Great Awakening/Enlightenment
advertisement

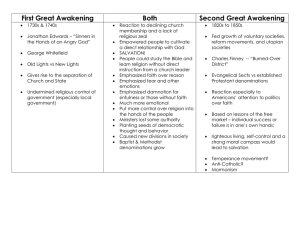
Enlightenment: Early 18th century European cultural movement that emphasized the power of human reason to understand and shape the world. Enlightenment thinkers: Copernicus Isaac Newton, Principia Mathematica, 1687 John Locke o Essay Concerning Human Understanding, 1690; Emphasized: Education Rational thought Purposeful action o Two Treatises of Government, 1690; Emphasized: Political authority derived from social compacts to preserve Natural rights to life, liberty, and property Reverend Andrew Eliot, Congregationalist minister; “there is nothing in Christianity that is contrary to reason.” Reverend John Wise; religious covenant of ordinary church members. Benjamin Franklin o Pennsylvania Gazette, 1729 o Poor Richard’s Almanack, 1732-1757 Nonreligious periodicals that drew from Deism and the Grand Architect Fundamental principles drawn from empirical research and scientific reasoning: Law-like order of the natural world Power of human reason “natural rights” of individuals (i.e. right to self-government) Progressive improvement of society American Pietism and the Great Awakening: 18th Century evangelical Christian movement that stressed the individual’s personal relationship with God. Pietism appealed to believer’s hearts rather than their minds. Revivals promoted religious enthusiasm Spread by German migrants. Great Awakening Thinkers: Theodore Jacob Frelinghuysen preached to German Americans William and Gilbert Tennent preached to Scots-Irish Presbyterians Jonathan Edwards sparked a New England Revivalism in Puritan New England George Whitefield carried John Wesley’s message of pietism to America Controversy: Old lights vs. New Lights Great Awakening undermined legally established churches and their tax-supported ministers. o Placed less stress on university trained ministers o Challenged the authority of all ministers o Minister’s authority comes from the conversion experience; not theological training. o Led to the founding of new colleges under the New Light: Princeton by New Light Presbyterians Columbia by New York Anglicans Brown by Baptists Rutgers subsidized by Dutch Reformed Church Legacy: New sense of authority among the many; rather than education for the privileged few.