Structure of DNA
advertisement

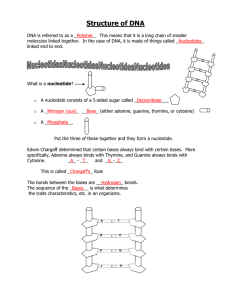
Nucleotides Starter What is DNA ? Where will you find DNA in a cell? Nucleotides Aims: •What are the components of DNA? •How are these components arranged within the DNA double helix? •What is the function of DNA? Watch the video. Answer the questions on your worksheet. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=54n8DLreEe4 DNA (and RNA) is a nucleic acid It is made from lots of nucleotide monomers joined together by condensation reactions to form a polynucleotide. Its function is to act as an information carrying molecule that determines the structure of proteins, including enzymes. Nucleotide Three parts Four Adenine types Look at all Guanine this Cytosine Nitrogen! Thymine Nucleotide Three parts Purines have two rings Four Adenine types Guanine Cytosine Thymine Nucleotide Three parts Pyrimidines have one ring Four Adenine types Guanine Cytosine Thymine Nucleotide Three parts Deoxyribose sugar Phosphate Group Three parts Nucleotide Rungs are bases Sides are phosphates and sugars (deoxyribose) Rungs are bases The rungs (bases) are held together by hydrogen bonds Sides are phosphates and sugars (deoxyribose) The rungs (bases) are held together by hydrogen bonds This means that when DNA needs to be copied, the two strands can be easily split apart The rungs (bases) are held together by hydrogen bonds This means that when DNA needs to be copied, the two strands can be easily split apart When the molecules twist into a helix, they are held in a stable structure, by the formation of hydrogen bonds between each coil of the helix. 10 bases for each complete turn (3.4nm) What is the relationship between the quantities adenine and thymine in DNA? What is the relationship between the quantities of guanine and cytosine in DNA? What about the ratio in different species? Nucleotides TASK: Complete the questions on your sheet. The notes in your Unit 2 booklet are up to you to do in your own time. All questions to be completed for homework. THE END