I • Peptide of 8 or 9 amino acids – MHC-I with peptide to cell membrane via golgi and exocytic vesicle • Uninfected cells usually coated with MHC-I with self proteins ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Peptide presentation by MHC II molecules – Phagocytized proteins degraded in phagolysosomes by APCs – MHC-II molecule synthesized in ER • Invariant chain (Ii) placed in cleft – Ii provides stability and prevents MHC-II from binding with ER peptides – Lysosomal and exocytic vesicles merge – Invariant chain replaced with degraded peptide • cleft open at ends; longer peptides (30 aa) presented – Fused vesicle migrates to cell membrane ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Antigen processing and presentation – Abbas Fig 5-8 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Cross-presentation of Ag – iDCs phagocytise virally infected cells – Some peptides migrate to cytoplasm and processed to MHC I – Also, some cytoplasmic peptides from phagocytised cells processed to MHC II ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Cross-presentation of Ag to CD8 T cells. Abbas Fig 5-7 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presenting cells • Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) = Dendritic cells (DCs), B cells, and Macs • Dendritic cells = “only APC that can initiate Ag specific response” – – – – – Presumably from myeloid and lineage Precursor DCs in blood; differentiate into immature DCs (iDC) iDC recognized antigen with TLR and other receptors; activated Pinocytosis/phagocytosis and cytokine production, now DC DCs can no longer phagocytose; go to T-cell area of lymph nodes where they present Ag to T cells – Langerhan’s cells are skin DC ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presentation to T cells • T Lymphocytes – Recognize antigens (on dendritic cells) in peripheral lymphoid organs, resulting in expansion of Ag-specific lymphocyte pool – Differentiate into effector cells and memory cells – Effector lymphocytes become activated when they recognize Ag – Activation of T cells requires recognition of Ag displayed on APCs, costimulators, and cytokines produced by both APC and T cell ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE antigen presentation to T cells • Activation of CD4 T Cells – MHC II on APC binds with TCR • TCR recognizes foreign protein + MHC self proteins – Interaction strengthened by binding of CD4 to MHC II molecule – Signal transmitted via TCR/CD3 complex zeta proteins – Adhesion molecule interactions • LFA-3 on APC with CD2 on T cell • ICAM-1 on APC with LFA-1 on T cell – Costimulatory signals also required • B7 on APC to CD28 on T cell • cytokines • Partial activation without adequate costimulatory signal = Anergy or apoptosis; method to eliminate self-reacting cells or induce tolerance ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE Helper T cell Function • TH1 and TH2 CD4 (helper) T cells – TH0 cells mature into TH1 or TH 2 depending on • • • • Nature and concentration of antigen How antigen presented Type of APC Cytokines – TH1 = IgM, IgG, activated Macs – TH2 = humoral response; IgA, IgE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE Cytotoxic T cells • Activation of CD8 T cells = cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) – Precursors in nodes bind TCR + CD8 to MHC-1 of APC + costim • TCR recognizes foreign protein in self MHC molecule – Specific clone expands by ~100,000 – Activated CTLs bind with target cell – Granulysin, granzymes and perforin released from granules = apoptosis – Also interaction of FasL on CTL with Fas on target = apoptosis • Apoptosis – Cell DNA and internal membranes fragment – Shrink to “apoptotic bodies” which are easily phagocytosed – “Clean” cell death as apposed to necrosis HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • HIR = production of antibodies by plasma (B) cells • Some Definitions – Albumin, globulin = serum proteins • Gamma-globulin = immunoglobulin – – – – – – – – Immunogen, antigen Epitope (linear, conformational) Hapten; carrier Adjuvant (alum, Freunds, liposomes, CW components) Immune tolerance (dose, co-stimulators, transplants ) T (cell) independent antigen; T dependent Ag Route of Ag administration Immunoglobulin superfamily on next slide HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunoglobulin (antibody) structure HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunoglobulin structure – Heavy chain determines class/subclass IgM, G, A, D, E • Mu, gamma, alpha, delta, epsilon – Light chain (kappa, lambda) – Domains – constant and variable • One variable domain on each lt chain and one variable domain on each hvy chain • Three constant domains on hvy chain of IgG and IgA; four on IgM and IgE • One constant domain on lt chains • Variable domains on hvy/lt chains have 3 complementary determining regions (CDRs) – complements epitope structure HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunoglobulin structure – Fab portion; variable region – Fc portion; • C’ fixatin; • bind to Fc receptors on effector cells • Fc of IgG and IgA involved with transfer across placenta and mucosa – Hinge region – – – – – • Papain = 2 Fab + Fc; Pepsin = F(ab)2 Fc Membrane-spanning portion Interchain disulfide bonds Isotype = IgD, IgM, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgA1, IgA2, IgE Allotype = variation of isotype in different individuals Idiotype = protein sequences in variable region • Interacts with epitope HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunoglobulin Classes HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Membrane-associated antibodies – All isotypes may be membrane-associated on B cells – All membrane-associated AAs monomeric – Last CH region has 26 AAs with hydrophobic side chains • Membrane spanning region • Secreted antibodies – – – – Found in blood and other extracellular fluids IgG and IgE are monomeric IgD negligible IgM and IgA are multimeric • Have tail pieces on end of hvy chains which are bound to J chains HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunoglobulin Isotypes – IgD = <1% of serum Ig • membrane Ig on early B-cells – IgM = 5-10% of serum Ig • membrane Ig on early B-cells – IgD and IgM are only isotypes that can be expressed together on same cell • 5 day half-life in serum • Serum IgM pentameric; 10 Ag-binding sites; tail piece and j chain • Complement fixation; opsonin; bacteriolysis • First isotype after immunization; then wanes HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunoglobulin Isotypes – IgG = 85% of serum Ig • • • • • 4 subclasses; all monomeric 23 day half-life T cells required Complement fixation; opsonin Maternal IgG transported across placenta and neonatal intestinal epithelium • Second isotype after immunization; persists – Also anamnestic (booster) response HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunoglobulin Isotypes – IgA = 5-15% of serum Ig • 2 subclasses; both dimer, trimer? with tail piece and J chain • IgA transported across epithelial cells has additional secretory component – IgE = <1% of serum Ig • Bind to Fc receptors on Mast cells, basophils and eosinophils • Immediate hypersensitivity • Parasite infections Transport of IgA through Epithelial Cells HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Neonatal Immunity: Neonates lack ability to mount effective immune response. Therefore, use maternal IgG and IgA – IgG transported across placenta into fetal circulation – IgG and IgA in breast milk ingested • IgG and IgA neutralize organisms in gut • IgG transported across gut epithelium into circulation – Neonatal Fc receptor for IgG on placta and gut epithelium cells HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE B cell development HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunogenetics – Chromosomes 2, 22, 14 have genes for kappa, lambda, hvy chains – Variable region genes upstream from constant region genes – Genetic recombination events to form variable region of hvy and lt chains: • V (variable) and J (joining) segments for light chains – ~ 300 V gene segments and ~5 J segments = ~ 1500 possible • V, D (diversity), and J segments for hvy chains – 300 - 1000 V genes, 12 D genes, and 6 J genes = <100,000 possible – Association of hvy and light chain = > 1,000,000 possible HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Immunogenetics (continued) • Class switching – Genes for constant region of hvy chain in set order • IgM, D, G3, G1, G2, G4, E, A1, A2 – Different constant region genes deleted in response to T cell cytokines HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Production of antibodies by B cell – B cell receptor = Ig molecule specific for non-self antigens • Cells with receptors for self antigens removed during development in bone marrow • Ig = IgD and IgM on naive B cells – B cell receptor complex • IgM or IgD + Ig alpha/Ig beta with immunoreceptor tyrosinebased activity motif (ITAM) • Signal transducing receptor initiates activation signal via Ig ITAM – Ultimately activates factors that induce transcription of genes B Cell Antigen Receptor Complex HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Antibody response to T (cell) independent antigens • Surface Ig receptors recognize repeating sites on Ag – Long polysaccharides • Get cross-linking of many Ig receptors, activating signal cascade • Clonal expansion and plasma cell development of specific B cells • Disadvantages of T independent response – No T cell cytokines for class switching; IgM only – Ab has lower affinity for Ag (limited affinity maturation?) – No response in young (<2yr) children HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Antibody response to T (cell) dependent antigens – Ig receptors on B cell recognize Ag but cross-linking inadequate to activate cell – Therefore need second signal from T helper cell; thus – 1) Ag binds to Ig receptor on B cell as above – 2) Some bound Ag internalized, processed and presented in MHC-II surface molecule to T cell (which has receptor for this Ag); i.e., B cell functions as APC. T cell, so activated, secretes cytokines which are received by and stimulate the B cell – 3) The two signals stimulate the B cell to replicate, clonal expansion • A) Plasma cells which produce and secrete the Ig of the receptor – In nodes and bone marrow • B) Memory cells with the same receptor – Anamnestic (booster) response HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Activation of B cells: continued – A second signal may be provided by C’ receptor – Interaction of B cell with T cell via CD40 (B cell) – CD40L (T cell) – Class switching from influence of helper T cell cytokines – Initial = IgM – INFg = IgG – IL-4 = IgA, IgE – IL-5 = IgA (also induces eosinophil production) – Somatic mutation = increased affinity – Primary and Secondary responses • Primary immune response = strong IgM • Secondary immune response (second exposure to Ag) = faster, more IgG C’ in B Cell Activation T Cell - Mediated B Cell Activation HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE • Antibodies inactivate microorganisms by – Agglutination – Neutralization • Antibody to toxins • Antibody to microbial surface molecules that bind to host cells – Opsonization • Natural killer cells have receptors for IgG • Eosinophils have receptors for IgG, IgA, and IgE – Complement fixation • Neutrophils, macrophages have receptors for C3b • Gram negative organisms susceptible to MAC