Topographic Maps: Understanding Contour Lines & Elevation
advertisement

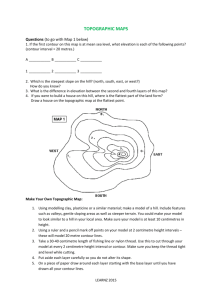
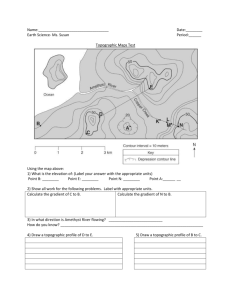
Topographic Maps Lesson Objectives Define a topographic map and state its uses. Describe how contour lines show the elevations, shape, and slope of the land. Compare a satellite photo to a topographic map. What is a topographic map? A topographic map, also known as a contour map, is a map that shows the shape of the land using contour lines. It is a map that shows an elevation field, meaning how high and low the ground is in relation to sea level. What are contour lines? Contour lines are lines that connect points that are of the same elevation. They show the exact elevation, the shape of the land, and the steepness of the land’s slope. Considering this, could they ever touch or cross? Contour Intervals A contour interval is the difference in elevation between two contour lines that are side by side. Remember that a contour interval is NOT the distance between the two lines – to get the distance you need to use the map scale. Index Contours Index contours – contour lines that are labeled to help you find the contour interval. What if my contour lines are close together? If the contour lines are close together, then that indicates that area has a steep slope What if my contour lines are far apart? If the contour lines are far apart, then that indicates the land has a gentle slope (low slope). What do depressions in the map look like? A depression, such as the inside of a dead volcano, is represented by Hachure lines, regular contour lines with small segments sticking out from it. The first hachure line is at the same elevation as the contour line before it. More on Contour Lines Contour lines form V’s that point upstream when they cross a stream. It is important to remember that they point in the opposite direction as the flow of water. Now that I know what a topographic map is, how do I read it? First determine the contour interval (the distance between each contour line) Then determine the map scale (usually at the bottom of the map) Identify any hills or depressions 0 ft is equal to water level, because elevation is based on how much higher a point is then the water nearby Reading a topographic map cont. Look for areas where the contour lines are close together – they indicate a steep area. Look for areas where the contour lines are spread apart – they indicate a gentle slope. Shows 3D in a 2D way from a birds eye view http://raider.muc.edu/~mcnaugma/Topographic%20Maps/contour.h 2. What about areas between the contours? 1. What is the elevation for each letter? http://raider.muc.edu/~mcnaugma/Topographic%20Maps/contour.h Topographic Maps Map Reading Activity: Topography 1. Approximately how tall is Able Hill? _______________________ ____ 3. Approximately how tall is Baker Hill? _______________________ ____ 4. Which mountain is taller, and by about how much? _______________________ ____ 5. How many meters of elevation are there between contour lines on the topographic map? _______________________ ____ 6. Which mountain has steeper slopes? _______________________ ____ 7. Are the contour lines closer together on Able Hill or Baker Hill? _______________________ ____ Answers 1. Elevations on the topographic map are in color as follows: Red-over 50m, Orange-from 40-50m, Yellow-from 3040m, Light green-from 20-30m, Dark green-from 10-20m, Purple-from 010m. 2. Approximately how tall is Able Hill? about 42m 3. Approximately how tall is Baker Hill? about 51m 4. Which mountain is taller, and by about how much? Baker Hill by about 9m 5. How many meters of elevation are there between contour lines on the topographic map? 10 m 6. Which mountain is steeper? Baker Hill 7. Are the contour lines closer together on Able Hill or Baker Hill? Baker Hill Topographic Maps 1. Color the elevations on the topographic map as follows. Red: 50m and higher, Orange: 40-50m, Yellow: 30-40m, Light green: 20-30m, Dark green: 10-20m, Purple: 0-10m. 2. Finish the mountain diagram below the topographic map, completing Oak Hill and drawing Ash Hill with proper elevations. 3. Approximately how tall is Ash Hill? _________________________ __ 4. Approximately how tall is Oak Hill? _________________________ __ 5. Which mountain is taller? _________________________ __ 6. How many meters of elevation are there between contour lines on the topographic map? _________________________ __ 7. Are the contour lines closer together on Ash Hill or Oak Hill? _________________________ __ 8. Which mountain has steeper slopes? _________________________ __ Answers 1. The elevations on the topographic map are as follows: Red-over 50m, Orange-from 40-50m, Yellow-from 3040m, Light green-from 20-30m, Dark green-from 10-20m, Purple-from 010m. 2. Oak Hill and Ash Hill are completed with proper elevations as shown. 3. Approximately how tall is Ash Hill? About 51-52m 4. Approximately how tall is Oak Hill? About 41-45m 5. Which mountain is taller? Ash Hill 6. How many meters of elevation are there between contour lines on the topographic map? 10m 7. Are the contour lines closer together on Ash Hill or Oak Hill? Ash Hill 8. Which mountain has steeper slopes? Ash Hill Review Questions How are contour lines drawn on maps? How does a contour map show whether a slope is gentle or steep? How is distance measured on a contour map?