Ch 3 Sec 2 MCJ
advertisement

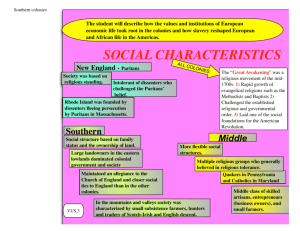
METACOGNITIVE READING LOG Name: __________________________________ Chapter 3 Section 2 New England Colonies Important Ideas & Information in the Text (p.) p. 67 The Voyage of the Mayflower *1500s – King Henry VIII creates Church of England *dissenters Religious Freedom and Self-Government *Separatists *persecuted by King James *fled to Holland for tolerance *got permission from VA Company to settle in America *Pilgrims p. 68 The Pilgrims Found Plymouth *traveled on Mayflower *land near Cape Cod and settle at Plymouth *charter didn’t apply so they needed government *Mayflower Compact *starving time *saved by Squanto who taught them how to plant crops *1621 First Thanksgiving The Puritans Come to Massachusetts Bay *1620s many speaking against king and the Church of England *Puritans *persecuted *leave for America The Great Migration *1629 – Massachusetts Bay Colony received royal charter to settle in New England *freedom to govern itself * founded Boston *1630 – 1640 20,000 settlers cross Atlantic *Great Migration My Thoughts, Feelings, Questions, Vocabulary V: disagree with official church V: group that wanted to separate from Church of England V: to mistreat V: acceptance of different opinions V: person who goes on religious journey Q: Same as Muslims?? V: document that established self-government and majority rule Q: Does this still exist?? V: dissenters who wanted to reform the church V: movement of thousands of settlers to New England Important Ideas & Information in the Text (p.) My Thoughts, Feelings, Questions, Vocabulary p. 69 The New England Way *ideal society – religious commonwealth of tight-knit Q: Was it really ideal and would it last today communities *church governed by congregations V: people who belong to the same church *Puritan church known as “Congregationalist” *New England Way *chose its minister *set up its own town *meetinghouse *Puritan values *hard work – honor God *education – all children needed to read Bible *representative government – town meetings T: Beginnings of our representative government and self-government *Democratic rights *”freemen” or investors to vote *John Winthrop changed “freeman” to mean male church member Massachusetts Bay “Seeds” New England *Puritans threatened by those who questioned their ways *disagreements forced many to leave *colonies grew p. 70 Rhode Island Welcomes Dissenters *Roger Williams challenges Puritan ideas *no right to take Native American lands by force *no one should be forced to attend church *Puritans shouldn’t impose their religious beliefs on others *church and state should be separate *Williams banished *founded Rhode Island (1636) *guaranteed religious tolerance *separation of church and state *first Baptist Church in America *Anne Hutchinson – dissenter *clergy were not the “elect” – chosen by God *challenged church authority *banished from Massachusetts V: first governor of Massachusetts Bay Colony T: Exactly why they left England V: dissenter who founds Rhode Island V: forced to leave a place V: banished from Massachusetts Important Ideas & Information in the Text (p.) My Thoughts, Feelings, Questions, Vocabulary p. 70 con’t *John Wheelwright - dissenter *established New Hampshire (1679) V: dissenter who established New Hampshire p. 71 Connecticut Extends Voting Rights *Thomas Hooker – dissenter *Connecticut (1639) *Fundamental Orders of Connecticut *non-church members could vote *expanded representative government The Fight for Tolerance *Puritans wouldn’t allow others to worship freely Puritans Persecute Quakers *Quakers *tremble at the word of the Lord *God could be known through inner light *women were spiritually equal to men *persecuted *jailed *whipped *banished *executed *became martyrs Mary Dyer – death led to greater tolerance V: dissenter who founded Connecticut V: first written constitution in America Q: Contradiction?? V: Protestant dissenters T: one who dies for something they believe in V: Quaker martyr p. 72 Creating a New England *New England colonies had much in common New England Foundations *origins in eastern counties of England *lived in towns *religious dissenters *disagreed with the Church of England and the Catholic Church *Protestant groups: *Puritans *Quakers *Separatists *Baptists T: could afford trip *middle ranks of society Important Ideas & Information in the Text (p.) p. 72 con’t *highly skilled and educated *traveled in companies – families, friends and neighbors Questions About an Established Church *creating a new world *New England colonies had established church *Rhode Island tolerated all denominations/Judaism Important Ideas & Information in the Text (p.) p. 73 Democratic Traditions *established democratic traditions and selfgovernment *Congregational churches of Puritans were self-governing *Massachusetts- Puritan men elected the governor and legislature *voting rights expanded in Rhode Island and Connecticut *towns controlled own affairs *town meeting – symbol of local self-government My Thoughts, Feelings, Questions, Vocabulary