Digestion Workbook
advertisement

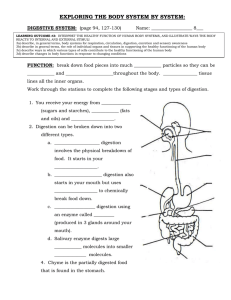
Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook DIGESTION -WORKBOOK 1. What is digestion? 2. What is the difference between digestion and absorption? 3. Compare the composition of the food we eat with the molecules that our cells actually use. 4. How many teeth do adults have? What are the four types of teeth and their function? 5. What is a hydrolytic enzyme? What is the enzyme in saliva? What reaction does it catalyze? 6. Using a labeled diagram, explain why when you swallow food or liquid, it doesn't usually go up your nose and down your windpipe. 1 Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook 7. Describe the process of peristalsis in the esophagus. How can a combination of circular and longitudinal muscles cause this action? 8. What are the functions of the stomach? 9. What is gastric juice? Where is it produced? What is it composed of? What does it do? 10. Give a one sentence description, using your own words, of the function of the following digestive components: Name Function 1. mouth 2. pharynx 3. epiglottis 4. cardiac sphinctor 5. esophagus 6. pepsinogen 11. How come, if your stomach is full of acid and protein-digesting enzymes, doesn't it digest itself? 2 Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook 12. a) Majority of digestion takes place in this organ: b) Structure of this organ: b) Length of this organ: c) Three parts of this organ are called: 13. a) Length of the duodenum: b) What controls flow of material into the duodenum? c) What is this material that enters the duodenum called? d) What is main role of duodenum in digestion? e) What two organs produce secretions that end up in duodenum? 14. a) Liver produces what substance? b) Where is this substance stored? 15. What does bile do? 16. a) What compound does pancreatic juice contain? b) What does this substance do? c) What 3 important enzymes does pancreatic juice contain (name and function)? 3 Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook 17. a) What produces the intestinal juices in the small intestine? b) Where are these glands located? c) Two important intestinal juice enzymes and their functions are (name and function): 18. a) Draw a villus, and show the blood and lymph vessels within. 19. a) Where does absorption take place? b) Where do sugars and amino acids go? c) Where do glycerol and fatty acids go? 4 Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook 20. List 6 functions of the liver 21. Explain how the large intestine is structurally and functionally different from the small intestine. 22. What are the three main types of hormones regulating the digestive process? What do the do? 23. Trace the path of the blood from the small intestine to the heart. 5 Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook Using the diagram above explain the following: 24) What does your body do when it senses a high blood sugar level? 25) What does your body do when it senses a low blood sugar level? 6 Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook DIGESTO-MAN Draw and label all the digestive parts and enzymes Parts Duodenum Ileum Rectum Teeth Pharynx Mouth Esophagus Pancreas Cardiac Sphincter Large Intestine Jejunum Liver Stomach Pyloric Sphincter Small Intestine Gall Bladder Chemicals Trypsin Pepsin Pancreatic Amylase HCl Lipase Salivary Amylase Peptidase Nuclease Maltase NaHCO3 7 Ms. Isenor Name:_____________________________ Biology 12 Digestion Workbook DIGESTIVE ORGANS a. Mouth, salivary glands CARBOHYDRATE PROTEIN LIPID MECHANICAL OTHER FUNCTIONS Salivary amylase: digests starch to maltose b. Pharynx, esophagus Deglutition, peristalsis c. Stomach • Secretes intrinsic factor • Produces hormone stomach gastrin d. Pancreas Pancreatic lipase: digests about 80% of fats e. Intestinal juices f. Liver No enzymes for for digestion of carbohydrates g. Large intestine No enzymes for digestion of carbohydrates No enzymes for digestion of protein No enzymes for digestion of lipids 8