Bonding reading guide
advertisement

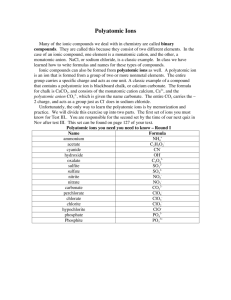
Reading Guide - Chapter 5 – Ionic Compounds Name Period Date Answer the following questions as you read through the chapter in Holt’s Chemistry – Visualizing Matter Textbook. The questions are in order, but be sure to read any information in the margins. Be thorough in your answers. Try to answer in your own words (it will help you learn more!). Part I: Simple Ions (page 158-161) 1. Define an ion? 2. An ion is like an atom, but the number of ____________________ does not equal the number of _______________, so it has a ___________________________________________? 3. Write the electron configuration for a sodium ion . 4. Even though the name of the element, sodium, is the same, a sodium ___________ behaves differently from a sodium ________. Using the same name for both the atom and ion signifies what? __________________________ 5. Chemical properties depend on the number of _____________________ and _______________________________. 6. A sodium ion only _________ electrons and they are configured just like the electrons in a ______________ atom: 7. Define a cation? 8. Define an anion? 9. Define electroneutrality? 10. A chlorine ion has the noble-gas configuration of ____________________. 11. Atoms and ions with the same configuration are said to be ______________________ with each other. 12. Perhaps you have noticed that in Table 5-1 the elements that form simple cations are _____________ and the elements that form simple anions are _________________________. 13. Atoms of nonmetals can achieve the stable noble-gas configuration by _______________ electrons. 14. ______________ electrons enables the atoms of some _______________ to match the electron number of the noble gas in the ________________ period. 15. Transition metals form stable ions too. Notice that part form Re-, these ions are all ____________________. 16. Refer to Table 5-1 (page 160) Write the cation & noble gas configuration for Magnesium: Write the anion & noble gas configuration for Sulfur: Part II: Ionic Bonding (pages 166-169) 17. Ionic compounds are __________ and ________________ combined in small whole-number proportions to produce a state of _____________________________________. 18. When two elements (Na+ & Cl-) are placed together, a violent ____________________ reaction occurs resulting in a white residue with the common name of _______________________. Chemists called it _____________________. 19. All ionic compounds are electrically ________________________. 20. Chemists use the word __________ to describe a force that holds atoms or ions together. 21. All salts are held together by ____________________________. This attraction goes beyond a _____________ cation and a __________ anion. The tight packing of the ions causes common salt to have a distinctive _____________ arrangement. 22. Define coulombic force? 23. IMPORTANT…Ionic compound do NOT consist of _____________________________. 24. The formula NaCl simply indicates that there is a ________________ ratio of ions in the salt. 25. Crystals of ionic compounds have ordered repeating units called a ______________. 26. The crystal structure of cesium chloride, CsCl, differs from that of NaCl because the Cs+ cation is significantly _______________ than the Na+ cation. Part III: Polyatomic Ions (pages 176-177) 27. Define polyatomic ion? 28. A simple ion could also be called _______________________. 29. Atoms in a polyatomic ion are ______________________ bonded, but the ion as a whole form ________________ bonds with other ions in the same way that the simple ions do. 30. ______________________ contain compounds with polyatomic ions. 31. Compounds containing polyatomic ions supply soil with ___________________, _______________________ and ________________________ in ratios to meets the needs of specific plants. 32. Most ionic compounds are called ___________________, whether their ions are simple of polyatomic.