PPT
advertisement

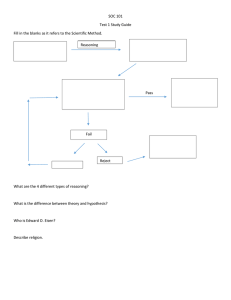
Early Contributors to Sociology Auguste Comte (1798-1857) • coined term “sociology” • positive philosophy==>positivism • evolution of social thought from religion to natural law to a reliance on observations on the five senses Theories of Society The Typology Tradition – Toennies: Gemeinschaft & Gesellschaft – Durkheim: Mechanical & Organic Solidarity – Weber: Traditional & Rational Society – Marx: Feudalism, Capitalism, & Socialism Ferdinand Toennies (1855-1936) Social Relationships • Gemeinschaft (community) – interaction based upon tradition and loyalty – ascribed order – undifferentiated society and labor – family like groups bounded by localities • Gesellschaft (Society) – interaction based on ration weighing of ends and means – achieved status – impersonal – complex division of labor – meritocracy and bureaucracy Emile Durkheim (1858-1917) • Mechanical Solidarity – similarity in local beliefs and activities (usually agriculture) – Collective Conscious – individualism is curbed • Organic Solidarity – Complex division of labor in the economy and society – interdependence of individuals and institutions – organic model Max Weber (1864-1920) • Traditional Society – based upon tradition authority – close family-like relationships – religion – common symbols and activities • Rational Society – based upon rationallegal authority – efficiency over custom – scientific – impersonal and bureaucratic Karl Marx (1818-1883) • • • • Stages of history Feudalism Serfs and Lords Capitalism Proletariat and Bourgeoises Class Conflict and Exploitation and class consciousness • Power Analyses and Hegemonic Control Social Darwinism •Evolved from Darwin’s theory of evolution (1858) •Herbert Spencer (1820-1903) •survival of the fittest •society is evolving and getting better •hunter-gatherers to modern society Contemporary Theory, and Research Cutting across all social paradigms: Macrotheory •aggregates or large groups •entire societies Microtheory •diads, triads, families •social life of small groups Structural Functionalism •social systems theory •components of society arise from structure and function •functions reaffirm society and societal values •manifest and latent functions Structural Functionalism What are the Manifest and Latent Functions of the York Galleria Mall? Conflict Paradigm •Karl Marx (1818-1883) •social behavior is seen as attempts to dominate or avoid domination •Class Conflict -- Proletariat Vs. Bourgeoisie •Utopian Society Role Theory •Ralph Linton (1895-1953) •Status •Roles •Role Conflict •Role Strain Symbolic Interaction •Simmel, Mead, and Cooley •Primary Group 1858-1918 •Looking-Glass Self •Taking The Role of the Other 1863-1931 1864-1929 •Common understanding of symbols •Interpreting symbols in context Exchange Paradigm •human behavior is seen through the evaluation of relative costs and benefits •rewards lead to actions •more value increases likelihood of action •high frequency of rewards diminishes the worth of the reward Ethnomethodology •reality is tentative •actors try to anticipate behavior on the basis of roles -- but social reality is continually being constructed when “rules” are broken •establish expectations -- rule breaking experiments Feminist Paradigm •gender differences in social organization •men control and dominate social processes to their advantage What’s Really Real? Views on Reality • Pre-modern View • Modern View • Postmodern View Major Theoretical Perspectives Theory Abstract statement explaining how and why some sets of concepts are linked. Helps interpret data Helps show us what questions to ask Helps generate. . . . hypotheses Sociological Research Ordinary Human Inquiry • Causal and Probabilistic • Tradition • Authority Sociological Research Sources of Errors in Inquiry • Inaccurate Observation • Overgeneralization • Selective Observation • Illogical Reasoning Sociological Research Types of Research •Quantitative •Qualitative Sociological Research The Conventional Research Model •Selecting and defining the problem •Reviewing previous research •Formulating Hypothesis (if appropriate) •Developing the research design •Collecting and analyzing the data •Drawing conclusions and reporting the findings The Wheel of Science •Nomothetic •Idiographic •Quantitative •Qualitative •Deductive •Inductive Sociological Research Data Collection and Analysis Techniques •Surveys •Questionnaire •Interview •Secondary data •Field Research •Participant Observation •Ethnography •Experiments Sociological Research Ethics in Social Research 1. NO HARM TO SUBJECTS 2. INFORMED CONSENT