Washington's Presidency
advertisement

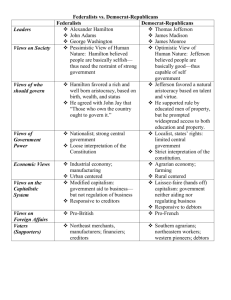
Issues Facing the New Government George Washington’s Presidency 1789 - 1797 No political party affiliation Won 100% of electoral vote in both elections Established precedent of only serving 2 terms as president Alexander Hamilton Washington’s Treasury Secretary Federalist Party Wanted to build a financially strong and independent US, especially for American industry and businesses Thomas Jefferson Washington’s Secretary of State DemocraticRepublican Party Wanted to protect states’ rights, USFrench relations Resigned in 1793 Henry Knox Washington’s Secretary of War Famous hero of the Revolutionary War Ft. Knox (in Kentucky) is named after him: (Remember: Forts are used in WAR) Supposedly died from swallowing a chicken bone Edmund Randolph Washington’s Attorney General Later became Secretary of State after Jefferson’s resignation, but then had to resign himself in 1795, due to scandal; he had been advising the French government on how to deal with Pres. Washington, potentially an act of treason Judiciary Act of 1789 Established the Federal Court system Made the Supreme Court the highest court in the U.S. President George Washington appointed John Jay as the 1st Chief Justice John Jay First Chief Justice (1789-95) Federalist Sent to England in 1794-5 to negotiate Jay’s Treaty (more on that in a later lesson) Resigned from the court in 1795 to become governor of New York Hamilton’s Economic Plan Most states had many debts left over from the Revolution Hamilton wanted the US to assume the states’ individual debts US would pay these debts by taxing whiskey and imported goods Hamilton also wanted to establish a national bank Constitutional opposition to Hamilton’s Plan Thomas Jefferson argued government did not have the constitutional power to create a bank (a strict interpretation of the Constitution) Hamilton argued that the “necessary and proper” clause allowed the government to do what was necessary to perform its functions (loose interpretation) Southern opposition to Hamilton’s Plan Taxes on imported goods would hurt southern farmers Many southern states had already paid their war debts South agreed to support Hamilton’s plan only after North agreed to move the capital from New York City to the Potomac River (Washington DC) Frontier opposition to Hamilton’s Plan Didn’t like tax on whiskey because that was how many frontiersmen made their living This opposition led to the Whiskey Rebellion of 1794 Whiskey Rebellion Pennsylvania farmers refused to pay whiskey tax and took up arms Pres. Washington responded by leading the US Army in putting down the rebellion Federal government demonstrated it could enforce its laws Federalists vs. Democratic-Republicans Federalists Led by Alexander Hamilton Favored strong national government Favored large landowners and merchants Favored tariffs and government regulations that supported business Loose interpretationists More popular in the North Pro-business Favored neutrality in the war between Britain and France Democratic-Republicans Led by Thomas Jefferson Favored strong state governments Favored small farmers Favored a “laissez-faire” approach where government did not regulate the economy Strict interpretationists More popular in the South Pro-farmers Favored France in their war against Britain Washington’s Farewell Address 1796 US should stay neutral and avoid “foreign entanglements” Good government is based on religion and morality Political parties are divisive and dangerous to national unity John Adams’ Presidency 1797 – 1801 Federalist Had been Washington’s VicePresident Beat out Jefferson in 1796 election by only 3 electoral votes, but lost to Jefferson in 1800 election Alien Acts of 1798 Allowed government to arrest and deport foreigners deemed “untrustworthy” Prevented poor immigrants (who tended to vote DemocraticRepublican) from voting Sedition Act of 1798 Limited free speech by making it illegal to publish "false, scandalous, and malicious writing" against the government or its officials Used to silence critics, who were usually from the other party: Democratic-Republicans The Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions Written in response to the Alien and Sedition Acts by Jefferson and James Madison Claimed that states do not have to obey or enforce federal laws that they believe to be unconstitutional – they can “nullify” the law: the Doctrine of Nullification Election of 1800 Presidential election was won by DemocraticRepublicans, but it was a tie between Jefferson and Aaron Burr Federalists had to choose which Dem.-Rep. to support; Hamilton decided to support Jefferson over Burr Sometimes called the “Peaceful Revolution” Burr-Hamilton Duel July 1804 Vice-President Burr challenged Hamilton to a duel in which Burr shot and killed Hamilton Burr was charged with murder, but acquitted and finished his term as VP The Midnight Judges Adams appointed a bunch of Federalist judges to life terms just before leaving office Jefferson ordered his Sec. of State James Madison to withhold their commissions, preventing them from taking office These denied judges sued in federal court John Marshall Chief Justice of the Supreme Court (18011835) A Federalist Longest serving Chief Justice in US History Established the Supreme Court’s authority to interpret constitutionality of laws Marbury v. Madison Court found that, while the judges had a right to be seated, the Supreme Court did not have jurisdiction in the case Declared the Judiciary Act of 1789, which had given the Court jurisdiction, to be in conflict with the Constitution and therefore unconstitutional Established precedent of judicial review – the Supreme Court decides whether laws violate the Constitution Thomas Jefferson’s Presidency 1801 – 1809 DemocraticRepublican Both he and John Adams died on July 4, 1826 – 50 years to the day after signing the Declaration of Independence! The Louisiana Purchase US acquired 828,800 square miles for a total purchase price of $23,213,568 About $0.03 per acre! Napoleon’s France needed the $$$ Begins US policy of pursuing economic prosperity through territorial expansion The Decline of the Federalists Federalists opposed the War of 1812 (a war with Britain), and staged a formal protest in 1814 Unfortunately, they protested just as news arrived that the US had won the war, causing them to lose popularity and fade from the political scene.